DNA Methylation in Young Women Breast Cancer
- 1. DNA Methylation in Young Women Breast Cancer PEDRO PENZUTI PACHECO SUPERVISORS: DR. WAYNE XU, DR. MARSHALL PITZ
- 2. Background ïĩ Breast Cancer (BC) is the leading cause of death from cancers for women under 40 years old [1]. Age has repeatedly shown to be an independent predictor of poor outcome [2]. ïĩ Is YWBC a unique disease? Or is it just the fact that YWBC is enriched with more aggressive BC types? ïĩ We briefly analyzed somatic mutation The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data and found no significant difference between the two cohorts. ïĩ Are there epigenomic factors that can differentiate between the two? [1] (Leclere et al., 2013) [2] Nixon AJ, Neuburg D, Hayes et al., 1994
- 3. Hypothesis ïĩ Are there differences in DNA methylation patterns between young and old women with BC? ïĩ If so, what are they? ïĩ Could these help explain what drives the aggressiveness of BC in young women?
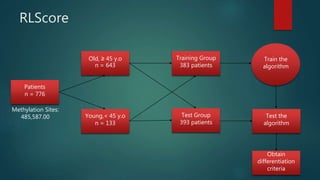
- 4. Methods ïĩ TCGA Methylation Data ïĩ 133 young patients (< 45 years old); 643 old patients (âĨ 45 years old) ïĩ Illumina Array Platform ïĩ Level 3 ïĩ Curated ïĩ Machine learning as the regression method. ïĩ RLScore ïĩ Data is split in half: training and test data. ïĩ Methylation site and gene function analysis. ïĩ Utilized annotation file to trace back methylation and gene location. ïĩ Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to investigate.
- 5. RLScore Patients n = 776 Young,< 45 y.o n = 133 Old, âĨ 45 y.o n = 643 Training Group 383 patients Test Group 393 patients Obtain differentiation criteria Train the algorithm Methylation Sites: 485,587.00 Test the algorithm
- 6. Differentiating Methylation Sites ïĩ 17 sites were found to be differentially methylated in the young vs old groups. ïĩ 4 in particular deserve to be highlighted Location Hyper or Hypomethylated Gene Regulatory Feature chr6:33588617- 33589909 Hypomethylated IP3R3 or ITPR3 Promoter Associated chr19:940723-942490 Hypermethylated ARID3A or BRIGHT Unclassified chr3:147077115- 147077672 Hypermethylated ? ? chr2:20068428- 20068907 Hypermethylated ? ?
- 7. IP3R3 / ITPR3 Coupling between type III IP3 receptor (IP3R3) and Big Potassium voltage- and Calcium-dependent (BKCA) channel have shown to stimulate BC cell proliferation [3]. Increased expression of IP3R3 is associated with increased aggressiveness of colon cancer and decreased long-term survival [4]. [3]:Mound A, Rodat-Despoix L, Bougarn S, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Matifat F. Molecular interaction and functional coupling between type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and BKCa channel stimulate breast cancer cell proliferation. [4]:Fonslow, Bryan R Stein, Benjamin D Webb et al. The type III inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is associated with aggressiveness of colorectal carcinoma Source: genecards.org
- 8. ARID3A [5] Samyesudhas SJ, Roy L, Cowden Dahl KD. Differential expression of ARID3B in normal adult tissue and carcinomas. [6] Bobbs A, Gellerman K, Hallas WM, Joseph S, Yang C, Kurkewich J, et al. ARID3B Directly Regulates Ovarian Cancer Promoting Genes. [7] Oguz Erdogan AS1, Ozdemirler N, Oyken M, Alper M, Erson-Bensan AE. ARID3B expression in primary breast cancers and breast cancer-derived cell lines. Source: genecards.org ïĩ First report showing ARID3A being implicated with BC. ïĩ ARID3B has shown to be differentially expressed in neuroblastoma and ovarian cancer [5]. ïĩ More recently, it has shown to regulate Ovarian Cancer promoting genes. ARID3B regulates target genes in the Wnt pathway that promote adhesion of ovarian cancer cells [6].
- 9. Conclusions and Future Perspective ïĩ We utilized a machine learning approach to try to identify methylation sites associated with YWBC. ïĩ There are significant differences in the methylation patterns between young and old women. ïĩ Some of the methylated sites in young women could help explain the aggressiveness of the tumors found in this group of patients. ïĩ Investigate ITPR3, ARID3A and all the other 13 sites in more depth. ïĩ Optimize the algorithm.
- 10. Acknowledgements

![Background
ïĩ Breast Cancer (BC) is the leading cause of death from cancers for women
under 40 years old [1]. Age has repeatedly shown to be an independent
predictor of poor outcome [2].
ïĩ Is YWBC a unique disease? Or is it just the fact that YWBC is enriched with more
aggressive BC types?
ïĩ We briefly analyzed somatic mutation The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data
and found no significant difference between the two cohorts.
ïĩ Are there epigenomic factors that can differentiate between the two?
[1] (Leclere et al., 2013)
[2] Nixon AJ, Neuburg D, Hayes et al., 1994](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a352694d-360f-49bb-8362-94c49cdcbfd6-160811224033/85/DNA-Methylation-in-Young-Women-Breast-Cancer-2-320.jpg)



![IP3R3 / ITPR3
Coupling between type III IP3 receptor (IP3R3) and Big
Potassium voltage- and Calcium-dependent (BKCA)
channel have shown to stimulate BC cell proliferation [3].
Increased expression of IP3R3 is associated with
increased aggressiveness of colon cancer and decreased
long-term survival [4].
[3]:Mound A, Rodat-Despoix L, Bougarn S, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Matifat F. Molecular interaction and functional coupling between type 3
inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and BKCa channel stimulate breast cancer cell proliferation.
[4]:Fonslow, Bryan R Stein, Benjamin D Webb et al. The type III inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is associated with aggressiveness of
colorectal carcinoma
Source: genecards.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a352694d-360f-49bb-8362-94c49cdcbfd6-160811224033/85/DNA-Methylation-in-Young-Women-Breast-Cancer-7-320.jpg)
![ARID3A
[5] Samyesudhas SJ, Roy L, Cowden Dahl KD. Differential expression of ARID3B in normal adult tissue and carcinomas.
[6] Bobbs A, Gellerman K, Hallas WM, Joseph S, Yang C, Kurkewich J, et al. ARID3B Directly Regulates Ovarian Cancer Promoting Genes.
[7] Oguz Erdogan AS1, Ozdemirler N, Oyken M, Alper M, Erson-Bensan AE. ARID3B expression in primary breast cancers and breast cancer-derived cell
lines.
Source: genecards.org
ïĩ First report showing ARID3A being implicated with BC.
ïĩ ARID3B has shown to be differentially expressed in neuroblastoma and ovarian
cancer [5].
ïĩ More recently, it has shown to regulate Ovarian Cancer promoting genes. ARID3B
regulates target genes in the Wnt pathway that promote adhesion of ovarian
cancer cells [6].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a352694d-360f-49bb-8362-94c49cdcbfd6-160811224033/85/DNA-Methylation-in-Young-Women-Breast-Cancer-8-320.jpg)

