Dividendpolicy by pakistani studend
- 1. DIVIDEND AND RETENTION POLICY By : Shafqat Ali MBA iv: University of Azad Jammu and Kashmir Muzaffarabad. Dated: 25-02-2013
- 2. Introduction : ’é© What is Dividend? ’é© What is dividend policy? ’é© Theories of Dividend Policy ’éż Relevant Theory ’ü« WalterŌĆÖsModel ’ü« │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs Model ’éż Irrelevant Theory ’ü« M-MŌĆÖs Approach ’ü« Traditional Approach
- 3. What is Dividend? ŌĆ£A dividend is a distribution to shareholders out of profit or reserve available for this purposeŌĆØ. - Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
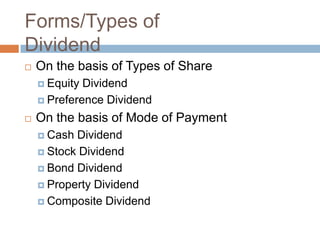
- 4. Forms/Types of Dividend ’é© On the basis of Types of Share ’éż Equity Dividend ’éż Preference Dividend ’é© On the basis of Mode of Payment ’éż Cash Dividend ’éż Stock Dividend ’éż Bond Dividend ’éż Property Dividend ’éż Composite Dividend
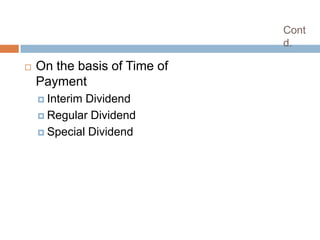
- 5. Cont d. ’é© On the basis of Time of Payment ’éż InterimDividend ’éż Regular Dividend ’éż Special Dividend
- 6. What is Dividend Policy : ’é© ŌĆ£ Dividend policy determines the division of earnings between payments to shareholders and retained earningsŌĆØ. - Weston and Bringham
- 7. Cont d. Dividend Policies involve the decisions, whether- ’éż To retain earnings for capital investment and other purposes; or ’éż To distribute earnings in the form of dividend among shareholders; or ’éż To retain some earning and to distribute remaining earnings to shareholders.
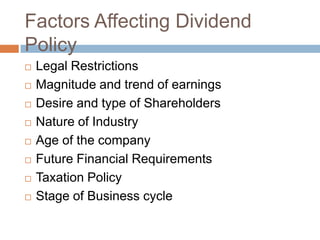
- 8. Factors Affecting Dividend Policy ’é© Legal Restrictions ’é© Magnitude and trend of earnings ’é© Desire and type of Shareholders ’é© Nature of Industry ’é© Age of the company ’é© Future Financial Requirements ’é© Taxation Policy ’é© Stage of Business cycle
- 9. Cont d. ’é© Regularity ’é© Requirements of Institutional Investors
- 10. Dimensions of Dividend Policy ’é© Pay-out Ratio ’éż Funds requirement ’éż Liquidity ’éż Access to external sources of financing ’éż Shareholder preference ’éż Difference in the cost of External Equity and Retained Earnings ’éż Control ’éż Taxes
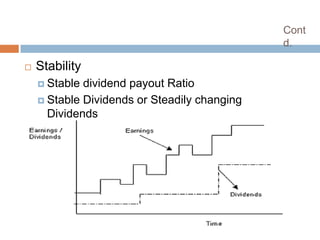
- 11. Cont d. ’é© Stability ’éż Stable dividend payout Ratio ’éż Stable Dividends or Steadily changing Dividends
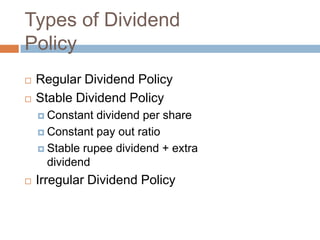
- 12. Types of Dividend Policy ’é© Regular Dividend Policy ’é© Stable Dividend Policy ’éż Constant dividend per share ’éż Constant pay out ratio ’éż Stable rupee dividend + extra dividend ’é© Irregular Dividend Policy
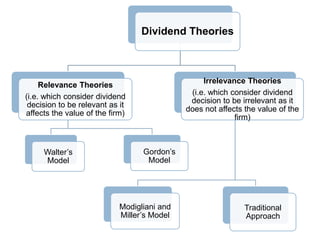
- 14. Dividend Theories Irrelevance Theories Relevance Theories (i.e. which consider dividend (i.e. which consider dividend decision to be irrelevant as it decision to be relevant as it does not affects the value of the affects the value of the firm) firm) WalterŌĆÖs │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs Model Model Modigliani and Traditional MillerŌĆÖs Model Approach
- 16. WalterŌĆÖs Model ’é© Prof. James E Walter argued that in the long- run the share prices reflect only the present value of expected dividends. Retentions influence stock price only through their effect on future dividends. Walter has formulated this and used the dividend to optimize the wealth of the equity shareholders.
