Donor selection ppt
Download as PPT, PDF40 likes22,813 views
This document discusses donor selection for blood donations. It outlines the types of blood donors as voluntary or replacement donors. The donor selection process includes registration, a medical history questionnaire, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Donors are deferred or rejected depending on medical conditions or test results. Proper donor selection is important to protect both the donor and recipient. Records of all donor information and the donation process are documented.
1 of 23
Downloaded 296 times






















Recommended
Compatability testing



Compatability testingSUNIL KUMAR PEDDANA
╠²
This document discusses compatibility testing, also known as pre-transfusion testing, which involves procedures to select blood and components that will be safely transfused and will not cause the recipient's red blood cells to be destroyed. The key steps in compatibility testing include properly identifying the recipient's blood sample, checking for antibodies, determining blood types, screening for irregular antibodies, selecting compatible blood, and performing a cross-match test between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's serum to ensure no reactions occur. The cross-match is the final compatibility test to verify ABO compatibility and detect any antibodies present in the recipient's serum.Final ppt sickle cell



Final ppt sickle cellDarlasrinivasarao Srinu
╠²
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation that results in abnormal hemoglobin and sickle-shaped red blood cells. It affects approximately 90,000-100,000 people in the United States, primarily those of African descent. Symptoms include episodes of severe pain, organ damage, infections, and stroke due to sickled cells blocking blood flow. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on pain management, blood transfusions, medications, and in some cases stem cell transplants or gene therapy.Blood Bank



Blood BankTshering Namgyal Wangdi
╠²
1. The document describes procedures for titrating anti-D antibodies, performing Du testing, cross matching donor and patient blood, and direct and indirect Coombs testing.
2. Key steps for titration include serially diluting a test serum, adding diluted serum to test tubes containing red blood cells, and determining the titer by the highest dilution showing agglutination.
3. Du testing, cross matching, and Coombs testing involve incubating patient and donor blood components together, then checking for agglutination with or without the addition of anti-globulin reagent to indicate blood compatibility.Donor selection



Donor selectionMusa Khan
╠²
Voluntary blood donors who meet selection criteria are the safest donors. Selection involves medical history screening, physical exam, and tests to ensure donor and recipient safety. Proper donor care before, during, and after donation through counseling, comfortable facilities, and addressing any reactions is important for donor retention and a sustainable blood supply. Donor selection, recruitment of low risk donors, and quality control at each stage helps ensure a safe blood transfusion system.Forward and reverse grouping by Negash Alamin



Forward and reverse grouping by Negash AlaminNegash Alamin
╠²
This document describes the forward and reverse blood grouping method used to determine a patient's blood type. The method involves separating a patient's blood into plasma and red blood cell components, mixing them in test tubes with known antibodies and blood cells, and observing for agglutination to identify reactions. If agglutination occurs, the corresponding antibody has detected the patient's blood type antigen. This method allows determining a patient's ABO blood group but not other minor blood types. It is routinely used in medical labs to identify a patient's blood type for transfusion compatibility testing.Anticoagulants and blood preservatives



Anticoagulants and blood preservativesAmita Praveen
╠²
The document discusses the history and development of anticoagulants and blood preservatives used for collecting, storing, and transfusing blood and blood components. It describes the early methods used and key discoveries that expanded the shelf life of red blood cells and platelets. The document also outlines the various anticoagulant solutions, additive solutions, and storage conditions used to maintain viability and prevent clotting during the collection, storage, and transportation of whole blood and its components prior to transfusion.APTT.pptx



APTT.pptxrajexh777
╠²
The document describes the procedure for performing an activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) test using citrated plasma. The test involves incubating plasma with brain extract, kaolin, and calcium chloride before measuring the clotting time. Prolonged APTT results indicate deficiencies in the intrinsic coagulation pathway, such as issues with factors VIII, IX, XI, or XIII; liver disease; vitamin K deficiency; or disseminated intravascular coagulation.Coombs test



