1 of 1
Download to read offline
Recommended


PISA matemáticas: CrecerInstituto Nacional de Evaluación Educativa
Ã˝
Este documento presenta un gráfico que muestra la estatura promedio de niños y niñas holandeses en 1998. El gráfico indica que las niñas son más altas que los niños entre los 11 y 13 años. Además, la tasa de crecimiento de la estatura de las niñas disminuye después de los 12 años según se puede ver por la pendiente más plana de la curva.

Evaluacion de la reproduccionmolina-jose
Ã˝
El documento explica conceptos clave del manejo reproductivo en ganadería como precocidad, ciclicidad, fertilidad y fecundidad. Define índices para evaluar la eficiencia reproductiva como el intervalo parto-celo, intervalo entre partos, porcentaje de preñez y número de servicios por concepción. Resalta la importancia de registros precisos y del balance nutricional para lograr una adecuada reproducción.

Presentación1 capacitaciónCarolina Mantilla
Ã˝
El documento presenta información sobre un taller de cultura de paz, incluyendo definiciones de conceptos como sexo, género, estereotipos de género y equidad de género. También explica la inteligencia emocional y cómo usarla en el trabajo y las organizaciones, identificando habilidades interpersonales e intrapersonales clave. Finalmente, enumera emociones básicas y complejas y sus objetivos.New microsoft office word document (3)



New microsoft office word document (3)Sayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Radiation sterilization uses ultraviolet (UV) light or ionizing radiation like gamma rays and electrons to kill microorganisms. Ionizing radiation creates free radicals that damage cells, while UV radiation excites electrons and destroys cellular structure. Pharmaceutical powders are more resistant to ionizing radiation than liquids, and certain drugs like penicillin and thiamine have been effectively sterilized with ionizing radiation. UV radiation is also used in hospitals to reduce bacterial contamination and control infection.Gabby



GabbySimonRoyals
Ã˝
Gabby enjoys reading because it allows her to explore new books and places. Her favorite book series is Ivy and Bean due to its humor and ability to transport her elsewhere. She likes cheerleading because she enjoys attending games and performing tumbling skills. Brownies are Gabby's favorite food as they contain chocolate and have a gooey texture. Dogs are her favorite animal since they are soft and cute.Respiratorysystemdock 131210122437-phpapp02



Respiratorysystemdock 131210122437-phpapp02Sayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The respiratory system allows for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper respiratory tract which filters and conditions incoming air, and the lower respiratory tract including the lungs where gas exchange occurs in small air sacs called alveoli. The respiratory cycle involves inspiration and expiration through contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Disorders can impact airflow and gas exchange, and lung function is measured through volumes like tidal volume and vital capacity.Circulatory system (1)



Circulatory system (1)Sayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
cxzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzczxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzxzcccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc4. the oxygen cycle



4. the oxygen cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless gas that is less dense than air and a poor conductor of heat and electricity. It cycles between the atmosphere, plants, animals, and oceans through photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct in plants, which is then used by animals through respiration and releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Oxygen levels on Earth have increased over time as photosynthesis evolved and continues to be balanced between the atmosphere and bodies of water.Nitrogen cycle



Nitrogen cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Nitrogen is essential for life but is predominantly found as unusable atmospheric N2. The nitrogen cycle converts N2 into biologically available forms through four processes: nitrogen fixation by bacteria and lightning, ammonification by decomposer bacteria, nitrification by more bacteria, and denitrification by yet more bacteria or burning of fossil fuels which converts it back to N2. Human activities like combustion, use of commercial fertilizers, and sewage discharge disrupt the natural nitrogen cycle.The phosphorus cycle



The phosphorus cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The document discusses the phosphorus cycle, which describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere and hydrosphere. Unlike other biogeochemical cycles, the atmosphere does not play a significant role in phosphorus movements. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plants and animals and is important for DNA, RNA, ATP, and building bones and teeth. The cycle occurs as phosphorus moves from land to ocean sediments and back again, with the main storage being in the Earth's crust as phosphates.Circulatory system



