discriminants.pptx
- 2. What is to be learned? ÔÇó What the discriminant is ÔÇó How we use the discriminant to find out how many solutions there are (if any)
- 3. Quadratic Formula x = -b + - b2  4ac 2a How many solutions? 1. x2 + 6x + 9 = 0 2. x2 + 8x + 9 = 0 3. x2 + 4x + 9 = 0 1 2 0
- 4. The Big Nasty Formula 2a x = -b + - b2  4ac How many solutions? 1. x2 + 6x + 9 = 0 2. x2 + 8x + 9 = 0 3. x2 + 4x + 9 = 0 1 2 0 The Discriminant tells you how many solutions you have zero positive negative
- 5. The Discriminant b2 ÔÇô 4ac If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is positive If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is zero If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is negative ´âá 0 solutions ´âá 2 solutions ´âá 1 solution
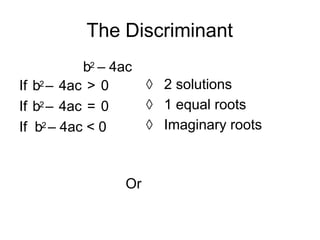
- 6. The Discriminant b2 ÔÇô 4ac If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is positive If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is zero If b2 ÔÇô 4ac is negative ´âá 0 solutions Or ´âá 2 solutions ´âá 1 solution
- 7. The Discriminant b2 ÔÇô 4ac If b2 ÔÇô 4ac > 0 If b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0 If b2 ÔÇô 4ac < 0 ´âá 2 solutions ´âá 1 equal roots ´âá Imaginary roots Or
- 8. Nature of Roots x2+ 5x ÔÇô 11 = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 1, b = 5, c = -11 Using Discriminant b2ÔÇô 4ac = 52 ÔÇô 4(1)(-11) = 25 + 44 = 69 2 real roots
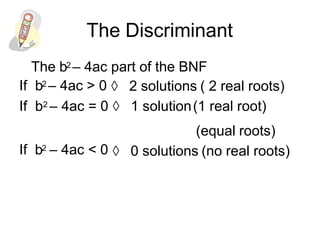
- 9. The Discriminant The b2 ÔÇô 4ac part of the BNF If b2 ÔÇô 4ac > 0 ´âá 2 solutions ( 2 real roots) If b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0 ´âá 1 solution(1 real root) (equal roots) If b2 ÔÇô 4ac < 0 ´âá 0 solutions (no real roots)
- 10. Nature of Roots x2+ 6x + 10 = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 1, b = 6, c = 10 Using Discriminant b2ÔÇô 4ac = 62 ÔÇô 4(1)(10) = - 4 no real roots Must be written like this
- 11. Key Question Find the nature of the roots of this equation 3m(m + 2) + 4m = 7 3m2 + 6m + 4m = 7 3m2 + 10m ÔÇô 7 = 0 c.f. am2 + bm + c = 0 a = 3, b = 10, c = -7 Using Discriminant b2ÔÇô 4ac = 102 ÔÇô 4(3)(-7) = 100 + 84 = 184
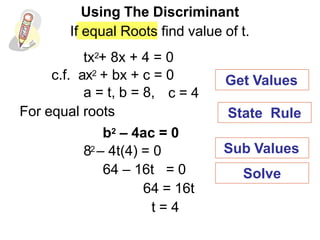
- 12. Using The Discriminant If equal Roots find value of t. tx2+ 8x + 4 = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = t, b = 8, For equal roots 64 ÔÇô 16t = 0 64 = 16t t = 4 b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0 82 ÔÇô 4t(4) = 0 c = 4 State Rule Get Values Sub Values Solve
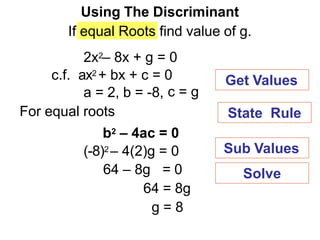
- 13. 64 ÔÇô 8g = 0 64 = 8g g = 8 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 2, b = -8, c = g For equal roots b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0 (-8)2 ÔÇô 4(2)g = 0 Using The Discriminant If equal Roots find value of g. 2x2ÔÇô 8x + g = 0 State Rule Get Values Sub Values Solve
- 14. Key Question If equal Roots find value of r. rx2ÔÇô 18x + 27 = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = r, b = -18,c = 27 For equal roots (-18)2 ÔÇô 4r(27) = 0 324 ÔÇô 108r = 0 324 = 108r r = 3 b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0
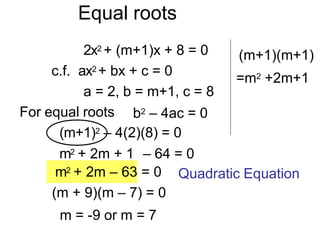
- 15. Equal roots 2x2 + (m+1)x + 8 = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 2, b = m+1, c = 8 For equal roots m2 + 2m ÔÇô 63 = 0 (m + 9)(m ÔÇô 7) = 0 m = -9 or m = 7 b2 ÔÇô 4ac = 0 (m+1)2 ÔÇô 4(2)(8) = 0 m2 + 2m + 1 ÔÇô 64 = 0 (m+1)(m+1) =m2 +2m+1 Quadratic Equation
- 16. No real roots? 2x2ÔÇô 8x + g = 0 c.f. ax2 + bx + c = 0 a = 2, b = -8, c = g For no real roots b2 ÔÇô 4ac < 0 (-8)2 ÔÇô 4(2)g < 0 64 ÔÇô 8g < 0 Inequation
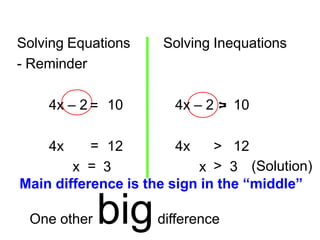
- 17. Solving Equations - Reminder 4x = 12 4x > 12 x = 3 x > 3 (Solution) 4x ÔÇô 2 = 10 Solving Inequations 4x ÔÇô 2 > = 10 Main difference is the sign in the ÔÇ£middleÔÇØ One other bigdifference
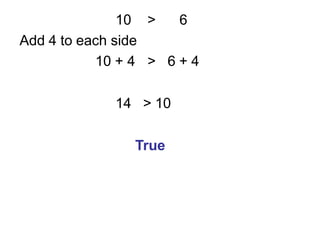
- 18. 10 > 6 Add 4 to each side 10 + 4 > 6 + 4 14 > 10 True
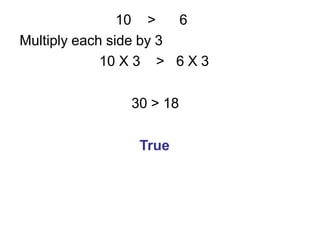
- 19. 10 > 6 Multiply each side by 3 10 X 3 > 6 X 3 30 > 18 True
- 20. 10 > 6 Divide each side by 2 10 ├À 2 > 6 ├À 2 5 > 3 True
- 21. 10 > 6 Divide each side by -2 10├À(-2) > 6├À(-2) -5 -3 False!!!!!!! > If dividing/multiplying by a negative you must turn sign round Sorted!
- 22. Back to. 64  8g < 0  8g < -64 g > 8 No real roots if g > 8