Coombs testManoj Mahato
╠²
This document provides information about the Coombs test, which is used to detect antibody or complement coating of red blood cells. It describes the history and principles of the test, as well as the direct and indirect Coombs test procedures. The direct Coombs test detects in vivo coating of red blood cells and is used to diagnose conditions like hemolytic disease of the newborn. The indirect Coombs test detects in vitro coating of red cells and is used for compatibility testing and antibody screening. Factors affecting the tests and causes of false positive and negative results are also outlined.Blood screening, quarantine and release



Blood screening, quarantine and releaseRafiq Ahmad
╠²
The document discusses procedures for screening donated blood for infectious diseases at a regional laboratory and blood bank. It provides details on:
1. The viruses, bacteria, parasites, and prions that are screened for, including HIV, HCV, HBV, HTLV, syphilis, malaria, and vCJD.
2. The screening markers and recommended tests used to detect these infectious agents, such as ELISA, chemiluminescence, and nucleic acid amplification technologies.
3. Protocols for quarantining and properly disposing of reactive blood units based on screening results, as well as archiving donor samples and blood components for further testing and research.Investigation of transfusion reaction



Investigation of transfusion reactionSHRUTHI VASAN
╠²
This document discusses the laboratory investigation of transfusion reactions. It begins by defining transfusion and transfusion reactions. It then outlines the initial measures taken before investigation, including maintaining IV saline and notifying physicians. The main laboratory investigations include clerical checks to identify errors, visual checks of plasma for hemolysis, and serology checks including ABO testing and direct antiglobulin testing on pre-and post-transfusion samples. If these preliminary tests have positive results, additional tests like grouping, antibody screening and crossmatching are repeated from before transfusion.Hb electrophoresis (principle materials and procedure)



Hb electrophoresis (principle materials and procedure)hussainshahid55
╠²
This document provides information on hemoglobin electrophoresis, including its definition, purpose, principles, procedures, materials, risks, results, factors that can affect the test, and applications. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is used to screen for and diagnose blood disorders by separating normal and abnormal hemoglobin types in blood based on their electrical charges. The procedure involves extracting hemoglobin from blood samples, running the samples through a gel or cellulose acetate strip using an electrical current, then staining and analyzing the strips to identify abnormal hemoglobin levels or variants that can indicate blood disorders.PLATELET COUNT by Dr. Pandian M .pptx



PLATELET COUNT by Dr. Pandian M .pptxDr. Pandian M
╠²
Dr. Pandian M describes the procedure for performing a platelet count. Platelets serve important hemostatic functions and their normal range is 1.5-4 lakhs/cumm. The procedure involves mixing blood with a diluting fluid in a Neubauer chamber, then counting platelets in grid squares under a microscope. For the sample, 40 platelets were counted in 1/50 mm3, indicating a platelet count of 2 lakhs/mm3 of blood, within the normal range. Abnormally high or low platelet counts can occur due to various bone marrow and other disorders.coombs test



coombs testMLT LECTURES BY TANVEER TARA
╠²
The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, detects antibodies or complement proteins attached to red blood cells. There are two types of Coombs tests - the direct Coombs test detects antibodies bound to red blood cells in vivo, while the indirect Coombs test detects antibodies in a patient's serum that can bind to red blood cells in vitro. The Coombs test is used to diagnose conditions like hemolytic disease of the newborn, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and hemolytic transfusion reactions. A positive Coombs test indicates red blood cell sensitization, while a negative test suggests the absence of sensitization.Crossmatching



Crossmatchingtareq chowdhury
╠²
This document discusses cross-matching, which is an important procedure for safe blood transfusion. Cross-matching involves testing a donor's red blood cells with a recipient's serum to check for antigen-antibody reactions. It helps detect atypical or clinically significant antibodies that could cause hemolytic transfusion reactions. There are two main types of cross-matches: major involves donor red cells and recipient serum, while minor uses recipient cells and donor serum. The document outlines different techniques for cross-matching like immediate spin, indirect antiglobulin, and albumin addition, and discusses factors that can cause positive cross-match results.Donor selection and blood collection



