Diversion head works
- 1. DIVERSION HEAD WORK Prof. M.B Chougule DKTEâYCP Ichalkaranji
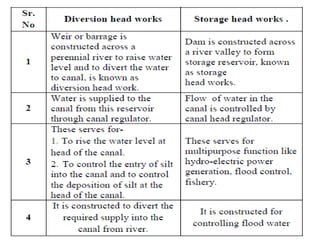
- 4. . âĒ diversion head works âĒ The works which are constructed at the head of the canal , in order to divert the river water towards the canal , so as to ensure regulated continuous supply of silt free water with certain minimum head into that canal is called as diversion head works. âĒ These are constructed on a river where adequate flow of river water is available throughout the year. âĒ If the storage on upstream of diversion head works is significant, it is called storage weir âĒ If it is constructed on downstream of dam for purpose of diverting water from upstream side of dam into canal, it is called pick up weir.
- 5. . âĒ LOCATION OF DIVERSION HEAD WORK:- âĒ It should be near the command area. The site which gives economical arrangement is usually selected. SITE SELECTION FOR HEAD WORK:- 1) Good foundation should be available. 2) The site should be such that weir can be aligned at right angle to the diversion of water in the river. 3) The site should be such that there should be sufficient space for location of head regulator and other component of the diversion headwork. 4) The overall cost should be less. 5) Proper approach way should be nearby site. 6) On the upstream side where water is retained, should not include costly land. 7) While construction of weir or barrages river should be available near the site. 8) The material and labours should be available nearby site. 9) The river should be perennial. 10)The river should have non erodible as well as non submersible banks. 11)The site should be narrow and well defined.
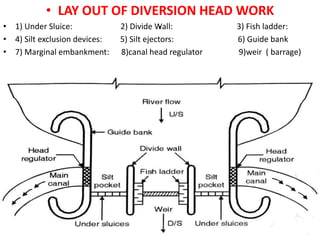
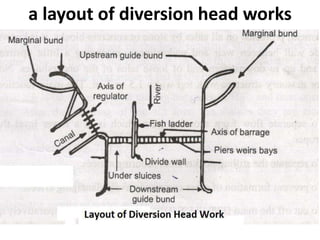
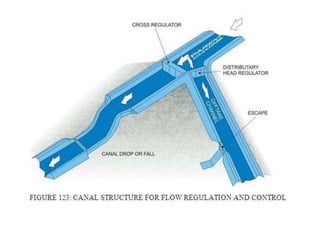
- 6. . âĒ LAY OUT OF DIVERSION HEAD WORK âĒ 1) Under Sluice: 2) Divide Wall: 3) Fish ladder: âĒ 4) Silt exclusion devices: 5) Silt ejectors: 6) Guide bank âĒ 7) Marginal embankment: 8)canal head regulator 9)weir ( barrage)
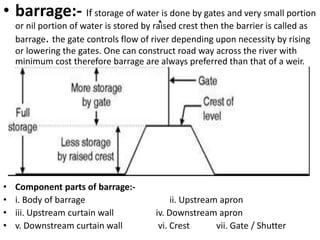
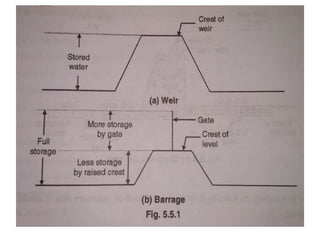
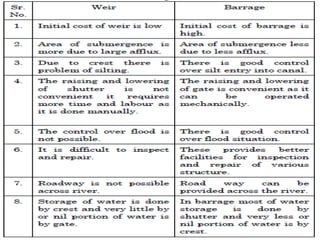
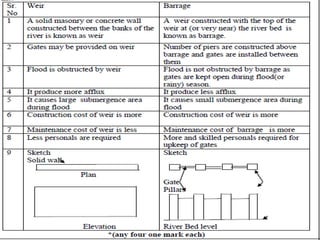
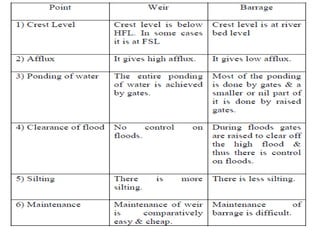
- 7. . âĒ Weir & Barrage:- âĒ Weir: It is an impervious barrier constructed across a river to raise its water level on its upstream side and divert the water into the canal taking off from its upstream side. âĒ Barrage: If storage of water is done by gates and very small portion or nil portion of water is stored by raised crest then the barrier is called as barrage. Barrage is a gate controlled weir. The heading up of water is effected by the gates alone. âĒ Weir afflux chances are more in floods. âĒ Barrage afflux chances are reduced by gates.
