Digital Commonwealth: Massachusetts History Online
ŌĆóDownload as PPTX, PDFŌĆó
1 likeŌĆó551 views
Using the Digital Commonwealth to Enhance Teaching. Presented at the MSLA conference on 3/10/14 by Kim Cochrane (Framingham University) and Debra DeJonker-Berry (Eastham Public Library).
1 of 22
Download to read offline



















Recommended
Library cooperation.



Library cooperation.Manu K M
╠²
Library cooperation refers to the sharing of resources between two or more libraries. It allows for a more comprehensive collection, avoids duplication, and reduces costs. Areas of cooperation include inter-library loans, cooperative acquisitions, cataloging, and more. Barriers to cooperation include inadequate funding, outdated technology, lack of standards, and reluctance to participate. However, the future of library cooperation involves sharing expertise and people to take advantage of current opportunities for sharing resources.Library cooperative systems



Library cooperative systemsKaren S Calhoun
╠²
The document summarizes a presentation given by Karen Calhoun at NALIS Forum in Sofia, Bulgaria on September 24, 2010. The presentation discussed the changing nature of libraries and information seeking, and opportunities for increased cooperation and integration among libraries. Key points included the dominance of search engines for information finding, the potential to make library collections more visible and discoverable online, and opportunities to share and syndicate metadata across institutions to improve discovery of resources.Library Networks



Library Networksisma anggini
╠²
Library networking involves cooperation between libraries to share resources and provide maximum access to users. It requires creating tools like union catalogs to make each library's collections accessible. Rational acquisition and fast interlibrary loan are important. Participating libraries must be willing to contribute records, train staff, and adopt standards. Networks aim to expand access and services while reducing costs through collaborative collection development and resource sharing. They allow libraries to offer more than they could individually.Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And Information



Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And InformationBaguio Central University
╠²
This is a power-point about Networking and Resource Sharing in Library and Information Services: the case study of Consortium Building
Prepared By: May Joyce M. DulnuanLibrarian building blocks; or, how to make the ideal librarian



Librarian building blocks; or, how to make the ideal librarianDom Bortruex
╠²
"Librarian building blocks" will explore recent changes and needs in librarianship, introduce strategies for learning new skills, and inspire participants to implement these skills. This presentation is for a general audience and will cover skills for all libraries. To build the ideal librarian, we determined what skills and knowledge a contemporary librarian needs to succeed. Since job postings and MLIS curriculum reflect current, popular trends in librarianship, we developed a data harvesting Python script that gathered the data for more than 600 librarian job postings and MLIS curriculum content. Based on this data, we will present which skills are being taught and which skills need to be taught. The presentation will explore what these changes in technology and librarianship mean for current librarians and how they can stay up to date in the continuously evolving field of librarianship.Libraries: Cooperation and Linkages



Libraries: Cooperation and LinkagesKevin Conrad Tansiongco
╠²
This document discusses the importance of library cooperation and linkages. It defines key terms like cooperation, linkages, consortium and network. It identifies the essential elements for building a consortium as mutual objectives, joint decision making and continuous improvement. Critical success factors include a shared vision, cost effectiveness, staff skills and adapting over time. Advantages of consortium building are a comprehensive collection, reduced costs, enhanced services and staff development. Challenges include developing teamwork, trust and a win-win approach. Examples of library cooperation efforts provided are interlibrary loan, cooperative collection development and membership in library associations. The presentation recommends libraries continue aiming to provide access to information through cooperation and linkages.[[edit]] this GLAM![[[edit]] this GLAM](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/nlapresentation-100408074606-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[[edit]] this GLAM](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/nlapresentation-100408074606-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[[edit]] this GLAM](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/nlapresentation-100408074606-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[[edit]] this GLAM](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/nlapresentation-100408074606-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[[edit]] this GLAMwittylama
╠²
Presentation at the National Library of Australia on 8 April 2010. http://www.nla.gov.au/news/story.php?id=306Networking Systems in Libraries



Networking Systems in LibrariesDavid Nzoputa Ofili
╠²
Presented at the 2018 LRCN National Workshop on
Electronic Resource Management Systems in Libraries,
held at the University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Enugu State, NigeriaFuller Disclosure: Getting More Collections into the Network Flow



Fuller Disclosure: Getting More Collections into the Network Flowkramsey
╠²
The document discusses how libraries can make more of their collections discoverable by being where users search for information online. It recommends focusing on collection-level descriptions rather than exhaustive item-level metadata. Libraries should digitize materials, share metadata across systems, and engage users to add descriptive information over time. The goal is to expose hidden collections and get them integrated into the online information landscape where discovery happens.Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And Information



Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And InformationBaguio Central University
╠²
1) Library consortia allow libraries to share resources and reduce costs through cooperation instead of competing. They have formed in countries like the UK, South Africa, and Nigeria.
2) Key elements of successful consortia include having mutual objectives, joint decision making, and continuous improvement. Critical success factors include a shared vision, cost effectiveness, accessible resources, and staff commitment.
3) Advantages include comprehensive collections, avoiding duplication, reduced costs, enhanced services, and staff development opportunities. Challenges include developing teamwork, trust, openness, and adopting a win-win approach.Library networking in india for resources sharing