Donor selection and blood collectionKriti Kriti
╠²
This document discusses donor selection and blood collection procedures. It outlines strategies for donor recruitment including voluntary, social persuasion, and remunerated donations. The donor selection process involves counseling, screening donors using a questionnaire and health check, and determining temporary or permanent deferrals. Blood collection follows standard safety procedures using approved equipment and materials while monitoring the donor's health.Blood component separation



Blood component separationariva zhagan
╠²
Blood can be separated into components like red blood cells, platelets, cryoprecipitate, and frozen plasma which are useful for different medical purposes. Whole blood is rarely used now due to the risk of volume overload. The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, detects the presence of antibodies and can be performed directly on a patient's red blood cells or indirectly by incubating their serum with donor red blood cells. A positive result in either test indicates the presence of antibodies.PT & aPTT 



PT & aPTT KalaivaniGanapathy
╠²
The document discusses prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) tests. PT measures the extrinsic and common coagulation pathway, while APTT measures the intrinsic and common pathways. Both tests are used to detect bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulant therapy. The document describes the principles, materials, procedures, normal values and causes of abnormal PT and APTT results. Prolonged PT can indicate liver disease or a fibrinogen abnormality. Prolonged APTT suggests a coagulation factor deficiency and can be seen in lupus or disseminated intravascular coagulation.Automation in hematology



Automation in hematologyDr Siddartha
╠²
Automation In Haematology.
Dept Of Lab Medicine
Basavatarakam Indo American Hospital And Research Institute
Pcv



PcvRandhirsinghbisht
╠²
This document discusses the determination of red blood cell indices including packed cell volume (PCV), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It describes the macrohematocrit or Wintrobe tube method for determining PCV which involves centrifuging a blood sample and measuring the ratio of packed red cells to total blood volume. Formulas are provided for calculating MCV from PCV and RBC count, MCH from hemoglobin and RBC count, and MCHC from hemoglobin and PCV. Normal ranges are listed for each index.Compatibility testing



Compatibility testingForensic Pathology
╠²
The document discusses compatibility testing protocols for blood transfusions. It describes how compatibility testing includes ABO and Rh grouping of donor and recipient samples, screening for unexpected antibodies, and a cross-match. Proper identification of donor and recipient samples is critical to avoid errors. The purpose is to select appropriately compatible blood and ensure the best results for the transfusion by preventing hemolysis or antibody-mediated destruction of transfused red blood cells.Apheresis



ApheresisSUNIL KUMAR PEDDANA
╠²
Apheresis is a medical technology in which blood is withdrawn from a donor or patient, separated into components, and at least one component is retained while the remainder is returned to the circulation. It is used to collect blood components like platelets, plasma, and stem cells for transfusion or therapeutic purposes. Apheresis can be performed manually or using automated machines that utilize centrifugation or filtration to separate components. It has various applications including collection of platelets, plasma exchange to remove antibodies or toxins, and stem cell collection for transplantation. Complications are usually minor but may include hypocalcemia, hypotension, and allergic reactions.Platelet count and hematocrit determination methods



Platelet count and hematocrit determination methodsNegash Alamin
╠²
1. The document describes the principles, procedures, and clinical significance of platelet count and hematocrit determination methods. Platelet count involves diluting blood with ammonium oxalate and counting platelets under a microscope, while hematocrit involves filling a capillary tube with blood and centrifuging it to measure the ratio of red blood cells to plasma.
2. Both tests help diagnose bleeding, clotting, and anemia issues by checking platelet and red blood cell levels. Abnormally high or low counts can indicate conditions like blood cancers, blood loss, kidney disease, or dehydration. Precise methods and calculations are required to obtain accurate results.Gel card technology ppt nc



Gel card technology ppt ncNainshi Bhatt
╠²
This document discusses gel card technology used in blood banking tests. It provides details on the history and development of gel cards, how they work, the types of tests they can be used for (including ABO typing, cross-matching, antibody screening), and their advantages over traditional tube-based methods such as improved sensitivity and reproducibility. Gel cards contain a gel matrix in microtubes that allows red blood cells to be separated based on agglutination during centrifugation, providing clear and standardized test results.Cross matching



