Dns system-ahmadullah-alnoor-at-af sig-2017-by-nitpaa
- 1. AGENDA ŌĆó Introduction ŌĆó Disclaimer ŌĆó Attribution ŌĆó Internet (Naming,Addressing, Routing) ŌĆó Domain Name System (DNS) ŌĆó DNS Abuse
- 2. INTRODUCTION ŌĆó Ahmadullah Alnoor ŌĆó Software Engineer ŌĆó Microsoft Development Center, Copenhagen, Denmark ŌĆó Masters in Distributed Systems, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden ŌĆó NITPAA Member
- 3. DISCLAIMER ŌĆó The views expressed in this Presentation are Personal and do not necessarily reflect the views of my employer. ŌĆó This Presentation is not from Microsoft.
- 4. ATTRIBUTION ŌĆó The Presentation is based on Sessions attending during ICANN 58 which was held in Copenhagen, Denmark. ŌĆó Visit https://schedule.icann.org/ for the source materials.
- 6. NAMING ŌĆó Name identifies an Object ŌĆó Examples of Names are ŌĆ” Kabul, www.bing.com ŌĆó Name says What something is or Who someone is ŌĆó Name does not say Where something or someone is
- 7. ADDRESSING ŌĆó Address identifies a Location ŌĆó Examples of address are ŌĆ” (34.5553┬░ N, 69.2075┬░ E), 13.107.21.200 ŌĆó Name Resolution maps a Name to an Address ŌĆó Address says Where someone or something is ŌĆó Address does not say How to reach the address.
- 8. ROUTING ŌĆó Route says How to reach an Address ŌĆó Examples of Route are ŌĆ” Road Signs, RoutingTables ŌĆó Route to Address is set before Traffic Arrives ŌĆó Traffic moves through the Route in steps or hops ŌĆó Traffic trusts each step/hop
- 10. WHY DNS ŌĆó Numbers are hard to remember. IP Addresses are many. ŌĆó 3.4 Billion IPv4 addresses, many many more IPv6 addresses ŌĆó Names are easier to remember
- 11. A DISTRIBUTED DATABASE ŌĆó Data is maintained locally and available globally. ŌĆó Scalable ŌĆó Maintainable ŌĆó Performant ŌĆó Resilient
- 12. NAME RESOLUTION ŌĆó The process of translating a (host) name to an (IP) address ŌĆó The process of translating an (IP) address to a (host) name
- 13. ARCHITECTURE
- 14. STRUCTURE
- 15. FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name ŌĆō www.example.com.
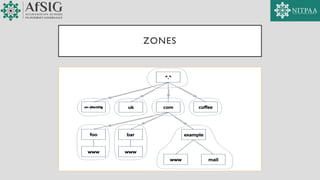
- 16. ZONES
- 17. ZONE FILE + RR ŌĆó Zone file contains all data for the Zone ŌĆó Zone data is stored as Resource Records
- 18. ZONE FILE SAMPLE
- 19. NAME SERVERS
- 20. GLUE
- 21. ROOT SERVERS ŌĆó Stub Resolvers, Recursive Resolves and Authoritative Name Servers cooperate. ŌĆó Resolvers have a hints file pointing to Root Name Servers.
- 23. ŌĆ”
- 24. ŌĆ”
- 25. ŌĆ”
- 26. CACHING
- 27. ŌĆ”
- 28. DNS ABUSE What is DNS Abuse?
- 29. MALICIOUS CONDUCT ŌĆó Misuse of DNS Infrastructure, Protocol and Processes ŌĆó Data Corruption ŌĆó Denial of Service ŌĆó PrivacyViolation
- 30. DOMAIN NAME ABUSE ŌĆó Phishing ŌĆó Malware ŌĆó Scams ŌĆó Illegal Goods ŌĆó Counterfeit Goods ŌĆó Fake Trademark Protection ŌĆó Fake Domain Sales
- 31. CACHE POISONING ŌĆó Change the DNS Cache in the Recursive Resolver to return fake records https://www.ipa.go.jp/files/000013084.png
- 32. DISTRIBUTED DENIAL OF SERVICE (DDOS) ŌĆó Many Bots/Zombie machines sends DNS Queries to a specific Name Server https://www.incapsula.com/images/illustrations/ddos-mini-site/nxdomain-dns-ddos.jpeg
- 33. DDOS AMPLIFICATION ŌĆó Using UDP (User Datagram Protocol) to generate traffic to a specific Name Server http://securityskeptic.typepad.com/.a/6a0120a55f18a4970c0153907539c1970b-pi