Docking techniques
- 2. Introduction âĒ Docking is an attempt to find the best matching between two molecules. âĒ A more serious definitionâĶ. âĒ Docking is a method which predicts the preferred orientation of one ligand when bound in an active site to form a stable complex. âĒ Finding the correct relative orientation of the âkeyâ which will open up the âlockâ. âĒ The protein can be thought of as the âlockâ and the ligand can be thought of as a âkeyâ.
- 3. Ligand in catalytic pocket Protein(Cysteine Protease) Protein with Ligand
- 4. Introduction Successful docking methods search high-dimensional spaces effectively and use a scoring function that correctly ranks candidate dockings
- 5. Molecular Docking Molecular docking Identification of correct ligand binding Prediction of binding affinity Rational Drug Design
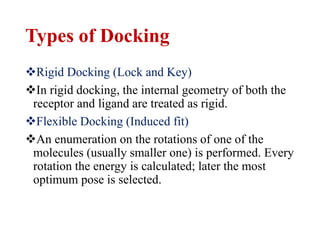
- 6. Types of Docking ïķRigid Docking (Lock and Key) ïķIn rigid docking, the internal geometry of both the receptor and ligand are treated as rigid. ïķFlexible Docking (Induced fit) ïķAn enumeration on the rotations of one of the molecules (usually smaller one) is performed. Every rotation the energy is calculated; later the most optimum pose is selected.
- 7. Docking can be betweenâĶ. âĒ Protein â Ligand âĒ Protein â Protein âĒ Protein â Nucleotide
- 8. Requirements âĒ Protein (Enzyme, peptide) âĒ Ligand (Drug, novel compound, testing compound, organic compound) âĒ Docking Software (Autodock) âĒ Result analysis
- 9. Target selection Protein preparation Docking Ligand selection Ligand preparation Docking Docking Result Evaluation Process of Molecular Docking Step:1 Step:2
- 10. Brutonâs tyrosine kinase inhibitors DOCKING DOCKING Screening of Compounds
- 11. ïķ SANJEEVINI â IIT Delhi ïķ GOLD â University of Cambridge ,UK ïķ AUTODOCK - Scripps Research Institute,USA ïķ GemDock(Generic Evolutionary Method for Molecular Docking) A tool, developed by Jinn-Moon Yang, a professor of the Institute of Bioinformatics, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan ïķ Hex Protein Docking - University of Aberdeen, UK ïķ GRAMM (Global Range Molecular Matching) Protein docking - A Center for Bioinformatics, University of Kansas, USA Docking Software
- 12. Limitations(Pharmacophore & Docking) âĒ The major limitation in virtual screening by pharmacophore is the absence of good scoring metrics. âĒ Whereas docking simulations are based on scoring functions trying to predict the affinity, and similarity searches utilize similarity metrics. âĒ Pharmacophore queries do not have a reliable, general scoring metric. âĒ Most commonly, the quality of fitting the ligand into a pharmacophore query is expressed by the root mean square deviation between the features of the query and atoms of the molecule.
- 13. Application âĒ Pharmacophore approaches are successful subfields of computer-aided drug design (CADD) which have become one of the major tools âĒ hit identification âĒ lead optimization âĒ rational design of novel drugs. âĒ Virtual screening (hit identification) âĒ Drug Discovery (lead optimization) âĒ Bioremediation