diarrhoeal disorders.pptx
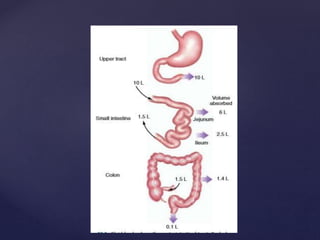
- 2. ’āæ Diarrhea is a symptom, not a disease, and therefore may occur in many conditions ’āæ passage of abnormally liquid or unformed stools at an increased frequency ’āæ Three or more bowel movements daily are considered to be abnormal ’āæ upper limit of stool weight is generally agreed to be 200 g daily ’āæ stool weight >200 g/d can generally be considered diarrheal
- 3. ’āæ Pseudodiarrhea: frequent passage of small stool with rectal urgency, tenesmus, or a feeling of incomplete evacuation ’āæ seen in IBS or proctitis. ’āæ Fecal incontinence: involuntary passage of rectal contents ’āæ neuromuscular disorders or structural anorectal problems. ’āæ ŌĆØ Overflow diarrheaŌĆØ: ’āæ due to fecal impaction readily detectable by rectal examination
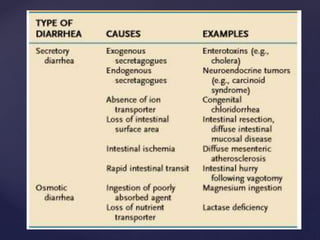
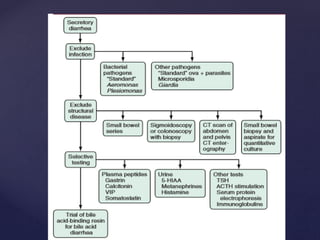
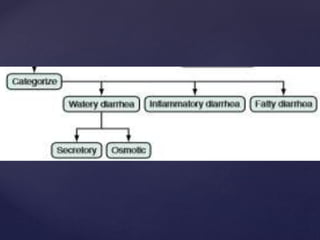
- 5. ’āæ osmotic diarrhea ’āæ Ingestion of poorly absorbed cations and anions or poorly absorbed sugars or sugar alcohols (e.g., mannitol, sorbitol) ’āæ Secretory diarrhea ’āæ many causes ’āæ net secretion of anions (chloride or bicarbonate) ’āæ net inhibition of sodium absorption. ’āæ most common cause of secretory diarrhea is infection. General types
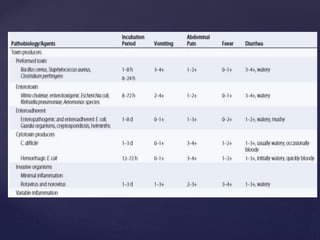
- 7. ’āæ > 90% of cases of acute diarrhea are due to infectious agents ’āæ often accompanied by vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain. ’āæ remaining 10% caused by medications, toxic ingestions, ischemia, food indiscretions, and other conditions. ’āæ resident fecal microflora, contain >500 taxonomically distinct species and play a role in suppressing the growth of ingested pathogens. ’āæ Disturbances of flora by antibiotics can lead to diarrhea by reducing the digestive function or by allowing the overgrowth of pathogens, such as Clostridium difficile
- 8. ’āæ Acute infection occurs ’āæ when the ingested agent overwhelms or bypasses ’āæ hostŌĆÖs mucosal immune and nonimmune defenses. (gastric acid, digestive enzymes, mucus secretion, peristalsis, and suppressive resident flora) Why?