Library networking in india for resources sharingTiqueRebecca
╠²
The document discusses library networking in India for resource sharing. It outlines reasons for the need of resource sharing, such as the deluge of information and declining information buying power of libraries. It describes how networking connects computers to share information and resources. Networks were built to tackle increasing demands for better services given financial pressures. The ultimate goal of library networks is to interlink information resources across location, format, medium, language and script. Several library networks established in major Indian cities are described, including Delnet, Calibnet, Malibnet, MyLibnet, Bonet, Punenet and Adinet. The national network, Inflibnet, aims to provide end-users a mechanism for sharing and using information resources through modern informationResources Sharing



Resources SharingVincent Sabroso
╠²
This document discusses resource sharing among libraries. It begins by explaining how the information revolution has led libraries to adopt new technologies and philosophies to disseminate information more cost effectively. It then describes how libraries have realized no single library can acquire all needed materials, making partnerships necessary. The document outlines three phases of development in resource sharing: individual cooperation, linking by technology, and consortia for e-resources. It provides definitions and goals of resource sharing, as well as key areas like interlibrary loans and shared cataloging. The document advocates for resource sharing through library networks and notes technological advances support greater cooperation. It concludes by listing assumptions and tips for effective resource sharing programs.The future of Library Cooperation in Southeast Asia



The future of Library Cooperation in Southeast AsiaFe Angela Verzosa
╠²
Plenary paper delivered at the Asian Library and Information Conference on ŌĆ£Libraries ŌĆō Gateways to Information and Knowledge in the Digital Age,ŌĆØ held at Dusit Thani Hotel, Bangkok, Thailand, 2004 Nov 21-24
LIBER's Strategy Supporting The Role of Libraries in the Open Science Environ...



LIBER's Strategy Supporting The Role of Libraries in the Open Science Environ...Jeannette Frey
╠²
Research libraries face many challenges but also many opportunities in the Open Science Environmenet. The new LIBER Strategy 2018-2022 will support member libraries in this process.RESOURCE SHARING: A LIBRARY PERCEPTIVE 



RESOURCE SHARING: A LIBRARY PERCEPTIVE IAEME Publication
╠²
In the recent past, Resource sharing concept has become prime factor and playing vital role in
libraries because of innovative developments in Information, Communication and Technology
(ICT). ICT has made easy to establish networks among libraries and share their information
resources quickly and instantly. Resource sharing has become prime reason for establishing
cooperation between libraries without any geographical barriers. The various reasons for resource
sharing are might be cost benefits, non-availability of resources, insufficient library funds, lack of
skills etc. In this paper, the attempt has been made to understand the various aspects of resource
sharing in modern library technological environment. Update on IMLS National Digital Platform 



Update on IMLS National Digital Platform Trevor Owens
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs for the DLF and NDSA conferences in Milwaukee with an update on opportunities for funding digital library projects at IMLSThe technology of library and information networks.ppt final



The technology of library and information networks.ppt finalYvonnie Canol
╠²
The document discusses different types of library and information networks:
1. Search service networks that allow users to search databases but not modify records or output.
2. Customized service networks that allow users to search, modify records for local use, and obtain printed and machine-readable products for their data.
3. Service center networks that provide training, consulting, and planning rather than direct automated services.
It also discusses trends in networking, such as vendors expanding services to new areas and interfaces between stand-alone systems and subnetworks that will eventually connect to a national network. As technology improves, more activities will be supported at regional and local levels through a distributed national database.Library Linkages



Library LinkagesFe Angela Verzosa
╠²
a lecture presented at the University of Sto. Tomas Public Forum, held at the Central Library Conference Hall, UST, Manila on 2005 Aug 26 Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"



Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Jill Grogg of LYRASIS, during the NISO event "The Power of Library Consortia: How Publishers and Libraries Can Successfully Negotiate," held on April 17, 2019.Platform Thinking: Frameworks for a National Digital Platform State of Mind



Platform Thinking: Frameworks for a National Digital Platform State of MindTrevor Owens
╠²
Talk presented as a closing keynote to the Biodiversity Heritage Library's National Digital Stewardship Residency program meeting at the National Museum of Natural History. This talk reviews the National Digital Platform framework developed by US IMLS in collaboration with various library, archives and museum stakeholders and presents a series of additional conceptual frameworks on the role of software in society and psychology. Collections unbound: collection directions and the RLUK collective collection



Collections unbound: collection directions and the RLUK collective collectionlisld
╠²
A presentation given to RLUK Members' meeting at the University of Warwick.
The library identity has been closely bound with its collection. However this is changing as research and learning behaviours evolve in a network environment. There are three interesting trends. First, atttention is shifting from a library-centric view of a locally owned collection to a user-centred view of a facilitated collection in places where the library can add value. Second, there is growing emphasis on support for creation, for the process of research, as well as for the products, the article or book. And third, we are seeing a changing perspective on the historic core, the print book collection. Increasingly, this is being seen in collective ways as institutions manage down print, or think about its management in cooperative settings, or retire collections as space is reconfigured around research and learning experiences. This presentation also provides preliminary findings for the analysis being carried out by OCLC Research of the RLUK collective collection. Cbhl apr2014



Cbhl apr2014Bianca Crowley
╠²
The document discusses the growth and development of the Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) digital library consortium. It notes that BHL has expanded to include 4 new member institutions and now comprises over 20 institutions globally. The collections have also grown substantially, with over 76,000 titles and 43 million pages digitized. BHL aims to increase engagement, partnerships, and financial sustainability while continuing to make biodiversity literature openly accessible online.Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...



Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Jill Morris of PALCI, during the NISO event "The Power of Library Consortia: How Publishers and Libraries Can Successfully Negotiate," held on April 17, 2019.Working collaboratively: scaling infrastructure, services, learning and innov...



Working collaboratively: scaling infrastructure, services, learning and innov...lisld
╠²
1. The document discusses collaborative activities in libraries, identifying three main areas: shared service infrastructure, cooperative negotiation and licensing, and professional development and networking.
2. It analyzes libraries through the lenses of an organizational perspective focused on infrastructure, engagement, and innovation, and a service configuration perspective oriented around collections, space, services, and support for student success and research.
3. The key is finding the right scale for collaborative activities to increase engagement, leverage infrastructure, and scale learning and innovation to support the evolving role of libraries.Resource sharing network protocol in library Science (presentation)



Resource sharing network protocol in library Science (presentation)Muhammad Kashif
╠²
This document discusses resource sharing between libraries. It outlines two protocols for resource sharing: conventional and advanced. The conventional protocol involves sharing printed materials through interlibrary loan based on union catalogs and lists. The advanced automated protocol utilizes technologies like the World Wide Web, online public access catalogs, electronic formats, email, MARC standards, Z39.50 for database searching, and digital libraries to share resources electronically. Resource sharing networks allow libraries to provide extensive access to information with limited budgets by collaborating and pooling resources.Resource sharing



Resource sharingAksha Radhanpuri
╠²
Resource sharing introduction , Resource sharing in Library ,Need for Resource Sharing ,Objectives of Resource Sharing , Resource Sharing Through Networks, Advantages
SOURCE & RESOURCE , Professional Ethics in Resource sharing , Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...



Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...Dr. Anjaiah Mothukuri
╠²
These PPTs are more useful to Library Science Students, for all types of the Competative Examinations, UGC-NET & SLET/LIS 6120 Observation Presentation



LIS 6120 Observation PresentationJoseph Mhanna
╠²
This document discusses the importance of union catalogs for libraries. It describes a transaction where a student requested a book that was available through one library's ebook collection but with usage restrictions. The librarian was then able to locate the book at their own library with no restrictions through their union catalog. Union catalogs allow libraries to provide access to a wider collection of materials, save librarians time searching multiple catalogs, and enhance user satisfaction by fulfilling requests that may not be fully met otherwise. The experience reinforced the value of a proposed local union catalog for libraries in Lebanon.Sharing Your Digital Collection



Sharing Your Digital CollectionWiLS
╠²
Andrea Coffin (WiLS) and Rose Fortier (Marquette University) presentation at the Brown Deer Public Library to Milwaukee County librarians. March 24th, 2014.The IMLS National Digital Platform & Your Library: Tools You Can Use



The IMLS National Digital Platform & Your Library: Tools You Can UseTrevor Owens
╠²
As libraries increasingly use digital infrastructure to provide access to content and resources, there are more and more opportunities for collaboration around the tools and services that they use to meet their usersŌĆÖ needs. To this end, the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) is making substantial investments in developing collaborative and sustainable technical and social digital infrastructure for libraries through the National Digital Platform initiative. In this talk, you will learn about a series of digital tools, services, training opportunities and resources IMLS is funding through the National Leadership Grants for Libraries Program and the Laura Bush 21st Century Librarian Program. The presentation will focus on ongoing projects and efforts that you and your library can get involved in and make direct use of. It will also provide insight into how you could develop competitive proposals for projects that could be funded through this national effort. More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Fuller Disclosure: Getting More Collections into the Network Flow



Fuller Disclosure: Getting More Collections into the Network Flowkramsey
╠²
The document discusses how libraries can make more of their collections discoverable by being where users search for information online. It recommends focusing on collection-level descriptions rather than exhaustive item-level metadata. Libraries should digitize materials, share metadata across systems, and engage users to add descriptive information over time. The goal is to expose hidden collections and get them integrated into the online information landscape where discovery happens.Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And Information



Networking And Resource Sharing In Library And InformationBaguio Central University
╠²
1) Library consortia allow libraries to share resources and reduce costs through cooperation instead of competing. They have formed in countries like the UK, South Africa, and Nigeria.
2) Key elements of successful consortia include having mutual objectives, joint decision making, and continuous improvement. Critical success factors include a shared vision, cost effectiveness, accessible resources, and staff commitment.
3) Advantages include comprehensive collections, avoiding duplication, reduced costs, enhanced services, and staff development opportunities. Challenges include developing teamwork, trust, openness, and adopting a win-win approach.Library networking in india for resources sharing