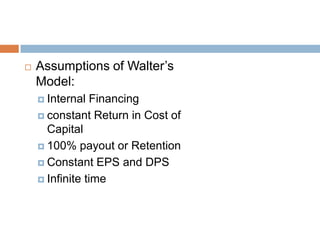
- 17. ’é© Assumptions of WalterŌĆÖs Model: ’éż Internal Financing ’éż constant Return in Cost of Capital ’éż 100% payout or Retention ’éż Constant EPS and DPS ’éż Infinite time
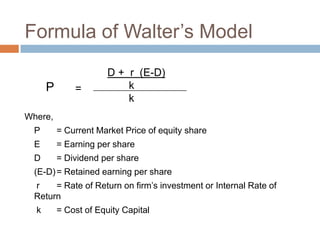
- 18. Formula of WalterŌĆÖs Model D + r (E-D) P = k k Where, P = Current Market Price of equity share E = Earning per share D = Dividend per share (E-D) = Retained earning per share r = Rate of Return on firmŌĆÖs investment or Internal Rate of Return k = Cost of Equity Capital
- 19. Illustration : ’é© Growth Firm (r > k): r = 20% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If D = Rs. 4 P = 4+(0) 0.20 /0 .15 = Rs. 26.67 0.15 If D = Rs. 2 P = 2+(2) 0.20 / 0.15 = Rs. 31.11 0.15
- 20. Illustration : ’é© Normal Firm (r = k): r = 15% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If D = Rs. 4 P = 4+(0) 0.15 / 0.15 = Rs. 26.67 0.15 If D = Rs. 2 P = 2+(2) 0.15 / 0.15 = Rs. 26.67 0.15
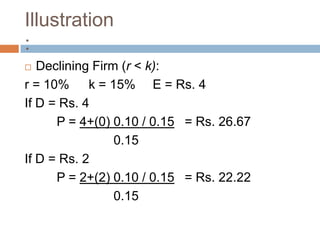
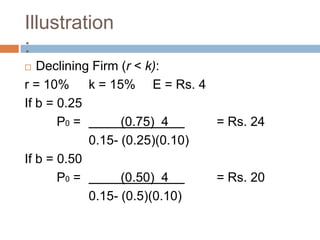
- 21. Illustration : ’é© Declining Firm (r < k): r = 10% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If D = Rs. 4 P = 4+(0) 0.10 / 0.15 = Rs. 26.67 0.15 If D = Rs. 2 P = 2+(2) 0.10 / 0.15 = Rs. 22.22 0.15
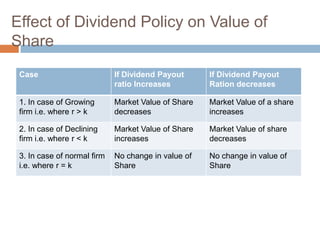
- 22. Effect of Dividend Policy on Value of Share Case If Dividend Payout If Dividend Payout ratio Increases Ration decreases 1. In case of Growing Market Value of Share Market Value of a share firm i.e. where r > k decreases increases 2. In case of Declining Market Value of Share Market Value of share firm i.e. where r < k increases decreases 3. In case of normal firm No change in value of No change in value of i.e. where r = k Share Share
- 23. Criticisms of WalterŌĆÖs Model ’é© No External Financing ’é© FirmŌĆÖs internal rate of return does not always remain constant. In fact, r decreases as more and more investment in made. ’é© FirmŌĆÖs cost of capital does not always remain constant. In fact, k changes directly with the firmŌĆÖs risk.
