Direct and indirect speech
- 1. Direct and Indirect Speech
- 2. By the end of the lesson I will: ŌĆó Understand the difference between direct and indirect speech. ŌĆó Be able to apply this knowledge in my writing. ŌĆó Accurately punctuate direct and indirect speech ŌĆó Know when and how to change pronouns and verb tenses in indirect speech.
- 3. Direct speech When we use direct speech in our writing: ŌĆó The exact words spoken must be put inside speech marks. ŌĆ£ ŌĆØ ŌĆó The first spoken word must have a capital letter. ŌĆó When a new speaker begins, we must start a new line.
- 4. ąŚą░ą╣ą╝ąĄąĮąĖą║ąĖ čéą░ ą┐čĆąĖčüą╗č¢ą▓ąĮąĖą║ąĖ čćą░čüčā č¢ ą╝č¢čüčåčÅ ąĘą╝č¢ąĮčÄčÄčéčīčüčÅ ą▓ čéą░ą║č¢ : This ŌĆō that These ŌĆō those Here ŌĆō there Now ŌĆō then Today ŌĆō on that today This week ŌĆō that week Yesterday ŌĆō the day before Last week ŌĆō the week before Tomorrow - the next day Next week ŌĆō the next week
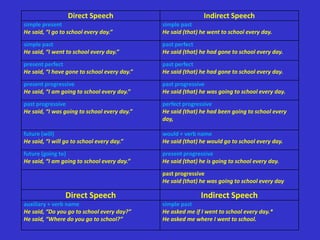
- 5. Direct Speech Indirect Speech simple present simple past He said, ŌĆ£I go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he went to school every day. simple past past perfect He said, ŌĆ£I went to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he had gone to school every day. present perfect past perfect He said, ŌĆ£I have gone to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he had gone to school every day. present progressive past progressive He said, ŌĆ£I am going to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he was going to school every day. past progressive perfect progressive He said, ŌĆ£I was going to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he had been going to school every day, future (will) would + verb name He said, ŌĆ£I will go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he would go to school every day. future (going to) present progressive He said, ŌĆ£I am going to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he is going to school every day. past progressive He said (that) he was going to school every day Direct Speech Indirect Speech auxiliary + verb name simple past He said, ŌĆ£Do you go to school every day?ŌĆØ He asked me if I went to school every day.* He said, ŌĆ£Where do you go to school?ŌĆØ He asked me where I went to school.
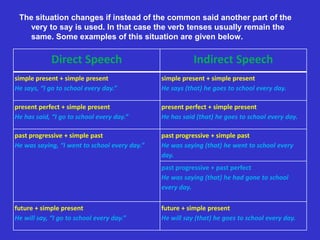
- 6. The situation changes if instead of the common said another part of the very to say is used. In that case the verb tenses usually remain the same. Some examples of this situation are given below. Direct Speech Indirect Speech simple present + simple present simple present + simple present He says, ŌĆ£I go to school every day.ŌĆØ He says (that) he goes to school every day. present perfect + simple present present perfect + simple present He has said, ŌĆ£I go to school every day.ŌĆØ He has said (that) he goes to school every day. past progressive + simple past past progressive + simple past He was saying, ŌĆ£I went to school every day.ŌĆØ He was saying (that) he went to school every day. past progressive + past perfect He was saying (that) he had gone to school every day. future + simple present future + simple present He will say, ŌĆ£I go to school every day.ŌĆØ He will say (that) he goes to school every day.
- 7. Another situation is the one in which modal constructions are used. If the verb said is used, then the form of the modal, or another modal that has a past meaning is used. Direct Speech Indirect Speech can could He said, ŌĆ£I can go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he could go to school every day. may might He said, ŌĆ£I may go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he might go to school every day. might He said, ŌĆ£I might go to school every day.ŌĆØ must had to He said, ŌĆ£I must go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he had to go to school every day. have to He said, ŌĆ£I have to go to school every day.ŌĆØ should should He said, ŌĆ£I should go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he should go to school every day. ought to ought to He said, ŌĆ£I ought to go to school every day.ŌĆØ He said (that) he ought to go to school every day.
- 8. Questions General questions Indirect Questions ŌĆ£Are you watching TV?ŌĆØ ŌĆ”I was watching TV. ŌĆ£Do you play chess?ŌĆØ ŌĆ”I played chess. ŌĆ£Does she go to school?ŌĆØ ŌĆ”she went to school. ŌĆ£Are you listening to me?ŌĆØ ŌĆ”I was listening to him. ŌĆ£Have you done your if, whether ŌĆ”I had done my homework. homework?ŌĆØ ŌĆ”I had skated the winter ŌĆ£Did you skate last winter?ŌĆØ before. ŌĆ£Will you see your friend ŌĆ”I should see my friend the tomorrow?ŌĆØ next day.
- 9. Direct speech Here are some examples of direct speech.
- 10. Direct Speech IŌĆÖve hurt my leg! ŌĆ£IŌĆÖve hurt my leg!ŌĆØ moaned the boy.
- 11. Direct speech Can you take a deep breath? ŌĆ£Can you take a deep breath?ŌĆØ asked the doctor.
- 12. Direct speech I like this dress. The woman said, ŌĆ£I like this dress.ŌĆØ
- 13. Direct Speech Use the correct punctuation to write what is being said. IŌĆÖve caught The train will three fish. leave in ten minutes! I love ice cream. Do you I am a know clever what girl. type of angle this is?
- 14. Indirect speech This is sometimes called REPORTED SPEECH. When we use indirect speech in our writing: ŌĆó We donŌĆÖt use speech marks. ŌĆó We usually have to change pronouns and verb tenses. ŌĆó We donŌĆÖt have to start a new line when we report a new speakerŌĆÖs words.
- 15. Indirect speech Here are some examples of indirect speech.
- 16. Direct Speech IŌĆÖve hurt my leg! The boy moaned that he had hurt his leg.
- 17. Direct speech Can you take a deep breath? The doctor asked the boy if he could take a deep breath.
- 18. Direct speech I like this dress. The woman said that she liked the dress.
- 19. Indirect Speech Use the correct punctuation to report what was said. IŌĆÖve caught The train will three fish. leave in ten minutes! I love ice cream. Do you I am a know clever what girl. type of angle this is?
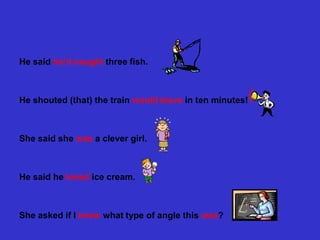
- 20. He said heŌĆÖd caught three fish. ąØąĄ shouted (that) the train would leave in ten minutes! She said she was a clever girl. He said he loved ice cream. She asked if I knew what type of angle this was?
- 21. QUESTIONS Is your father still in Moscow? We asked the girl if her father was still in Moscow. When did you fall ill? I wanted to know when he had fallen ill.
- 22. By the end of the lesson I will look for evidence to show that you will: ŌĆó Understand the difference between direct and indirect speech. ŌĆó Be able to apply this knowledge in your writing. ŌĆó Accurately punctuate direct and indirect speech ŌĆó Know when and how to change pronouns and verb tenses in indirect speech.