Digoxin
- 1. TDM OF DIGOXIN P. THENNARASU ASST PROFESSOR FACULTY OF PHARMACY SRIHER
- 2. TDM Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is the clinical practice of measuring specific drugs at designated intervals to maintain a constant concentration in a patient's bloodstream, thereby optimizing individual dosage regimens.
- 3. Indications for requesting plasma drug concentrations
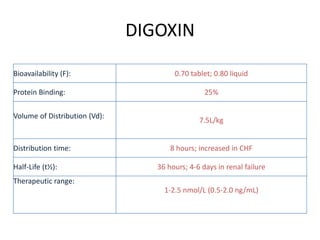
- 6. DIGOXIN Bioavailability (F): 0.70 tablet; 0.80 liquid Protein Binding: 25% Volume of Distribution (Vd): 7.5L/kg Distribution time: 8 hours; increased in CHF Half-Life (t¬Ω): 36 hours; 4-6 days in renal failure Therapeutic range: 1-2.5 nmol/L (0.5-2.0 ng/mL)
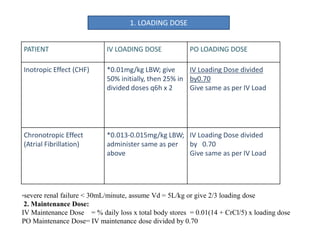
- 7. PATIENT IV LOADING DOSE PO LOADING DOSE Inotropic Effect (CHF) *0.01mg/kg LBW; give 50% initially, then 25% in divided doses q6h x 2 IV Loading Dose divided by0.70 Give same as per IV Load Chronotropic Effect (Atrial Fibrillation) *0.013-0.015mg/kg LBW; administer same as per above IV Loading Dose divided by 0.70 Give same as per IV Load *severe renal failure < 30mL/minute, assume Vd = 5L/kg or give 2/3 loading dose 2. Maintenance Dose: IV Maintenance Dose = % daily loss x total body stores = 0.01(14 + CrCl/5) x loading dose PO Maintenance Dose= IV maintenance dose divided by 0.70 1. LOADING DOSE
- 8. DRUG LEVEL MONITORING 1) Digoxin Serum Levels - when to measure: a) concern about compliance, or inadequate digoxin history; b) suspected toxicity of such severity that Digibind® may be required for therapy c) inadequate therapy despite high doses (little efficacy with levels <0.9nmol/L) d) drug interactions (e.g. amiodarone, verapamil) Note: There is a large overlap between toxic and therapeutic levels. When interpreting serum digoxin levels, monitor patient for efficacy and toxicity as level alone may be misleading.
- 9. 2) Digoxin Serum Levels - draw times: Trough levels preferred or minimum 6 hours post dose (due to long distribution t1/2) Steady state: 3-5 half-lives (= 5-7 days normal t1/2; 1-3 weeks renal dysfunction) Drug interactions: 2 days after interacting drug added to therapy
- 10. DRUG INTERACTIONS Drugs which cause INCREASED serum digoxin levels Drugs which cause DECREASED serum digoxin levels Amiodarone anticholinergic drugs diltiazem propafenone quinidine spironolactone verapamil antacids cholestyramine domperidone kaolin-pectin metoclopramide sulfasalazine D. DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 11. TOXICITY System Adverse Effect Cardiovascular apical slowing (<60bpm), AV conduction block, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular extrasystoles Central Nervous System confusion, forgetfulness, hallucinations, dizziness, psychosis, nightmares Visual colour changes, halos Gastrointestinal anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain (mesenteric ischemia)