Direct sequence spread spectrum
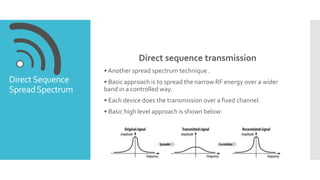
- 2. Direct sequence transmission • Another spread spectrum technique . • Basic approach is to spread the narrow RF energy over a wider band in a controlled way. • Each device does the transmission over a fixed channel. • Basic high level approach is shown below: DirectSequence SpreadSpectrum
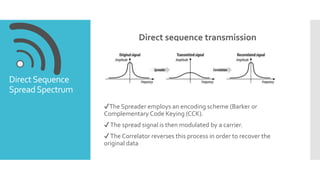
- 3. Direct sequence transmission ✔The Spreader employs an encoding scheme (Barker or Complementary Code Keying (CCK). ✔The spread signal is then modulated by a carrier. ✔The Correlator reverses this process in order to recover the original data DirectSequence SpreadSpectrum
- 4. DirectSequence SpreadSpectrum ď‚– Basic steps of DSSS technique: Narrowband radio signal is processed by a spreader 1. spreader applies a mathematical transform which convert narrowband input to a flat amplitude and spread frequency band. 2. On a carrier, to a narrow band receiver it looks like a low level noise. 3.The original signal can be recovered with a correlator, which inverse of the spreading process
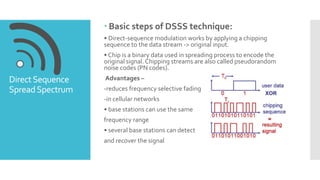
- 5. DirectSequence SpreadSpectrum  Basic steps of DSSS technique: • Direct-sequence modulation works by applying a chipping sequence to the data stream -> original input. • Chip is a binary data used in spreading process to encode the original signal.Chipping streams are also called pseudorandom noise codes (PN codes). Advantages – -reduces frequency selective fading -in cellular networks • base stations can use the same frequency range • several base stations can detect and recover the signal
- 6. DSSS operation • Higher spreading ratios • improve the ability to recover the transmitted signal • Require a higher chipping rate and a larger frequency band. • Require more expensive RF components operating at the higher frequency DirectSequence SpreadSpectrum