Library networking in india for resources sharingTiqueRebecca
╠²
The document discusses library networking in India for resource sharing. It outlines reasons for the need of resource sharing, such as the deluge of information and declining information buying power of libraries. It describes how networking connects computers to share information and resources. Networks were built to tackle increasing demands for better services given financial pressures. The ultimate goal of library networks is to interlink information resources across location, format, medium, language and script. Several library networks established in major Indian cities are described, including Delnet, Calibnet, Malibnet, MyLibnet, Bonet, Punenet and Adinet. The national network, Inflibnet, aims to provide end-users a mechanism for sharing and using information resources through modern informationResources Sharing



Resources SharingVincent Sabroso
╠²
This document discusses resource sharing among libraries. It begins by explaining how the information revolution has led libraries to adopt new technologies and philosophies to disseminate information more cost effectively. It then describes how libraries have realized no single library can acquire all needed materials, making partnerships necessary. The document outlines three phases of development in resource sharing: individual cooperation, linking by technology, and consortia for e-resources. It provides definitions and goals of resource sharing, as well as key areas like interlibrary loans and shared cataloging. The document advocates for resource sharing through library networks and notes technological advances support greater cooperation. It concludes by listing assumptions and tips for effective resource sharing programs.The future of Library Cooperation in Southeast Asia



The future of Library Cooperation in Southeast AsiaFe Angela Verzosa
╠²
Plenary paper delivered at the Asian Library and Information Conference on ŌĆ£Libraries ŌĆō Gateways to Information and Knowledge in the Digital Age,ŌĆØ held at Dusit Thani Hotel, Bangkok, Thailand, 2004 Nov 21-24
LIBER's Strategy Supporting The Role of Libraries in the Open Science Environ...



LIBER's Strategy Supporting The Role of Libraries in the Open Science Environ...Jeannette Frey
╠²
Research libraries face many challenges but also many opportunities in the Open Science Environmenet. The new LIBER Strategy 2018-2022 will support member libraries in this process.RESOURCE SHARING: A LIBRARY PERCEPTIVE 



RESOURCE SHARING: A LIBRARY PERCEPTIVE IAEME Publication
╠²
In the recent past, Resource sharing concept has become prime factor and playing vital role in
libraries because of innovative developments in Information, Communication and Technology
(ICT). ICT has made easy to establish networks among libraries and share their information
resources quickly and instantly. Resource sharing has become prime reason for establishing
cooperation between libraries without any geographical barriers. The various reasons for resource
sharing are might be cost benefits, non-availability of resources, insufficient library funds, lack of
skills etc. In this paper, the attempt has been made to understand the various aspects of resource
sharing in modern library technological environment. Update on IMLS National Digital Platform 



Update on IMLS National Digital Platform Trevor Owens
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs for the DLF and NDSA conferences in Milwaukee with an update on opportunities for funding digital library projects at IMLSThe technology of library and information networks.ppt final



The technology of library and information networks.ppt finalYvonnie Canol
╠²
The document discusses different types of library and information networks:
1. Search service networks that allow users to search databases but not modify records or output.
2. Customized service networks that allow users to search, modify records for local use, and obtain printed and machine-readable products for their data.
3. Service center networks that provide training, consulting, and planning rather than direct automated services.
It also discusses trends in networking, such as vendors expanding services to new areas and interfaces between stand-alone systems and subnetworks that will eventually connect to a national network. As technology improves, more activities will be supported at regional and local levels through a distributed national database.Library Linkages



Library LinkagesFe Angela Verzosa
╠²
a lecture presented at the University of Sto. Tomas Public Forum, held at the Central Library Conference Hall, UST, Manila on 2005 Aug 26 Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"



Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Jill Grogg of LYRASIS, during the NISO event "The Power of Library Consortia: How Publishers and Libraries Can Successfully Negotiate," held on April 17, 2019.Platform Thinking: Frameworks for a National Digital Platform State of Mind



Platform Thinking: Frameworks for a National Digital Platform State of MindTrevor Owens
╠²
Talk presented as a closing keynote to the Biodiversity Heritage Library's National Digital Stewardship Residency program meeting at the National Museum of Natural History. This talk reviews the National Digital Platform framework developed by US IMLS in collaboration with various library, archives and museum stakeholders and presents a series of additional conceptual frameworks on the role of software in society and psychology. Collections unbound: collection directions and the RLUK collective collection



Collections unbound: collection directions and the RLUK collective collectionlisld
╠²
A presentation given to RLUK Members' meeting at the University of Warwick.
The library identity has been closely bound with its collection. However this is changing as research and learning behaviours evolve in a network environment. There are three interesting trends. First, atttention is shifting from a library-centric view of a locally owned collection to a user-centred view of a facilitated collection in places where the library can add value. Second, there is growing emphasis on support for creation, for the process of research, as well as for the products, the article or book. And third, we are seeing a changing perspective on the historic core, the print book collection. Increasingly, this is being seen in collective ways as institutions manage down print, or think about its management in cooperative settings, or retire collections as space is reconfigured around research and learning experiences. This presentation also provides preliminary findings for the analysis being carried out by OCLC Research of the RLUK collective collection. Cbhl apr2014



Cbhl apr2014Bianca Crowley
╠²
The document discusses the growth and development of the Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) digital library consortium. It notes that BHL has expanded to include 4 new member institutions and now comprises over 20 institutions globally. The collections have also grown substantially, with over 76,000 titles and 43 million pages digitized. BHL aims to increase engagement, partnerships, and financial sustainability while continuing to make biodiversity literature openly accessible online.Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...



Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Jill Morris of PALCI, during the NISO event "The Power of Library Consortia: How Publishers and Libraries Can Successfully Negotiate," held on April 17, 2019.Working collaboratively: scaling infrastructure, services, learning and innov...



Working collaboratively: scaling infrastructure, services, learning and innov...lisld
╠²
1. The document discusses collaborative activities in libraries, identifying three main areas: shared service infrastructure, cooperative negotiation and licensing, and professional development and networking.
2. It analyzes libraries through the lenses of an organizational perspective focused on infrastructure, engagement, and innovation, and a service configuration perspective oriented around collections, space, services, and support for student success and research.
3. The key is finding the right scale for collaborative activities to increase engagement, leverage infrastructure, and scale learning and innovation to support the evolving role of libraries.Resource sharing network protocol in library Science (presentation)



Resource sharing network protocol in library Science (presentation)Muhammad Kashif
╠²
This document discusses resource sharing between libraries. It outlines two protocols for resource sharing: conventional and advanced. The conventional protocol involves sharing printed materials through interlibrary loan based on union catalogs and lists. The advanced automated protocol utilizes technologies like the World Wide Web, online public access catalogs, electronic formats, email, MARC standards, Z39.50 for database searching, and digital libraries to share resources electronically. Resource sharing networks allow libraries to provide extensive access to information with limited budgets by collaborating and pooling resources.Resource sharing



Resource sharingAksha Radhanpuri
╠²
Resource sharing introduction , Resource sharing in Library ,Need for Resource Sharing ,Objectives of Resource Sharing , Resource Sharing Through Networks, Advantages
SOURCE & RESOURCE , Professional Ethics in Resource sharing , Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...



Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...Dr. Anjaiah Mothukuri
╠²
These PPTs are more useful to Library Science Students, for all types of the Competative Examinations, UGC-NET & SLET/LIS 6120 Observation Presentation



LIS 6120 Observation PresentationJoseph Mhanna
╠²
This document discusses the importance of union catalogs for libraries. It describes a transaction where a student requested a book that was available through one library's ebook collection but with usage restrictions. The librarian was then able to locate the book at their own library with no restrictions through their union catalog. Union catalogs allow libraries to provide access to a wider collection of materials, save librarians time searching multiple catalogs, and enhance user satisfaction by fulfilling requests that may not be fully met otherwise. The experience reinforced the value of a proposed local union catalog for libraries in Lebanon.Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"



Grogg "Strategies for Cross-Boundary Consortial Collaboration"National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...



Morris "Libraries Redefining Sharing in an Increasingly Complex Consortium E...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...



Universal Bibliographic Control and Universal Availability of Publications (U...Dr. Anjaiah Mothukuri
╠²
Similar to Digital Commonwealth: Massachusetts History Online (20)
Sharing Your Digital Collection



Sharing Your Digital CollectionWiLS
╠²
Andrea Coffin (WiLS) and Rose Fortier (Marquette University) presentation at the Brown Deer Public Library to Milwaukee County librarians. March 24th, 2014.The IMLS National Digital Platform & Your Library: Tools You Can Use



The IMLS National Digital Platform & Your Library: Tools You Can UseTrevor Owens
╠²
As libraries increasingly use digital infrastructure to provide access to content and resources, there are more and more opportunities for collaboration around the tools and services that they use to meet their usersŌĆÖ needs. To this end, the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) is making substantial investments in developing collaborative and sustainable technical and social digital infrastructure for libraries through the National Digital Platform initiative. In this talk, you will learn about a series of digital tools, services, training opportunities and resources IMLS is funding through the National Leadership Grants for Libraries Program and the Laura Bush 21st Century Librarian Program. The presentation will focus on ongoing projects and efforts that you and your library can get involved in and make direct use of. It will also provide insight into how you could develop competitive proposals for projects that could be funded through this national effort. Digital Infrastructures that Embody Library Principles: The IMLS national dig...



Digital Infrastructures that Embody Library Principles: The IMLS national dig...Trevor Owens
╠²
Digital library infrastructures must not simply work. They must also manifest the core principles of libraries and archives. Since 2014, the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) has engaged with stakeholders from diverse library communities to consider collaborative approaches to building digital library tools and services. The ŌĆ£national digital platformŌĆØ for libraries, archives, and museums is the framework that resulted from these dialogs. One key feature of the national digital platform (NDP) is the anchoring of core library principles within the development of digital tools and services. This essay explores how NDP-funded projects enact library principles as part of the national framework. Digital collections: Increasing awareness and use



Digital collections: Increasing awareness and useButtes
╠²
This document discusses various strategies for increasing awareness and use of digital collections, including:
1) Creating print materials like bookmarks and press releases to promote collections.
2) Scheduling in-person events such as presentations and open houses.
3) Contacting media sources like newspapers, magazines, and blogs.
4) Sharing metadata through tools like OCLC WorldCat to increase global discovery.
5) Leveraging the web through a library's website, search engine registration, and social media platforms.Community Collaboration in the Creation of Digital Collections - 2015 OR Heri...