- 24. │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs Model ’ü▒ According to Prof. Gordon, Dividend Policy almost always affects the value of the firm. He Showed how dividend policy can be used to maximize the wealth of the shareholders. ’ü▒ The main proposition of the model is that the value of a share reflects the value of the future dividends accruing to that share. Hence, the dividend payment and its growth are relevant in valuation of shares. ’ü▒ The model holds that the shareŌĆÖs market price is equal to the sum of shareŌĆÖs discounted future dividend payment.
- 25. ’é© Assumptions: ’éż Allequity firm ’éż No external Financing ’éż Constant Returns ’éż Constant Cost of Capital ’éż Perpetual Earnings ’éż No taxes ’éż Constant Retention ’éż Cost of Capital is greater then growth rate (k>br=g)
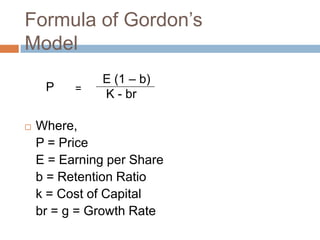
- 26. Formula of │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs Model E (1 ŌĆō b) P = K - br ’é© Where, P = Price E = Earning per Share b = Retention Ratio k = Cost of Capital br = g = Growth Rate
- 27. Illustration : ’é© Growth Firm (r > k): r = 20% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If b = 0.25 P0 = (0.75) 4 = Rs. 30 0.15- (0.25)(0.20) If b = 0.50 P0 = (0.50) 4 = Rs. 40 0.15- (0.5)(0.20)
- 28. Illustration : ’é© Normal Firm (r = k): r = 15% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If b = 0.25 P0 = (0.75) 4 = Rs. 26.67 0.15- (0.25)(0.15) If b = 0.50 P0 = (0.50) 4 = Rs. 26.67 0.15- (0.5)(0.15)
- 29. Illustration : ’é© Declining Firm (r < k): r = 10% k = 15% E = Rs. 4 If b = 0.25 P0 = (0.75) 4 = Rs. 24 0.15- (0.25)(0.10) If b = 0.50 P0 = (0.50) 4 = Rs. 20 0.15- (0.5)(0.10)
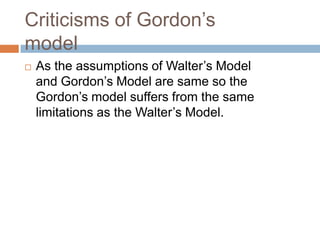
- 30. Criticisms of │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs model ’é© As the assumptions of WalterŌĆÖs Model and │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs Model are same so the │ę┤Ū░∙╗Õ┤Ū▓įŌĆÖs model suffers from the same limitations as the WalterŌĆÖs Model.
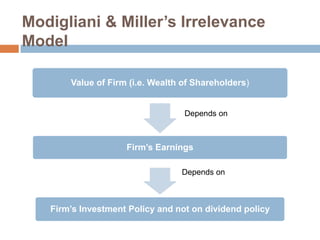
- 32. Modigliani & MillerŌĆÖs Irrelevance Model Value of Firm (i.e. Wealth of Shareholders) Depends on FirmŌĆÖs Earnings Depends on FirmŌĆÖs Investment Policy and not on dividend policy
- 33. Modigliani and MillerŌĆÖs Approach ’é© Assumption ’éż Capital Markets are Perfect and people are Rational ’éż No taxes ’éż Floating Costs are nil ’éż Investment opportunities and future profits of firms are known with certainty (This assumption was dropped later) ’éż Investment and Dividend Decisions are independent
- 34. M-MŌĆÖs Argument ’é© If a company retains earnings instead of giving it out as dividends, the shareholder enjoy capital appreciation equal to the amount of earnings retained. ’é© If it distributes earnings by the way of dividends instead of retaining it, shareholder enjoys dividends equal in value to the amount by which his capital would have appreciated had the company chosen to retain its earning.