Cross matchingMitalisingh30
╠²
The document discusses cross matching procedures for blood transfusions. It describes the two types of cross matching - major and minor. The major cross match mixes the donor's red blood cells with the patient's serum to check for antibodies that could cause hemolytic transfusion reactions. The minor cross match mixes the donor's serum with the patient's cells. Procedures like saline, albumin phase, and Anti-Human Globulin (AHG) are described for detecting various antibodies. Cross matching is important to ensure blood compatibility and prevent transfusion reactions.Reticulocyte count



Reticulocyte countPrbn Shah
╠²
This document provides information on reticulocyte counts, including definitions, staining procedures, counting methods, reference values, and interpretations. Key points include:
- Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that contain RNA and stain blue with supravital dyes.
- A reticulocyte count involves staining a blood smear and counting the number of reticulocytes per 1000 red blood cells to determine percentage.
- An increased reticulocyte count indicates bone marrow response to anemia or blood loss, while a decreased count may indicate bone marrow suppression.
- Factors like medications and transfusions can affect the test results. Proper technique and avoiding inclusionsPre transfusion testing, dr. rafiq



Pre transfusion testing, dr. rafiqRafiq Ahmad
╠²
This document discusses pre-transfusion testing procedures, including patient identification, blood sample collection and handling, compatibility testing, and crossmatching. The key steps are:
1) Performing ABO and Rh typing on the recipient's sample to determine blood type.
2) Screening for unexpected antibodies and identifying any present to guide compatible blood unit selection.
3) Crossmatching a recipient's plasma with donor red blood cells to confirm compatibility and detect antibodies.
4) Labeling and releasing crossmatched blood units for transfusion only after resolving any discrepancies.Coomb's test



Coomb's testNityanand Upadhyay
╠²
Coomb's test: Introduction, principle, application, clinical significance, requirements, procedure, interpretation and result.Transfusion Transmissible Infections



Transfusion Transmissible InfectionsRajesh Karyakarte
╠²
My Guest Lecture, "Transfusion Transmissible Infections", in the Continuing Medical Education (CME) on, "Rational Use of Blood".
Date: 07-12-2004Blood bank



Blood bankWasanaRuchi Heiyanthuduwa
╠²
This is a very short ppt about blood bank created by Wasana Heiyanthuduwa. I hope this will be useful to you especially for nursing students. More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Blood screening, quarantine and release



Blood screening, quarantine and releaseRafiq Ahmad
╠²
The document discusses procedures for screening donated blood for infectious diseases at a regional laboratory and blood bank. It provides details on:
1. The viruses, bacteria, parasites, and prions that are screened for, including HIV, HCV, HBV, HTLV, syphilis, malaria, and vCJD.
2. The screening markers and recommended tests used to detect these infectious agents, such as ELISA, chemiluminescence, and nucleic acid amplification technologies.
3. Protocols for quarantining and properly disposing of reactive blood units based on screening results, as well as archiving donor samples and blood components for further testing and research.Investigation of transfusion reaction



Investigation of transfusion reactionSHRUTHI VASAN
╠²
This document discusses the laboratory investigation of transfusion reactions. It begins by defining transfusion and transfusion reactions. It then outlines the initial measures taken before investigation, including maintaining IV saline and notifying physicians. The main laboratory investigations include clerical checks to identify errors, visual checks of plasma for hemolysis, and serology checks including ABO testing and direct antiglobulin testing on pre-and post-transfusion samples. If these preliminary tests have positive results, additional tests like grouping, antibody screening and crossmatching are repeated from before transfusion.Hb electrophoresis (principle materials and procedure)



Hb electrophoresis (principle materials and procedure)hussainshahid55
╠²
This document provides information on hemoglobin electrophoresis, including its definition, purpose, principles, procedures, materials, risks, results, factors that can affect the test, and applications. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is used to screen for and diagnose blood disorders by separating normal and abnormal hemoglobin types in blood based on their electrical charges. The procedure involves extracting hemoglobin from blood samples, running the samples through a gel or cellulose acetate strip using an electrical current, then staining and analyzing the strips to identify abnormal hemoglobin levels or variants that can indicate blood disorders.PLATELET COUNT by Dr. Pandian M .pptx