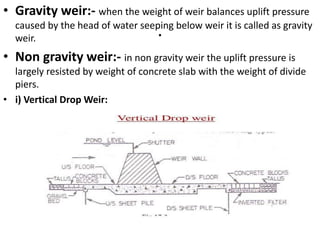
- 10. . âĒ TPES OF WEIR:- âĒ 1) gravity weir 2) non gravity weir âĒ 1) gravity weir âĒ Depending on material and design features, gravity weirs are subdivided into following types- âĒ (i)Vertical drop weir. âĒ (ii) Sloping weir âĒ a. Rock fill weirs. âĒ b. Concrete weirs âĒ Weirs are also classified as follows : âĒ (1) According to use and function. âĒ (a) Storage weir. (b) Pick up weir. âĒ (c) Diversion weir. (d)Waste weir. âĒ (2) According to control of surface flow. âĒ (3) According to the design of floors. âĒ (4) According to constructional material âĒ a) Masonry weir âĒ b) Rockfill weir âĒ c) Concrete weir
- 11. . âĒ Gravity weir:- when the weight of weir balances uplift pressure caused by the head of water seeping below weir it is called as gravity weir. âĒ Non gravity weir:- in non gravity weir the uplift pressure is largely resisted by weight of concrete slab with the weight of divide piers. âĒ i) Vertical Drop Weir:
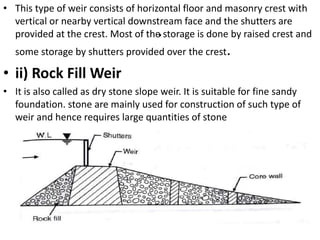
- 12. . âĒ This type of weir consists of horizontal floor and masonry crest with vertical or nearby vertical downstream face and the shutters are provided at the crest. Most of the storage is done by raised crest and some storage by shutters provided over the crest. âĒ ii) Rock Fill Weir âĒ It is also called as dry stone slope weir. It is suitable for fine sandy foundation. stone are mainly used for construction of such type of weir and hence requires large quantities of stone
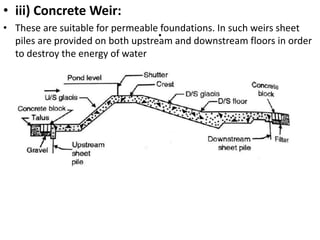
- 13. . âĒ iii) Concrete Weir: âĒ These are suitable for permeable foundations. In such weirs sheet piles are provided on both upstream and downstream floors in order to destroy the energy of water
- 14. . âĒ According to use and function. âĒ a) Storage Weir : âĒ It is high weir constructed for storing water. It is also called as diversion weir. In such weirs shutters may or may not be provided. âĒ b) Pick Up Weir : âĒ These are constructed when command area is far away from reservoir either due to rolling topography or because the land is not cultivable and if there is broken or rolling topography on one or both banks of parent river in which construction of canal may be costly.
- 15. . âĒ A solid weir usually with crest gates constructed in concrete or stone masonry located at some distance downstream of dam forming a large reservoir to raise the water level up to FSL of canal is known as pickup weir . âĒ Situations: It is proposed in the following situations- âĒ i) In case of broken or rolling topography on one or both banks of the parent river where canal construction is costly. âĒ ii)In case of command area is too far away from the reservoir may be due to rolling topography. âĒ iii) In case of land nearby the reservoir is not cultivable. âĒ iv) The command area not near the reservoir. âĒ v) Canal has to run idle. âĒ Vi) Geographically difficult terrain so that the canal alignment is âĒ very costly or impossible.
