Distal end of Radius Fractures
- 2. ŌĆó ÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖøÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓĖŖÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣äÓĖŚÓĖó ÓĖŁÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖĖ 14ÓĖøÓĖĄ ŌĆó ÓĖŁÓĖ▓ÓĖŖÓĖĄÓĖ× ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖōÓĖŻ ŌĆó ÓĖĀÓĖ╣ÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖźÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖÖÓĖ▓ ÓĖł.ÓĖÖÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖŖÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖĪÓĖ▓
- 4. ŌĆó Present illness 4 hr PTA ÓĖéÓĖōÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖ Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖźÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖŚÓ╣łÓĖ▓ outstretch ÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖČÓĖüÓĖøÓĖ¦ÓĖöÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖéÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ ÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ ÓĖéÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖźÓĖöÓĖźÓĖć Ó╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖŖÓĖ▓ Ó╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖÜÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓ╣üÓĖ£ÓĖź
- 5. ŌĆó Primary Survey A: can speak,c-spine not tender B: equal breath sound,CCT negative C: v/s stable,no active bleed D: E4V5M6,pupil 3 mm RTLBE E: tender at rt wrist,limit ROM due to pain
- 6. ŌĆó Secondary survey Allergy: no food/drug allergy Medication: no current medication Past history: no previous medical/surgical history Last meal: last meal 11 hr PTA Event: as in PI
- 7. ŌĆó Physical Examination GA: A Thai male,good conscious,well co-operative v/s: BT 36C,PR 102/min,BP 117/57mmHg,RR 20/min HEENT: not pale conjunctivae,anicteric sclerae Skin: no wound Heart: normal S1S2,no murmur Lung: clear both lung,equal breath sound Abdomen: soft,not tender,normoactive bowel sound Extremities: no wound,deformities at rt wrist,mild tender,limit ROM due to pain,neurovascular intact
- 9. Film Rt. Wrist AP,Lat
- 10. ŌĆó Diagnosis closed fracture at rt distal end of radius(colles' fracture)
- 11. Distal radius fractures ŌĆó Most common orthopaedic injury with a bimodal distribution ŌŚ” younger patients - high energy ŌŚ” older patients - low energy / falls ŌĆó 50% intra-articular Osteoporosis ŌŚ” high incidence of distal radius fractures in women >50 ŌŚ” distal radius fractures are a predictor of subsequent fractures Ō¢¬ DEXA scan is recommended in woman with a distal radius fracture
- 12. Classification ŌĆó Fernandez: based on mechanism of injury ŌĆó Frykman: based on joint involvement (radiocarpal and/or radioulnar) +/- ulnar styloid fx ŌĆó Melone: divides intra-articular fxs into 4 types based on displacement ŌĆó AO: comprehensive but cumbersome
- 14. Common distal end radius fracture Colles' fracture ŌĆó Very common extra-articular fractures of the distal radius ŌĆó Most frequently seen in elderly women ŌĆó Fall in to wrist dorsiflexion ŌĆó Dinner fork deformity ŌĆó Transverse fracture at distal radial metaphysis ŌĆó Dorsal displacement of the distal fragment
- 15. Common distal end radius fracture Smith's fracture(reverse Colles) ŌĆó Fall in to wrist palmarflexion ŌĆó Volar displacement of the distal fragment
- 16. Common distal end radius fracture Barton's fracture ŌĆó Intra-articular fracture ŌĆó Shearing force ŌĆó Volar type/Dorsal type ŌĆó Usually associated subluxation/dislocation of the carpal bone
- 17. Common distal end radius fracture Die-punch fracture ŌĆó A depression fracture of the lunate fossa of the distal radius ŌĆó High energy compression force
- 18. Imaging
- 20. Treatment ŌĆó Successful outcomes correlate with ŌŚ” accuracy of articular reduction ŌŚ” restoration of anatomic relationships ŌŚ” early efforts to regain motion of wrist and fingers ŌĆó Nonoperative ŌŚ” closed reduction and cast immobilization Ō¢¬ indications Ō¢¬ extra-articular Ō¢¬ <5mm radial shortening Ō¢¬ dorsal angulation <5┬░ or within 20┬░ of contralateral distal radius
- 21. Treatment ŌĆó Operative ŌŚ” surgical fixation (CRPP, External Fixation, ORIF) Ō¢¬ indications: radiographic findings indicating instability (pre- reduction radiographs best predictor of stability) Ō¢¬ displaced intra-articular fx Ō¢¬ volar or dorsal comminution Ō¢¬ articular margins fxs Ō¢¬ severe osteoporosis Ō¢¬ dorsal angulation >5┬░ or >20┬░ of contralateral distal radius Ō¢¬ >5mm radial shortening Ō¢¬ comminuted and displaced extra-articular fxs (Smith's fx) Ō¢¬ progressive loss of volar tilt and loss of radial length following closed reduction and casting Ō¢¬ associated ulnar styloid fractures do not require fixation
- 22. Close reduction ŌĆó What should concern in close reduction? 1. Dorsal and radial displacement 2. Shortening of radius 3. Loss of normal 10 volar tilt in lateral view
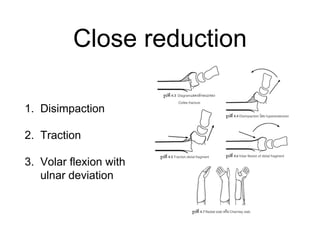
- 23. Close reduction 1. Disimpaction 2. Traction 3. Volar flexion with ulnar deviation
- 24. Complication ŌĆó Early ŌĆó Edema ŌĆó EPL rupture ŌĆó CTS ŌĆó Late ŌĆó Malunion ŌĆó Prolong stiffness
- 25. ŌĆó Follow up ÓĖłÓĖĖÓĖöÓĖĪÓĖĖÓ╣łÓĖćÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖłÓĖŗÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ 1.ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓĖ¬ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖ░Ó╣üÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖüÓĖŗÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖÖ Ó╣å 2.ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖŗÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖóÓ╣īÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖłÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖü ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖ┤Ó╣łÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ 3.Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖü slab Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪÓĖöÓĖĄÓ╣üÓĖźÓ╣ēÓĖ¦ Non displaced fracture ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖü ÓĖŁÓĖ▓ÓĖłÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖō 1-2 ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖøÓĖöÓĖ▓ÓĖ½Ó╣ī ÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖö ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖłÓĖŗÓ╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣üÓĖźÓ╣ēÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖłÓĖÖÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖÜ 6 ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖøÓĖöÓĖ▓ÓĖ½Ó╣ī Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖ¢ÓĖŁÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖŁÓĖü Displaced fracture ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖ▓ close reduction ÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖćÓ╣üÓĖŻÓĖüÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣āÓĖÖ 2-3 ÓĖ¦ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪ ÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖöÓĖĄ ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖü 1-2 ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖøÓĖöÓĖ▓ÓĖ½Ó╣ī Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖ╣Ó╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖŗÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖóÓ╣ī ÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖ▒ÓĖŹÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖüÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖÜ 6 ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖøÓĖöÓĖ▓ÓĖ½Ó╣ī Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖ¢ÓĖŁÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖØÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖŗÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖóÓ╣īÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖü (clinical union)
- 26. ŌĆó Plan of treatment Hematoma block then close reduction and short arm AP slab Pain control : paracetamol 1 tab oral prn q 4-6hr D/C + F/U 1 wk with film Wrist AP,Lat
- 27. Film Rt. Wrist AP,Lat Post close reduction