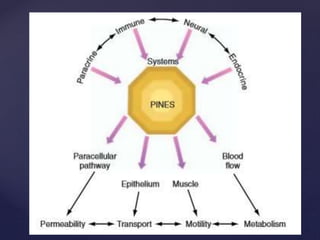
- 10. ’āæ PINES regulatory system in the intestine ’āæ integrates paracrine, immune, neural, and endocrine systems ’āæ produces coordinated changes in mucosal and muscular function that permit adaptive responses to changing conditions. ’āæ can widen or narrow the paracellular pathway that governs passive transmucosal permeability of electrolytes ’āæ accelerate or retard the transepithelial transport of nutrients and electrolytes by affecting membrane channels and pumps, ’āæ alter motility by relaxing or contracting the various muscle layers in the intestine ’āæ increase or decrease mucosal blood flow, thereby influencing intestinal metabolism. ’āæ Diarrhea may be an appropriate response to acute infection. ’āæ Maladaptive responses may be responsible for chronic diarrhea
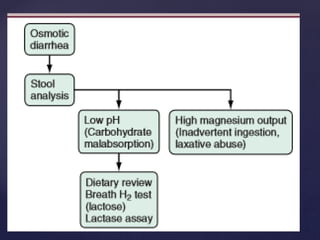
- 11. ’āæ Osmotic diarrhoea ’āæ The presence in the intestinal lumen of a large quantity of poorly absorbable, osmotically active solutes ’āæ Lactase deficiency (lactose intolerance), exogenous intake of a high-carbohydrate diet, laxatives, antacids (magnesium- containing), drugs (colchicine, lactulose), gastrointestinal lavage solutions such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), infections (e.g. giardiasis), generalised malabsorption syndromes ’āæ . Clinically, osmotic diarrhoeas subside on fasting. pathophysiology
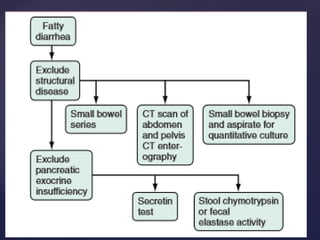
- 12. ’āæ Secretory diarrhoea ’āæ occurs due to abnormal ion transport in intestinal epithelial cells. ’āæ Congenital defects of ion absorption (Cl-/HCO-3 or Na+/H+, e.g. chloridorrhoea), diffuse mucosal disease (e.g. tropical sprue, lymphoma, inflammatory bowel disease), abnormal mediators such as bacterial toxins, enteric hormones (e.g. VIPoma, glucagonoma, carcinoid syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome), laxatives, drugs which alter intracellular cAMP, cGMP, calcium or protein kinases, bile acid and fatty acid malabsorption, hyperthyroidism, collagen vascular diseases and toxins (metals such as arsenic, seafood, tea, coffee, cola, alcohol, insecticides). ’āæ do not subside with fasting Pathophysiology contd.,.
- 13. ’āæ Abnormal motor function ’āæ contributes to most cases of secretory diarrhoea ’āæ excessive fluid secretion increases small intestinal peristalsis reflexly. ’āæ diarrhoeas predominantly due to abnormal motility include tumour-associated diarrhoea (carcinoid syndrome, medullary carcinoma of thyroid), metabolic causes (hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus), post-surgical patients (vagotomy, cholecystectomy, gastrectomy, ileal resection). ’āæ hypomotility of the intestine can cause bacterial overgrowth which may lead to diarrhoea as well. pathophysiology
- 14. ’āæ Abnormal fluid and electrolyte transport (exudation) ’āæ Inflammation and ulceration of the intestine ’āæ cause abnormality in the absorption of fluid and electrolyte ’āæ exudation of mucus, proteins and blood, all of which cause diarrhoea. pathophysiology
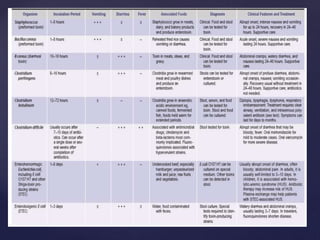
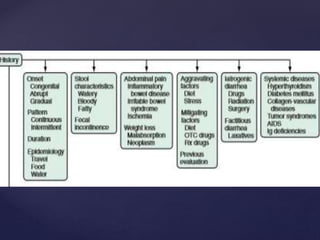
- 15. ’āæ Travelers: ’āæ enterotoxigenic or enteroaggregative Escherichia coli ’āæ Campylobacter, Shigella, Aeromonas, Salmonella ’āæ norovirus, Coronavirus ’āæ giardiasis, cyclospora five high-risk groups
- 16. ’āæ Consumers of certain specific foods: ’āæ Diarrhea closely following food consumption suggest infection with Salmonella, Campylobacter ’āæ Shigella from chicken ’āæ enterohemorrhagic E. coli (O157:H7) from undercooked hamburger ’āæ Bacillus cereus from fried rice or other reheated food ’āæ Staphylococcus aureus or Salmonella from mayonnaise or creams ’āæ Salmonella from eggs ’āæ Listeria from uncooked foods or soft cheeses ’āæ Vibrio species, Salmonella, or acute hepatitis A from seafood, especially if raw.