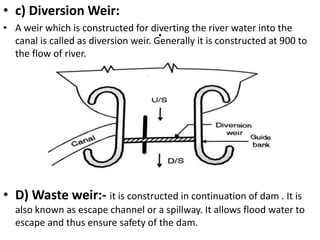
- 16. . âĒ c) Diversion Weir: âĒ A weir which is constructed for diverting the river water into the canal is called as diversion weir. Generally it is constructed at 900 to the flow of river. âĒ D) Waste weir:- it is constructed in continuation of dam . It is also known as escape channel or a spillway. It allows flood water to escape and thus ensure safety of the dam.
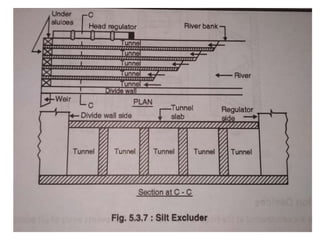
- 17. . âĒ UNDER SLUICE âĒ Under sluice are opening provided in the body of weir at low level. âĒ These are located at same side from which canal is taking off. The crest of under sluice is kept lower than crest of weir due to which water is attracted towards it and thus ensure easy diversion into canal.
- 19. . âĒ FUNCTIONS OF UNDERSLUICE:- âĒ 1) it control entry of silt into canal. âĒ 2) it lowers the HFL. âĒ 3) it helps in passing low river flood without lifting shutters. âĒ 4) it helps to pass silt on downstream side of weir. âĒ whenever silt is remover the gates of head regulator are closed and of sluice are opened through these sluice the silt which is deposited is removed and it goes on downstream side when all silt is removed silt gates are closed and regulator gates are opened.
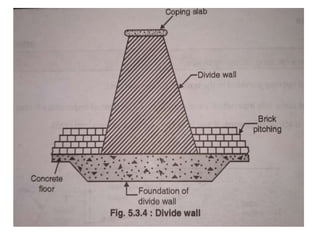
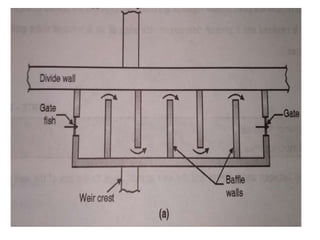
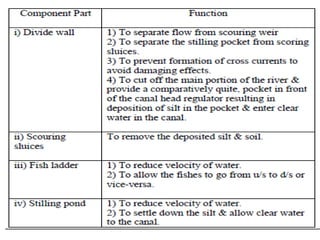
- 20. . âĒ DIVIDE WALL:- âĒ it is wall constructed between under sluices and the weir at right angle to the axis of the weir to divide the river channel. âĒ Function of divide wall:- âĒ 1) it separates the under sluices from weir. âĒ 2) it also helps in reducing velocity of flow near the head regulator due to which silt is deposited and clear water passes in to canal. âĒ 3) it prevents vortices means flow in circular motion.
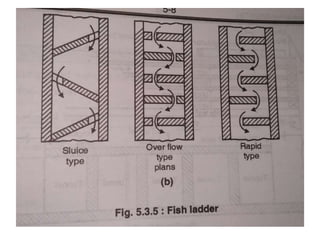
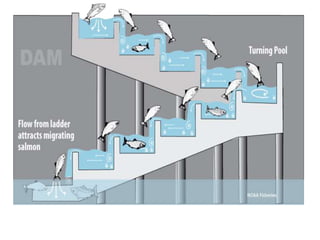
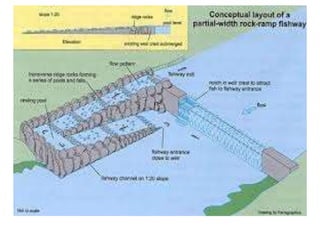
- 23. FISH LADDER âĒ It is passage provided adjacent to divide wall for the movement of fish from upstream to downstream and vice versa. âĒ It allows free access to fish so that they can travel from colder water to hot water âĒ It has been observed that fish moves from old water to warm water and in monsoon they again move towards upstream or downstream of the work. âĒ These are provided with various fashion like sluice type in which the baffle wall is in zig zag way over flow type in which V notches are provided in staggered arrangement etc.
