Direct and Indirect Speech
- 2. Army Public School & College (Boys), Saddar Karachi APSACS OSP ROUND 2 Class: XII - Karachi Board Week 01: Lecture - 01 Date: 02-December-2020 Subject: Compulsory English Section: Grammar Topic: Direct & Indirect Speech Teacher Name: Nijad Ansari (Lecturer)
- 3. TABLE OF CONTENT 1. Introduction 2. Direct and Indirect 3. Reporting and Reported Speech 4. Changes for Making Indirect 5. Change in Pronoun 6. Change in Tenses 7. Change in Modals 8. Change in Adverbs
- 4. INTRODUCTION There are two ways to convey a message of a person, or the words spoken by a person to the other person. DIRECT SPEECH INDIRECT SPEECH John said, ŌĆ£I will give you a pen.ŌĆØ (DIRECT SPEECH) John said that he would give you a pen. (INDIRECT SPEECH)
- 5. DIRECT SPEECH If we repeat the words of a person exactly in his own words to someone, it is called Direct Speech. Ex: John said to me, ŌĆ£I am very happy about your success.ŌĆØ INDIRECT SPEECH If we express the essence of main points of a person words with a few modifications, it is called Indirect Speech or Reported Speech. Ex: John said that he was very happy about my success.ŌĆØ
- 6. REPORTING AND REPORTED SPEECH He said, ŌĆ£He likes apples.ŌĆØ REPORTING VERB: The verb used to introduce the reported speech is called Reporting Verb. Reporting Verb Reported Speech
- 7. CHANGES FOR MAKING INDIRECT SPEECH ŌĆó Omission of Commas ŌĆó Use of ŌĆśthatŌĆÖ ŌĆó Change of Pronoun ŌĆó Change of Tense ŌĆó Change of Adverb
- 8. EXAMPLES She says, ŌĆ£I am ill.ŌĆØ She says that she is ill. He said, ŌĆ£The exam is not difficult.ŌĆØ He said that the exam was not difficult. They said, ŌĆ£We can speak perfect English.ŌĆØ They said that they could speak perfect English. ŌĆ£Are you a medical student?ŌĆØ I asked John. I asked John whether he was a medical student. ŌĆ£Do you want to read this book?ŌĆØ I said to her. I questioned her whether she wanted to read that book
- 9. CHANGES IN PRONOUN IN INDIRECT SPEECH First Person He said to me, ŌĆ£I like coffee.ŌĆØ Second Person He said to me, ŌĆ£You look happy.ŌĆØ Third Person I we Change with Subject You Change with Object He She It They No Change
- 10. CHANGE THE PRONOUN FROM THE GIVEN SENTENCES i. He says, ŌĆ£I am busy.ŌĆØ ii. They say, ŌĆ£We need to buy some new clothes.ŌĆØ iii. John says, ŌĆ£I was absent.ŌĆØ iv. They say to me, ŌĆ£You will be happy.ŌĆØ v. I say, ŌĆ£She is a good student.ŌĆØ
- 11. Answers He says, ŌĆ£I am busy.ŌĆØ He says that he is busy. They say, ŌĆ£We need to buy some new clothes.ŌĆØ They say that they need to buy some new clothes. John says, ŌĆ£I was absent.ŌĆØ John says that he was absent. They say to me, ŌĆ£You will be happy.ŌĆØ They tell me that I will be happy. I say, ŌĆ£She is a good student.ŌĆØ I say that she is a good student.
- 12. CHANGES IN TENSES IN INDIRECT SPEECH ŌĆó If we have Present or Future Tense in reporting speech, there will be no change in tense of reported speech. ŌĆó If we have Past Tense in reporting speech, we will change tense of reported speech. Direct Speech Indirect Speech Simple Present Simple Past Present Continuous Past Continuous Present Perfect Past Perfect Present Perfect Continuous Past Perfect Continuous Simple Past Past Perfect Past Perfect No Change Past Perfect Continuous No Change Will / Shall Would
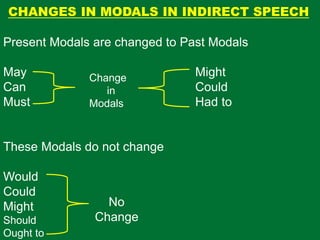
- 13. CHANGES IN MODALS IN INDIRECT SPEECH Present Modals are changed to Past Modals May Might Can Could Must Had to These Modals do not change Would Could Might Should Ought to Change in Modals No Change
- 14. CHANGE TENSE FROM THE GIVEN SENTENCES i. He said to me, ŌĆ£You are not busy.ŌĆØ ii. They said, ŌĆ£We are taking online classes.ŌĆØ iii. Lucy said, ŌĆ£I washed clothes.ŌĆØ iv. John said to Dora, ŌĆ£You had bought new clothes.ŌĆØ v. I said to them, ŌĆ£She has not been learning Chinese.ŌĆØ
- 15. Answers He said to me, ŌĆ£You are not busy.ŌĆØ He told me that I was not busy. They said, ŌĆ£We are taking online classes.ŌĆØ They said that they were taking online classes. Lucy said, ŌĆ£I washed clothes.ŌĆØ Lucy said that she had washed clothes. John said to Dora, ŌĆ£You had bought new clothes.ŌĆØ John told Dora that she had bought new clothes. I said to them, ŌĆ£She has not been learning Chinese.ŌĆØ I told them that she had not been learning Chinese.
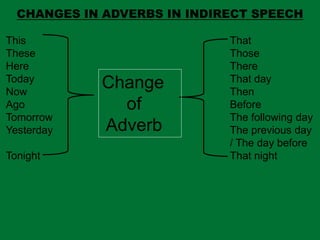
- 16. CHANGES IN ADVERBS IN INDIRECT SPEECH This That These Those Here There Today That day Now Then Ago Before Tomorrow The following day Yesterday The previous day / The day before Tonight That night Change of Adverb
- 17. CHANGE TENSE FROM THE GIVEN SENTENCES i. I said to Michael, ŌĆ£She is not busy now.ŌĆØ ii. They said, ŌĆ£We shall go to college tomorrow.ŌĆØ iii. John said to Lucy, ŌĆ£You washed clothes yesterday.ŌĆØ iv. Mike said to children, ŌĆ£You will buy a car in this month.ŌĆØ v. David said to them, ŌĆ£My exam will start the next month.ŌĆØ
- 18. Answers I said to Michael, ŌĆ£She is not busy now.ŌĆØ I told Michael that she was not busy then. They said, ŌĆ£We shall go to college tomorrow.ŌĆØ They said that they would go to college the next day. John said to Lucy, ŌĆ£You washed clothes yesterday.ŌĆØ John told to Lucy that she had washed clothes the previous day. Mike said to children, ŌĆ£You will buy a car in this month.ŌĆØ Mike told children that they would buy a car in that month. David said to them, ŌĆ£My exam will start the next month.ŌĆØ David told them that his exam would start the following month.