PLATELET COUNT by Dr. Pandian M .pptxDr. Pandian M
╠²
Dr. Pandian M describes the procedure for performing a platelet count. Platelets serve important hemostatic functions and their normal range is 1.5-4 lakhs/cumm. The procedure involves mixing blood with a diluting fluid in a Neubauer chamber, then counting platelets in grid squares under a microscope. For the sample, 40 platelets were counted in 1/50 mm3, indicating a platelet count of 2 lakhs/mm3 of blood, within the normal range. Abnormally high or low platelet counts can occur due to various bone marrow and other disorders.coombs test



coombs testMLT LECTURES BY TANVEER TARA
╠²
The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, detects antibodies or complement proteins attached to red blood cells. There are two types of Coombs tests - the direct Coombs test detects antibodies bound to red blood cells in vivo, while the indirect Coombs test detects antibodies in a patient's serum that can bind to red blood cells in vitro. The Coombs test is used to diagnose conditions like hemolytic disease of the newborn, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and hemolytic transfusion reactions. A positive Coombs test indicates red blood cell sensitization, while a negative test suggests the absence of sensitization.Crossmatching



Crossmatchingtareq chowdhury
╠²
This document discusses cross-matching, which is an important procedure for safe blood transfusion. Cross-matching involves testing a donor's red blood cells with a recipient's serum to check for antigen-antibody reactions. It helps detect atypical or clinically significant antibodies that could cause hemolytic transfusion reactions. There are two main types of cross-matches: major involves donor red cells and recipient serum, while minor uses recipient cells and donor serum. The document outlines different techniques for cross-matching like immediate spin, indirect antiglobulin, and albumin addition, and discusses factors that can cause positive cross-match results.Donor selection and blood collection



Donor selection and blood collectionKriti Kriti
╠²
This document discusses donor selection and blood collection procedures. It outlines strategies for donor recruitment including voluntary, social persuasion, and remunerated donations. The donor selection process involves counseling, screening donors using a questionnaire and health check, and determining temporary or permanent deferrals. Blood collection follows standard safety procedures using approved equipment and materials while monitoring the donor's health.Blood component separation



Blood component separationariva zhagan
╠²
Blood can be separated into components like red blood cells, platelets, cryoprecipitate, and frozen plasma which are useful for different medical purposes. Whole blood is rarely used now due to the risk of volume overload. The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, detects the presence of antibodies and can be performed directly on a patient's red blood cells or indirectly by incubating their serum with donor red blood cells. A positive result in either test indicates the presence of antibodies.PT & aPTT 



PT & aPTT KalaivaniGanapathy
╠²
The document discusses prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) tests. PT measures the extrinsic and common coagulation pathway, while APTT measures the intrinsic and common pathways. Both tests are used to detect bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulant therapy. The document describes the principles, materials, procedures, normal values and causes of abnormal PT and APTT results. Prolonged PT can indicate liver disease or a fibrinogen abnormality. Prolonged APTT suggests a coagulation factor deficiency and can be seen in lupus or disseminated intravascular coagulation.Automation in hematology



Automation in hematologyDr Siddartha
╠²
Automation In Haematology.
Dept Of Lab Medicine
Basavatarakam Indo American Hospital And Research Institute
Pcv



PcvRandhirsinghbisht
╠²
This document discusses the determination of red blood cell indices including packed cell volume (PCV), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It describes the macrohematocrit or Wintrobe tube method for determining PCV which involves centrifuging a blood sample and measuring the ratio of packed red cells to total blood volume. Formulas are provided for calculating MCV from PCV and RBC count, MCH from hemoglobin and RBC count, and MCHC from hemoglobin and PCV. Normal ranges are listed for each index.Compatibility testing