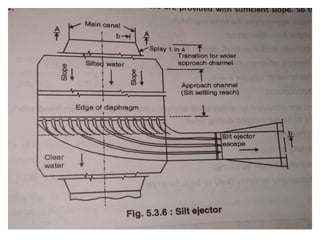
- 30. . âĒ Silt exclusion devices:- âĒ The device which are constructed at the head of main canal which prevents entry of silt particles into canal are called as silt exclusion devices. âĒ Silt ejectors:- âĒ The structure which is constructed across the canal to eject silt accumulated in canal section is called silt ejector. âĒ Silt ejector consist of tunnel which is connected parallel to the flow of the canal and then turns 90 degree to eject silt. âĒ The length of tunnel provided may be different. These are provided with sufficient slope. So that silt should not be deposited in its bed.
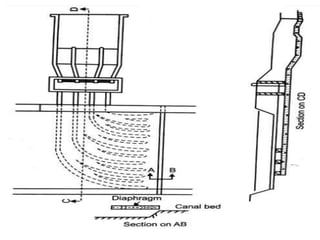
- 34. Silt excluder:- âĒ It is structure in the under sluices to pass water containing silt on downstream through under sluices so that only clear water enters into the the head regulator. âĒ These are parallel to the axis of head regulator, silt excluder prevents the entry of silt into the canal. âĒ It consist of number of small tunnels with their roof slab at same level. The crest of the head regulator and the tunnels are of different length.
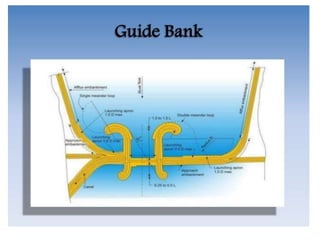
- 36. . âĒ GUIDE BANK:- âĒ Guide banks are provided on either side of diversion head work. In alluvial soil to prevent river from out flanking the work. âĒ The main object of guide banks are:- âĒ 1) it prevent oblique approach to the head regulator . âĒ 2) it protect regulator from river attack. âĒ 3) it increases maximum discharge at all point. âĒ 4) it prevent out flanking of structure. âĒ 5) it create reasonable water way for a weir. âĒ 6) To separate flow from the scouring weir which is at lower level âĒ than proper weir. âĒ 7) To separate the silting packet from scouring sluices âĒ 8) To prevent formation of cross currents to avoid domain effects âĒ 9) To cut off the main portion of the river and provide a comparatively âĒ quite packet in front of the canal head regulator resulting in deposition âĒ of silt in the pocket and enter clear water in canal
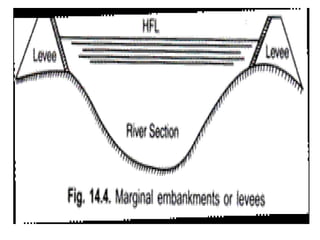
- 38. Marginal embankment:- âĒ Marginal embankment are provided on either bank of river upstream of diversion head work to protect the land and property which is likely to be submerged during flood. âĒ It helps in :- âĒ 1) reduce the intensity of flood. âĒ 2) it prevents bed level of the river by silting. âĒ 3) it protect land and property which is likely to be submerged. âĒ SCOURING SLUICE:- âĒ It helps in scour out the deposited bed silt.
