Discomycetes
- 2. Contents ÔÇó Introduction ÔÇó Habitat ÔÇó Classification ÔÇó Apothecium Structure ÔÇó Conclusion ÔÇó Reference
- 3. Introduction A vast group-2,720 genera and 28,650 species. This includes the members with cup-shaped/ saucer-shaped, some are club-shaped, mushroom-like, sponge-like etc.. These produce fructification called Apothecium, is the main feature of identification. Discomycetes are Ascomycetes with apothecium.
- 4. Habitat Most of the members are saprobes in nature but few are parasites, cause serious diseases of economic plants. Some are coprophillus and also constitute lichens. For instance., Sclerotinia fruticola- Brown rot in pear Quercus -Mycorrhizae forming
- 5. Classification Discomycetes- grossly classified- based on the presence/ absence of Operculum. ÔÇó Inoperculate ÔÇó Operculate
- 6. Ainsworth divided Discomycetes into 6 orders viz., ÔÇó Pezizales ÔÇó Tuberales ÔÇó Rhytismatales ÔÇó Ostropales ÔÇó Helitiales ÔÇó Cyttariales Each order contains some families and few genus
- 7. Pezizales ÔÇó Largest of operculate Discomycetes usually saprobes on soil, dead wood, plant debris/ humus ÔÇó Apothecia may be fleshy/ brittle/ leathery / rarely gelatinous ÔÇó The asci are arranged in a distinct hymenium with paraphyses ÔÇó Edible- Morchella esculenta
- 8. PEZIZA BADIA PEZIZA CEREA
- 9. Tuberales ÔÇó Commonly called Truffles ÔÇó Used as food, in liquor making, for scenting tobacco, in perfumes etc ÔÇó The ascomata remains closed and are fleshy to leathery/ globose with a hymenium ÔÇó Mycorrhizae- Quercus
- 10. TUBER RUFUM
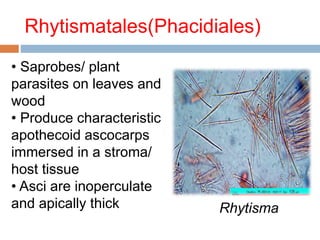
- 11. Rhytismatales(Phacidiales) ÔÇó Saprobes/ plant parasites on leaves and wood ÔÇó Produce characteristic apothecoid ascocarps immersed in a stroma/ host tissue ÔÇó Asci are inoperculate and apically thick Rhytisma
- 12. Ostropales ÔÇó Saprobes / parasites of herbaceous/ woody stem ÔÇó Crustose lichen formation ÔÇó Asci- long and cylindrical ÔÇó Young ascal apex, thick, traversed by a pore through which ascospores are discharged
- 13. Crustose lichen with Apothecia
- 14. Helotiales ÔÇó Inoperculate forms ÔÇó Saprobes on soil, dead wood, dung and parasites that cause plant diseases (Sclerotinia spp.) ÔÇó Ascocarps may be superficial or immersed in substratum
- 15. Cyttariales ÔÇó Large ascomata-spherical to pyriform ÔÇó Asci are operculate ÔÇó Cushion of epiplasm remains between ascospores CYTTARIA ESPINOSAE
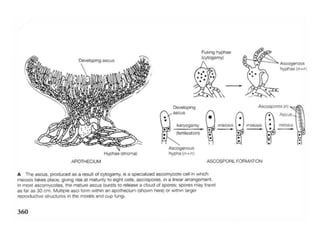
- 16. Apothecium ÔÇó It is divided into 3 anatomical regions - Hymenium - Subhymenium - Excipulum ÔÇó Hymenium is made of cylindrical/ club-shaped asci and paraphyses in a palisade layer ÔÇó Subhymenium is a zone of tissue that give give rise to asci and paraphyses ÔÇó Excipulum- 2 parts- ectal and medullary
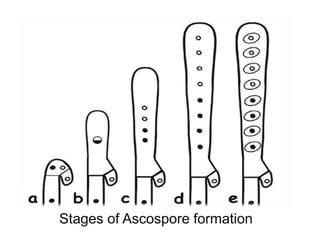
- 18. Stages of Ascospore formation
- 19. Conclusion The members commonly produce asci within apothecium, may be operculate/ inoperculate. Morchellaceae under Pezizales has the members like mushrooms, which resemble the mushrooms.
- 20. Reference ÔÇó R.S. MEHROTRA & K.R. ANEJA (2010) AN INTRODUCTION TO MYCOLOGY Pg no. 363-389 New Age International (p) Ltd., Publishers ÔÇó JOHN WEBSTER, 1970, Introduction to fungi, pg no. 246-272. Cambridge university press ÔÇóhttp://www.symbiology.com/pdf/Gargas7 .pdf