- 35. ’é© Hence, the division of earnings between dividends and retained earnings is IRRELEVANT from the point of view of shareholders.
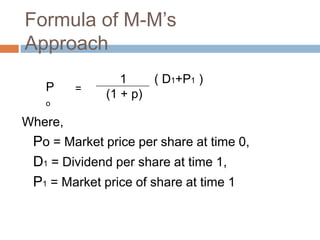
- 36. Formula of M-MŌĆÖs Approach 1 ( D1+P1 ) P = (1 + p) o Where, Po = Market price per share at time 0, D1 = Dividend per share at time 1, P1 = Market price of share at time 1
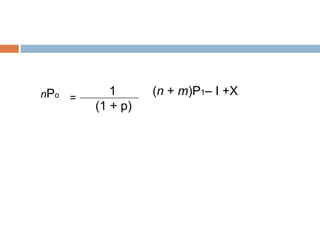
- 37. 1 (nD1+nP1) nPo = (1 + p) ’é© The expression of the outstanding equity shares of the firm at time 0 is obtained as: 1 {nD1+(n + m)P1- mP1} nPo = (1 + p)
- 38. mP1 = I ŌĆō (X ŌĆō nD1) Where, X = Total net profit of the firm for year 1 nPo 1 [nD1+ (n + m)P1ŌĆō {I ŌĆō (X ŌĆō = nD1)}] (1 + p) nPo 1 nD1+ (n + m)P1ŌĆō I +X ŌĆō nD1 = (1 + p)
- 39. nPo 1 (n + m)P1ŌĆō I +X = (1 + p)
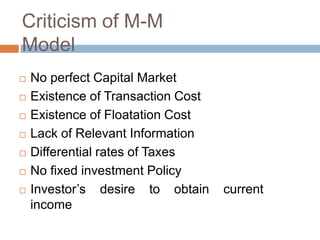
- 40. Criticism of M-M Model ’é© No perfect Capital Market ’é© Existence of Transaction Cost ’é© Existence of Floatation Cost ’é© Lack of Relevant Information ’é© Differential rates of Taxes ’é© No fixed investment Policy ’é© InvestorŌĆÖs desire to obtain current income
- 41. Traditional Approach ’é© This theory regards dividend decision merely as a part of financing decision because ’éż The earnings available may be retained in the business for re-investment ’éż Or if the funds are not required in the business they may be distributed as dividends. ’é© Thus the decision to pay the dividends or retain the earnings may be taken as a residual decision
- 42. ’é© This theory assumes that the investors do not differentiate between dividends and retentions by the firm ’é© Thus, a firm should retain the earnings if it has profitable investment opportunities otherwise it should pay than as dividends.
- 43. Synopsis ’é© Dividend is the part of profit paid to Shareholders. ’é© Firm decide, depending on the profit, the percentage of paying dividend. ’é© Walter and Gordon says that a Dividend Decision affects the valuation of the firm. ’é© While the Traditional Approach and MMŌĆÖs Approach says that Value of the Firm is irrelevant to Dividend we pay.
- 44. Bibliograph y ’é© Google ’é© Financial management by prasanna chandra.























![mP1 = I ŌĆō (X ŌĆō nD1)
Where,
X = Total net profit of the firm for year
1
nPo 1 [nD1+ (n + m)P1ŌĆō {I ŌĆō (X ŌĆō
=
nD1)}]
(1 + p)
nPo 1 nD1+ (n + m)P1ŌĆō I +X ŌĆō nD1
=
(1 + p)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dividendpolicybypakistanistudend-130226103442-phpapp02/85/Dividendpolicy-by-pakistani-studend-38-320.jpg)