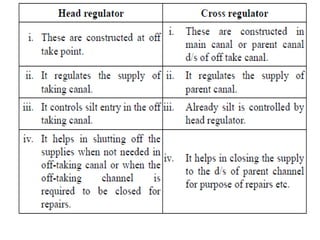
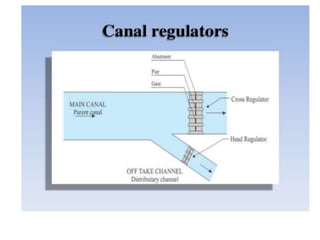
- 39. . âĒ HEAD REGULATOR:- âĒ 1) It regulates the supply of water entering in canal. âĒ 2) It controls the entry of silt into canal âĒ 3) It prevents the river flood entering the canal âĒ Stilling Pond: âĒ In still can be taken outing pond water made stil where deposition of silt takes place due to sedimentation and from which silt can be taken out. âĒ 1) To reduce velocity of water. âĒ 2) To settle down the silt and allow clear water to the canal.
- 45. .âĒ barrage:- If storage of water is done by gates and very small portion or nil portion of water is stored by raised crest then the barrier is called as barrage. the gate controls flow of river depending upon necessity by rising or lowering the gates. One can construct road way across the river with minimum cost therefore barrage are always preferred than that of a weir. âĒ Component parts of barrage:- âĒ i. Body of barrage ii. Upstream apron âĒ iii. Upstream curtain wall iv. Downstream apron âĒ v. Downstream curtain wall vi. Crest vii. Gate / Shutter
- 48. . âĒ i. Body of barrage : âĒ To raise the water level on upstream side. âĒ ii. Upstream Apron : âĒ To protect main body of barrage during floods. âĒ iii. Upstream curtain wall : âĒ To reduce uplift pressure. âĒ iv. Downstream Apron : âĒ To protect downstream bed of river. âĒ v. Downstream curtain wall : âĒ To protect downstream and floor from uplift pressure. âĒ vi. Crest wall: âĒ To raise water level and divert the water into the canal. âĒ vii. Gate / Shutter : âĒ During the floods, the gates are raised to clear off the high flood level, enabling the high flood to pass downstream with maximum afflux. âĒ
- 49. . Advantages of Barrage:- 1) Area under submergence of water is less. 2) Cost of rehabilitation is less 3) It is economical as cost of protective and energy dissipation work is less 4) All the stored water can be utilized for irrigation & other purposes. 5) Collected silt in the barrage can be regularly removed hence used with full capacity throughout its life. 6) as small afflux is caused above HFL the area under flooding is less 7)These are low cost flood banks. 8) More safe that weir as afflux is less. 9) It is economical as cost of protective and energy dissipation is less. 10) More control on flood discharge through gates. 11) Preffered in flat longitudinal sloped region & flow having heavy chances of silt. Disadvantages of barrage:- âĒ 1) Storage capacity is less as compared to dams. âĒ 2) Maintenance cost is more. âĒ 3)initial cost is more.
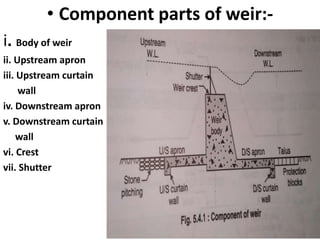
- 50. . âĒ Component parts of weir:- i. Body of weir ii. Upstream apron iii. Upstream curtain wall iv. Downstream apron v. Downstream curtain wall vi. Crest vii. Shutter
- 54. . i. Body of weir:- it is generally made of masonry. Its function is to raise water level on upstream side . It should be strong enough to resist water pressure. ii. Upstream apron :- it protect weir during floods from eroding action. Its length depends upon discharge of river and weir length it is also help to prevent leakage in subsoil and it minimizes uplift water pressure if any exist. iii. Upstream curtain wall :- it is provided to reduce the uplift pressure . Its length depends upon the nature of soil. iv. Downstream apron:- downstream apron serves like energy dissipaters. These are provided for destroying kinetic energy and thus prevent downstream side from erosion. Its length depends upon the height of fall nature of soil discharge etc. v. Downstream curtain wall:- it protect downstream floor from uplift pressure. Its length is depend upon the length of weir. vi. Crest:- it is the top of the weir. It must be strong and durable as it has to resist water pressure oftenly during floods. During flood water flows over from the crest . vii. Shutter:- shutters are provided at the top of weir. It also helps in raiseng the water level on upstream of river. Shutters must be strong to resist water pressure.
- 55. .
- 59. a layout of diversion head works