- 17. ’āæ Immunodeficient persons: ’āæ Common enteric pathogens cause a more severe and protracted diarrheal illness, ’āæ Mycobacterium species, certain viruses (cytomegalovirus, adenovirus, and herpes simplex), and protozoa (Cryptosporidium, Isospora belli, Microsporida, and Blastocystis hominis) ’āæ agents transmitted venereally per rectum (e.g., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Treponema pallidum, Chlamydia) may contribute to proctocolitis.
- 18. ’āæ Daycare attendees and their family members: ’āæ Infections with Shigella, Giardia, Cryptosporidium, rotavirus, ’āæ Institutionalized persons: ’āæ Infectious diarrhea due to C.difficile ’āæ one of the most frequent categories of nosocomial infections in many hospitals and long-term care facilities
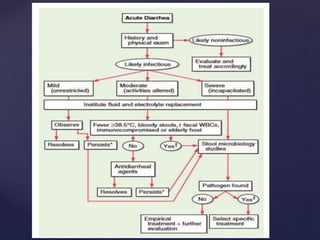
- 20. ’āæ Acute diarrhea: lasts < 2 weeks ’āæ Chronic diarrhea: lasts > 2 weeks. ’āæ Mild diarrhea: Ōēż 3 stools per day. ’āæ Moderate diarrhea: Ōēź 4 stools per day with local symptoms (abdominal cramps, nausea, tenesmus). ’āæ Severe diarrhea: Ōēź 4 stools per day with systemic symptoms (fever, chills, dehydration) Duration & frequency are important
- 21. ’āæ infectious agents ( viruses, bacteria, and protozoa) ’āæ food intolerance ’āæ inorganic agents (eg, sodium nitrite) ’āæ organic substances (eg, mushrooms, shellfish) ’āæ drugs ’āæ emotional stress Acute diarrhea ŌĆō causes
- 22. ’āæ syndromes that produce inflammatory or bloody diarrhea ’āæ Syndromes that produce noninflammatory, non bloody, or watery diarrhoea classification of infectious diarrhea
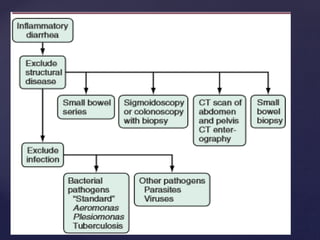
- 23. ’āæ colonic involvement by ’āæ invasive bacteria ’āæ parasites ’āæ toxin production. ’āæ Patients complain of frequent bloody, small-volume stools, often associated with fever, abdominal cramps, tenesmus, and fecal urgency ŌĆ£inflammatory diarrheaŌĆØ
- 24. ’āæ Shigella ’āæ Salmonella ’āæ Campylobacter ’āæ Yersinia ’āæ invasive strains of Escherichia coli ’āæ E coli O157:H7 ’āæ Shiga-toxinŌĆōproducing strains of E coli (STEC) ’āæ Entamoeba histolytica ’āæ C difficile Common causes of infective diarrhoea
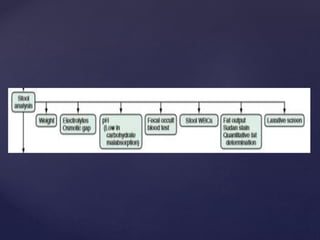
- 25. ’āæ fecal leukocytes ’āæ Fecal neutrophil marker lactoferrin, calprotectin ’āæ Stool culture is definitive for etiologic diagnosis investigations
- 26. ’āæ generally milder ’āæ affects the small intestine ’āæ interferes with salt and water balance ’āæ large-volume watery diarrhea, often with nausea, vomiting, and cramps. ’āæ caused by viruses or toxins Noninflammatory diarrhea
- 27. ’āæ Rotavirus ’āæ norovirus ’āæ astrovirus ’āæ enteric adenoviruses ’āæ vibriones (Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus) ’āæ enterotoxin-producing E coli ’āæ Giardia lamblia ’āæ Cryptosporidia ’āæ agents causing foodborne gastroenteritis.
