DNA damage.ppt
- 1. Types of damage There are five main types of damage to DNA due to endogenous cellular processes: oxidation of bases [e.g. 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG)] and generation of DNA strand interruptions from reactive oxygen species, alkylation of bases (usually methylation), such as formation of 7- methylguanine, 1-methyladenine, 6-O-Methylguanine hydrolysis of bases, such as deamination, depurination, and depyrimidination.
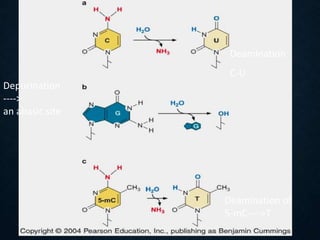
- 2. DNA UNDERGOES DAMAGE SPONTANEOUSLY FROM HYDROLYSIS(╦«ĮŌ) AND DEAMINATION(╚ź░▒╗∙) ? This is ironic since the proper structure of the double helix depends on an aqueous environment.
- 3. Deamination C-U Depurination ----> an abasic site Deamination of 5-mC---->T
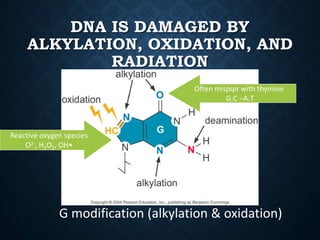
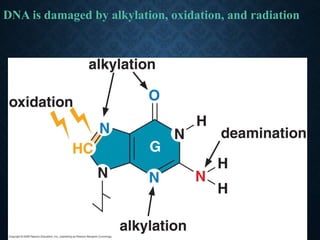
- 4. DNA IS DAMAGED BY ALKYLATION, OXIDATION, AND RADIATION Often mispqir with thymine G:C ©CA:T Reactive oxygen species O2-, H2O2, OH? G modification (alkylation & oxidation)
- 5. Thymine dimer by ultraviolet light Incapable of base-pairing and cause the DNA polymerse to stop during replication
- 6. Clastogenic ©C ionizing radiation and agents like bleomycin that cause DNA to break are said to be clastogenic.
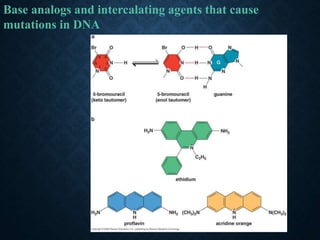
- 7. MUTATIONS ARE ALSO CAUSED BY BASE ANALOGS AND INTERCALATING AGENTS Base analogues
- 8. Intercalating agents which cause the deletion or addition of a base pair or a few base pairs
- 9. DNA DAMAGE DNA undergoes damage spontaneously from hydrolysis and deamination
- 10. DNA is damaged by alkylation, oxidation, and radiation
- 11. Thymine dimer caused by UV light
- 12. Base analogs and intercalating agents that cause mutations in DNA
- 13. Ames test for carcinogens
- 14. Bruce N. Ames Professor of the Graduate School Division of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, UC Berkeley
- 15. REPAIR OF DNA DAMAGE

![Types of damage
There are five main types of damage to DNA due to endogenous cellular
processes:
oxidation of bases [e.g. 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG)] and generation of
DNA strand interruptions from reactive oxygen species,
alkylation of bases (usually methylation), such as formation of 7-
methylguanine, 1-methyladenine, 6-O-Methylguanine
hydrolysis of bases, such as deamination, depurination, and depyrimidination.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnadamage-221005095702-82d15704/85/DNA-damage-ppt-1-320.jpg)