Community Collaboration in the Creation of Digital Collections - 2015 OR Heri...Samuel W. Shogren, MPA., LEAD assoc.
╠²
This document summarizes the Washington County Heritage Online (WCHO) collaborative project. It began as a partnership between the Washington County Museum and Pacific University Library to digitize and provide online access to their collections. It has since expanded to include 11 contributing partners who have digitized over 8,000 objects. The project uses ContentDM to make these collections accessible online. It discusses the collaborative process, standards used, training provided, and lessons learned about balancing the needs of institutional and community partners.Next Steps for IMLS's National Digital Platform



Next Steps for IMLS's National Digital PlatformTrevor Owens
╠²
This keynote, at the Upper Midwest Digital Collections Conference, provides and update on the National Digital Platform and 20 projects supported to enhance it. The national digital platform is a way of thinking about and approaching the digital capability and capacity of libraries across the US. In this sense, it is the combination of software applications, social and technical infrastructure, and staff expertise that provide library content and services to all users in the US. As libraries increasingly use digital infrastructure to provide access to digital content and resources, there are more and more opportunities for collaboration around the tools and services that they use to meet their usersŌĆÖ needs. It is possible for each library in the country to leverage and benefit from the work of other libraries in shared digital services, systems, and infrastructure.
We need to bridge gaps between disparate pieces of the existing digital infrastructure, for increased efficiencies, cost savings, access, and services. To this end, IMLS is focusing on the national digital platform as an area of priority in the National Leadership Grants to Libraries program and the Laura Bush 21st Century Librarian program. We are eager to explore how this way of thinking and approaching infrastructure development can help states make the best use of the funds they receive through the Grants to States program. WeŌĆÖre also eager to work with other foundations and funders to maximize the impact of our federal investmentSimpson "Digitization and the Open Content Alliance - A New Approach to Resou...



Simpson "Digitization and the Open Content Alliance - A New Approach to Resou...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
This presentation was provided by Evan Simpson of Brandeis University, during the NISO event "Collaborative Library Resource Sharing: Standards, Developments, and New Models for Cooperating," held October 7 - October 8, 2008.Digital Strategy



Digital StrategyChantez Neymoss
╠²
The document outlines the Digital Strategy of the Charlotte Mecklenburg Library. It discusses the formation of workgroups to develop guiding principles. The workgroups focused on areas like content, community, digitization, user experience and infrastructure. The workgroups presented proposed guiding principles to a steering committee. The guiding principles aim to create a unified digital platform, remove barriers to access, foster an interactive online community, empower individual users, provide digital programming, and preserve local history through digitization.Digital Strategy



Digital StrategyChantez Neymoss
╠²
The Digital Strategy document summarizes the process undertaken by Charlotte Mecklenburg Library to develop a digital strategy. A steering committee and five workgroups composed of 76 staff members researched best practices. The workgroups developed guiding principles in areas like content, community, digitization, user experience, and infrastructure. The principles aim to create a unified digital platform, remove barriers to access, foster an interactive community, empower individuals, expand programming digitally, preserve local history, and equip staff for the digital future. The project involved research, staff and community input, and an implementation plan.Exploring Cultural History Online -- Winding Rivers Library System Kickoff Event



Exploring Cultural History Online -- Winding Rivers Library System Kickoff EventRecollection Wisconsin
╠²
║▌║▌▀Żs from the Winding Rivers Library system's Exploring Cultural History Online kickoff event, La Crosse, Wisconsin, June 19, 2014. The WRLS ECHO project is an LSTA-funded initiative to digitize photographs and postcards held by member libraries and local historical societies in the region. Presented by Emily Pfotenhauer, Recollection Wisconsin Program Manager, WiLS.
Bringing Local History Online



Bringing Local History OnlineRecollection Wisconsin
╠²
Presented at the Capital Region regional meeting in Brodhead, Wisconsin for the Wisconsin Historical Society and the Wisconsin Council for Local History, August 14, 2014.Digital Strategy



Digital StrategyChantez Neymoss
╠²
The document outlines the Digital Strategy project of the Charlotte Mecklenburg Library. It discusses how the project was divided into five workgroups that researched and developed guiding principles for the library's digital future. The workgroups focused on areas like content, community engagement, digitization, user experience, and infrastructure. The workgroups were overseen by a steering committee. The guiding principles developed address issues like creating a unified digital platform, removing barriers to access, fostering an interactive online community, empowering individual users, expanding programming opportunities digitally, and preserving local history through digital archives.Next Steps for IMLS's National Digital Platform



Next Steps for IMLS's National Digital PlatformTrevor Owens
╠²
This document summarizes projects funded by the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) related to developing a National Digital Platform. It describes 7 projects improving open source digital library software tools and communities, 4 projects focused on scaling up shared services, 2 applied research projects related to collections at scale, and 3 projects aimed at improving access for all and inclusion. It provides brief descriptions and links to more information for each of the 20 projects. The overall goal is to expand the digital capability and capacity of libraries across the United States by prioritizing promising digital tools and services.NC Government & Heritage Library overview - 2010