Circulatory systemSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The circulatory system uses the heart to pump blood through vessels around the body. It has two circuits - pulmonary circulation between the heart and lungs, and systemic circulation between the heart and body. The heart has four chambers that pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood around the body in a continuous cycle. Blood vessels include arteries carrying blood away from the heart, veins returning it, and capillaries where exchange occurs. The circulatory system transports blood cells, platelets, plasma, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, carbon dioxide and waste products.Respiratory system dock



Respiratory system dockSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The respiratory system allows for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper respiratory tract which filters and conditions incoming air, and the lower respiratory tract including the lungs where gas exchange occurs in small air sacs called alveoli. The respiratory cycle involves inspiration and expiration through contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Disorders can impact airflow and gas exchange, and lung function is measured through volumes like tidal volume and vital capacity.Nucleic acid 1



Nucleic acid 1Sayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
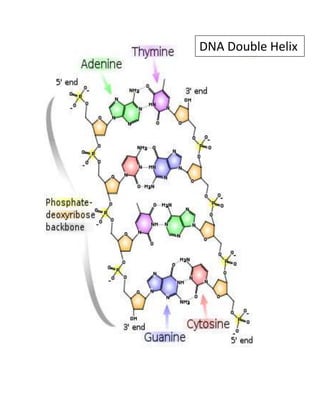
Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides and there are two types: DNA and RNA. DNA is a long macromolecule made of deoxyribonucleotides that carry genetic information. The bases in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine. Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. The backbone of DNA consists of deoxyribose sugars linked by phosphate groups.Rna



RnaSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
RNA is a long macromolecule consisting of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bridges. The main types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis. tRNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis according to the mRNA sequence. rRNA is the major component of ribosomes and plays a catalytic and structural role in protein synthesis.More Related Content
More from Sayeed Ahmad (7)
4. the oxygen cycle



4. the oxygen cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless gas that is less dense than air and a poor conductor of heat and electricity. It cycles between the atmosphere, plants, animals, and oceans through photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct in plants, which is then used by animals through respiration and releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Oxygen levels on Earth have increased over time as photosynthesis evolved and continues to be balanced between the atmosphere and bodies of water.Nitrogen cycle



Nitrogen cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Nitrogen is essential for life but is predominantly found as unusable atmospheric N2. The nitrogen cycle converts N2 into biologically available forms through four processes: nitrogen fixation by bacteria and lightning, ammonification by decomposer bacteria, nitrification by more bacteria, and denitrification by yet more bacteria or burning of fossil fuels which converts it back to N2. Human activities like combustion, use of commercial fertilizers, and sewage discharge disrupt the natural nitrogen cycle.The phosphorus cycle



The phosphorus cycleSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The document discusses the phosphorus cycle, which describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere and hydrosphere. Unlike other biogeochemical cycles, the atmosphere does not play a significant role in phosphorus movements. Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plants and animals and is important for DNA, RNA, ATP, and building bones and teeth. The cycle occurs as phosphorus moves from land to ocean sediments and back again, with the main storage being in the Earth's crust as phosphates.Circulatory system



Circulatory systemSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The circulatory system uses the heart to pump blood through vessels around the body. It has two circuits - pulmonary circulation between the heart and lungs, and systemic circulation between the heart and body. The heart has four chambers that pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood around the body in a continuous cycle. Blood vessels include arteries carrying blood away from the heart, veins returning it, and capillaries where exchange occurs. The circulatory system transports blood cells, platelets, plasma, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, carbon dioxide and waste products.Respiratory system dock



Respiratory system dockSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
The respiratory system allows for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It consists of the upper respiratory tract which filters and conditions incoming air, and the lower respiratory tract including the lungs where gas exchange occurs in small air sacs called alveoli. The respiratory cycle involves inspiration and expiration through contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Disorders can impact airflow and gas exchange, and lung function is measured through volumes like tidal volume and vital capacity.Nucleic acid 1



Nucleic acid 1Sayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides and there are two types: DNA and RNA. DNA is a long macromolecule made of deoxyribonucleotides that carry genetic information. The bases in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine. Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. The backbone of DNA consists of deoxyribose sugars linked by phosphate groups.Rna



RnaSayeed Ahmad
Ã˝
RNA is a long macromolecule consisting of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bridges. The main types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis. tRNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis according to the mRNA sequence. rRNA is the major component of ribosomes and plays a catalytic and structural role in protein synthesis.