- 28. ’āæ most common noninfectious cause of acute diarrhea ’āæ antibiotics, cardiac antidysrhythmics, antihypertensives, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, certain antidepressants, chemotherapeutic agents, bronchodilators, antacids, and laxatives. Side effect of medications
- 29. ’āæ caused by toxins present in consumed foods. ’āæ preformed toxin : S.aureus / B.cereus ’āæ short incubation period (1-6hrs) ’āæ Vomiting a major complaint ’āæ fever is usually absent ’āæ toxin can be detected in the food ŌĆ£Food poisoningŌĆØ
- 30. ’āæ organism present in the food: ex: Clostridium perfringens. ’āæ produces toxin after ingestion ’āæ incubation period is longer-(8-16 hours) ’āæ Vomiting less prominent ’āæ abdominal cramping is frequent ’āæ fever is often absent ’āæ Toxin can be detected in food or stool specimens ŌĆ£Food poisoningŌĆØ
- 35. ’āæ acute gastroenteritis: ’āæ Mostly self limited ’āæ does not require therapy ’āæ supportive measures ’āæ replacement of fluids and electrolytes ’āæ Bismuth compounds ’āæ Racecadotril 1.5 mg/ kg 8th hourly ’āæ very rarely, management of hypovolemic shock and respiratory compromise management
- 36. ’āæ mild diarrhea: ’āæ increased ingestion of juices and clear soups is adequate ’āæ In severe cases of dehydration (postural lightheadedness, decreased urination) ’āæ oral glucose-based rehydration solutions can be used ’āæ oral rehydration solution (ORS) ’āæ in children: 50 to 100 ml/kg over 4-6 hours ’āæ in adults: 200 to 1000 ml/kg. ’āæ Once the patient is rehydrated 100-200 ml/kg of ORS is given every 24 hours until diarrhoea ceases ’āæ Rarely parenteral fluid replacement is needed ’āō When symptoms persist beyond 3ŌĆō4 days ’āō accompanied by fever or bloody diarrhea ’āō if the patient is immunocompromised ’āō cultures of stool are usually obtained. Management contd.,.
- 37. ’āæ If a pathogen is isolated, specific treatment can be instituted ’āæ Cannot alter the natural history of disease for most pathogens ’āæ antibiotic therapy for shigella & campylobacter shortens the duration of symptoms by 2ŌĆō3 days, ’āæ antibiotic therapy for infections with E coli O157:H7 symptoms not affected and increases risk of developing hemolytic-uremic syndrome. ’āæ Salmonella infection therapy may prolong carrier status and increases relapses Status of antibiotic therapy
- 38. ’āæ Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin 500 mg bid for 5 days ’āæ Rifaximin: 400 mg bid for 5 days ’āæ Doxycycline: 100 mg bid for 5 days ’āæ TMP-SXZ: 2 tab bid for 5 days ’āæ Metronidazole: 400 mg 8th hrly for 5 days Antibiotic options
- 48. ’āæ Ciprofloxacin, 500 mg orally every 12 hours for 5 days, ’āæ