NC Government & Heritage Library overview - 2010Government & Heritage Library
╠²
Overview of the strengths, resources, services and challenges for the NC Government & Heritage Library in 2010.Building Strong Community Connections Through Digital Collections



Building Strong Community Connections Through Digital CollectionsUBC Library
╠²
Presented at the 2013 British Columbia Library Association annual conference in Richmond, BC May 10, by Michael Conroy, Community Digital Projects Analyst & Coordinator, BC Digitization Coalition, and Simon Neame, Director, Irving K. Barber Learning Centre.Digital initiatives in archival preservation



Digital initiatives in archival preservationFe Angela Verzosa
╠²
presented at the International Conference on Challenges in Preserving and Managing Cultural Heritage Resources, held on 2005 October 19-21 at the Institute of Social Order, Ateneo de Manila University, Quezon City, PhilippinesWelcome to the Mountain West Digital Library: The Power of Partnership



Welcome to the Mountain West Digital Library: The Power of PartnershipSandra McIntyre
╠²
Webinar from the Mountain West Digital Library
Sandra McIntyre, MWDL Director
Rebekah Cummings, MWDL Assistant Director/Outreach Librarian
The Mountain West Digital Library (MWDL) provides a central search portal to over 800,000 digital resources from memory institutions in Utah, Nevada, Idaho, Arizona, and Hawaii. As a program of the Utah Academic Library Consortium for the last twelve years, MWDL brings together 122 partners, including academic libraries, public libraries, archives, museums, historical societies, and government agencies, to share expertise and resources for digitization, hosting, and aggregated search. As one of the first six service hubs to the Digital Public Library of America, MWDL provides the on-ramp for DPLA participation to memory institutions in the Mountain West.
Sandra and Rebekah will talk about how the MWDL network came together and how partners work together across the region. They will also discuss how to join the Mountain West Digital Library, what it means to be an MWDL partner, and the benefits of partnership.
Digital forsyth oa_week



Digital forsyth oa_weekErik Mitchell
╠²
Digital Forsyth is a collaborative digital library between Winston Salem State University, Forsyth County Public Library, Wake Forest University, and Old Salem Museums and Gardens, funded by an LSTA grant. It contains over 15,000 digitized images and facilitates access to cultural and historical materials from Forsyth County through digitization. Its mission is to increase knowledge of the past and inform future generations by making collections accessible online. It aims to become the definitive online repository of cultural heritage resources in Forsyth County and provide openly licensed digital content to the community.Eastern Shores Library System digitization project



Eastern Shores Library System digitization projectRecollection Wisconsin
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation about the Recollection Wisconsin digitization project. It discusses why libraries and museums digitize materials, an overview of the Recollection Wisconsin program and its goals of making more Wisconsin historical materials available online. It covers topics like selecting materials for digitization, copyright issues to consider, and ways to promote and support use of digital collections once completed. The presentation aims to provide guidance to participating institutions on best practices for contributing to the statewide Recollection Wisconsin online collection.Valerie Johnson: Supporting the Archives Sector via Collaboration



Valerie Johnson: Supporting the Archives Sector via CollaborationNetwerk Digitaal Erfgoed
╠²
Presentation during World Digital Preservation Day 2018 and International Conference 'Memory Makers' organised by DPC and the Dutch Digital Heritage NetworkCommunity Collaboration in the Creation of Digital Collections - 2015 OR Heri...



Community Collaboration in the Creation of Digital Collections - 2015 OR Heri...Samuel W. Shogren, MPA., LEAD assoc.
╠²
Simpson "Digitization and the Open Content Alliance - A New Approach to Resou...



Simpson "Digitization and the Open Content Alliance - A New Approach to Resou...National Information Standards Organization (NISO)
╠²
Exploring Cultural History Online -- Winding Rivers Library System Kickoff Event



Exploring Cultural History Online -- Winding Rivers Library System Kickoff EventRecollection Wisconsin
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
╠²
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgBISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHEffective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatFunctional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdf



Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfSamarHosni3
╠²
Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfInterim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
╠²
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠²
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ģ Soft Tissue Therapy ŌĆō The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
Ō£ģ Sports Taping Techniques ŌĆō Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
Ō£ģ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia ŌĆō A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØYear 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
╠²
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
Digital Commonwealth: Massachusetts History Online
- 1. Introducing ŌĆ” Kim Cochrane, CAGS, MLS kcochrane1@framingham.edu Debra DeJonker-Berry, MLS, CAS ddejonker-berry@clamsnet.org Digital Commonwealth Outreach Committee March 11, 2014
- 2. Mission Statement The Digital Commonwealth serves as the open-access online discovery platform to the digital objects representing the breadth and depth of the rich cultural heritage of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Its member institutions are located all over the state and are comprised of libraries, archives, historical societies, museums, and cultural institutions. Working for victory Lawrence CLU AFL From Lawrence Public Library
- 3. Digital Commonwealth IsŌĆ” ŌĆó Collaboration of cultural organizations in Massachusetts that want to make digitized versions of their collections widely accessible ŌĆó 501c 3 organization (Pending) ŌĆó Website (current system) providing access to digitized collections ŌĆó Website (future new system) administered by the Boston Public Library providing access to digital content
- 4. Digital Commonwealth organizational structure ŌĆó 5.01(c)(3) non-profit Pending ŌĆó Board of Directors ŌĆó Standing committees ŌĆóConference ŌĆóPortal, Repository, Technology and Standards ŌĆóOutreach ŌĆóNominating ŌĆóDevelopment ŌĆó BPL is partner and technology provider Buckland Center School students and teachers, 1893 from Buckland Historical Society
- 5. Members of Digital Commonwealth FY2013 100+ members ŌĆó Public Libraries ŌĆó Museums ŌĆó Historical Societies ŌĆó Universities and colleges ŌĆó Archives ŌĆó Special libraries
- 6. ŌĆó Web Portal Access to Digital Library Collections in Mass ŌĆōcontains only the metadata that enables the discovery of the digital objects; it does not contain the actual digital objects. Core Services Children working with hay, Charlemont, Mass. From Jones Library Special Collections
- 7. Core Services ŌĆó Repository for Storage of Digital Collections created by member organizations - stores and maintains both metadata and digital objects according to a framework of policies and standards. By means of its technological infrastructure, the repository provides access to the digital content. Recruiting at the State Armory in Cambridge Massachusetts, 1916 From: MA National Guard Museum and Archives Worcester
- 8. Core Services ’üĘGuidance, instruction and assistance on applying appropriate technologies used in the production of digital library resources. ’üĘHosting an annual conference in Massachusetts on digital library issues Cranberry picking, Yarmouth, Mass. From: Jones Library Special Collections
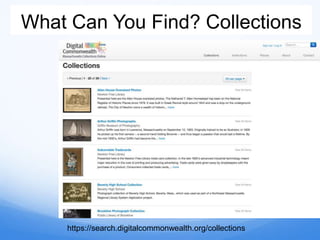
- 9. What Can You Find? Collections https://search.digitalcommonwealth.org/collections
- 10. Who we are - Participants https://search.digitalcommonwealth.org
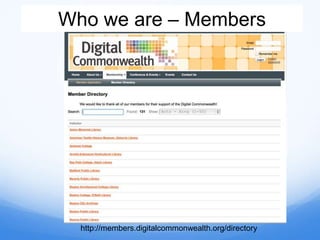
- 11. Who we are ŌĆō Members http://members.digitalcommonwealth.org/directory
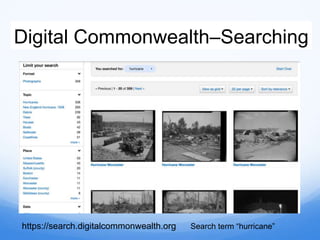
- 12. Digital CommonwealthŌĆōSearching https://search.digitalcommonwealth.org Search term ŌĆ£hurricaneŌĆØ
- 13. Digital Commonwealth - Behind the Scenes https://admin-hydratest.bpl.org Need username/password
- 14. Digital Commonwealth ’éŚ Contribute to a statewide initiative. The Digital Commonwealth is a membership- supported statewide collaboration. Members have the opportunity to shape statewide policy making around the digitization, preservation and presentation of historic materials. ’éŚ Participate in the Boston Public Library's free digitization program. The BPL will help you select, digitize and create metadata for your historic materials and other documents. ’éŚ Post your materials to the Digital Commonwealth's Repository. The Digital Commonwealth, in partnership with the Boston Public Library, is creating a next- generation file repository for members to store their materials in. The BPL also has a relationship with the Internet Archive; many digitization program participants get their monographs posted on the IA.
- 15. Digital Commonwealth ’éŚ Share your metadata in the Digital Commonwealth's Portal. The Digital Commonwealth, in partnership with the Boston Public Library, is a creating a next-generation Portal. Members contribute metadata about their digital assets in this aggregated search portal through: ’éŚ Having their collections harvested into our Portal from their existing OAI-harvestable feeds. ’éŚ Working with the BPL to have their collections harvested from the DC's Repository. ’éŚ Participate in the Digital Public Library of America. Digital Commonwealth members will have their content harvested into this national effort to collect ŌĆ£the riches of AmericaŌĆÖs libraries, archives, and museums.ŌĆØ
- 19. Opportunities for members ŌĆó BPL digitizing grant ŌĆó Workshops ŌĆó Training ŌĆó Get involved! ŌĆó Help test new portal/repository ŌĆó Outreach committee ŌĆó Help organize upcoming training and/or roundtable discussions ŌĆó Conference committee
- 20. Join the Digital Commonwealth http://digitalcommonwealth.memberlodge.org
- 21. Practically Digital: Doing What It Takes: 2014 Conference http://digitalcommonwealth.org/blog/?p=221
- 22. Questions? Kim Cochrane, CAGS, MLS Curriculum Librarian Co-Director, NASA Educator Resource Center Coordinator, Curriculum and Instructional Technology, Education Technology Henry Whittemore Library Framingham State University kcochrane1@framingham.edu Debra DeJonker-Berry, MLS, CAS Director Eastham Public Library ddejonker-berry@clamsnet.org Digital Commonwealth digitalcommonwealth@gmail.com