Compatibility testingForensic Pathology
╠²
The document discusses compatibility testing protocols for blood transfusions. It describes how compatibility testing includes ABO and Rh grouping of donor and recipient samples, screening for unexpected antibodies, and a cross-match. Proper identification of donor and recipient samples is critical to avoid errors. The purpose is to select appropriately compatible blood and ensure the best results for the transfusion by preventing hemolysis or antibody-mediated destruction of transfused red blood cells.Apheresis



ApheresisSUNIL KUMAR PEDDANA
╠²
Apheresis is a medical technology in which blood is withdrawn from a donor or patient, separated into components, and at least one component is retained while the remainder is returned to the circulation. It is used to collect blood components like platelets, plasma, and stem cells for transfusion or therapeutic purposes. Apheresis can be performed manually or using automated machines that utilize centrifugation or filtration to separate components. It has various applications including collection of platelets, plasma exchange to remove antibodies or toxins, and stem cell collection for transplantation. Complications are usually minor but may include hypocalcemia, hypotension, and allergic reactions.Platelet count and hematocrit determination methods



Platelet count and hematocrit determination methodsNegash Alamin
╠²
1. The document describes the principles, procedures, and clinical significance of platelet count and hematocrit determination methods. Platelet count involves diluting blood with ammonium oxalate and counting platelets under a microscope, while hematocrit involves filling a capillary tube with blood and centrifuging it to measure the ratio of red blood cells to plasma.
2. Both tests help diagnose bleeding, clotting, and anemia issues by checking platelet and red blood cell levels. Abnormally high or low counts can indicate conditions like blood cancers, blood loss, kidney disease, or dehydration. Precise methods and calculations are required to obtain accurate results.Gel card technology ppt nc



Gel card technology ppt ncNainshi Bhatt
╠²
This document discusses gel card technology used in blood banking tests. It provides details on the history and development of gel cards, how they work, the types of tests they can be used for (including ABO typing, cross-matching, antibody screening), and their advantages over traditional tube-based methods such as improved sensitivity and reproducibility. Gel cards contain a gel matrix in microtubes that allows red blood cells to be separated based on agglutination during centrifugation, providing clear and standardized test results.Cross matching



Cross matchingMitalisingh30
╠²
The document discusses cross matching procedures for blood transfusions. It describes the two types of cross matching - major and minor. The major cross match mixes the donor's red blood cells with the patient's serum to check for antibodies that could cause hemolytic transfusion reactions. The minor cross match mixes the donor's serum with the patient's cells. Procedures like saline, albumin phase, and Anti-Human Globulin (AHG) are described for detecting various antibodies. Cross matching is important to ensure blood compatibility and prevent transfusion reactions.Reticulocyte count



Reticulocyte countPrbn Shah
╠²
This document provides information on reticulocyte counts, including definitions, staining procedures, counting methods, reference values, and interpretations. Key points include:
- Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that contain RNA and stain blue with supravital dyes.
- A reticulocyte count involves staining a blood smear and counting the number of reticulocytes per 1000 red blood cells to determine percentage.
- An increased reticulocyte count indicates bone marrow response to anemia or blood loss, while a decreased count may indicate bone marrow suppression.
- Factors like medications and transfusions can affect the test results. Proper technique and avoiding inclusionsPre transfusion testing, dr. rafiq



Pre transfusion testing, dr. rafiqRafiq Ahmad
╠²
This document discusses pre-transfusion testing procedures, including patient identification, blood sample collection and handling, compatibility testing, and crossmatching. The key steps are:
1) Performing ABO and Rh typing on the recipient's sample to determine blood type.
2) Screening for unexpected antibodies and identifying any present to guide compatible blood unit selection.
3) Crossmatching a recipient's plasma with donor red blood cells to confirm compatibility and detect antibodies.
4) Labeling and releasing crossmatched blood units for transfusion only after resolving any discrepancies.Coomb's test



Coomb's testNityanand Upadhyay
╠²
Coomb's test: Introduction, principle, application, clinical significance, requirements, procedure, interpretation and result.Transfusion Transmissible Infections



Transfusion Transmissible InfectionsRajesh Karyakarte
╠²
My Guest Lecture, "Transfusion Transmissible Infections", in the Continuing Medical Education (CME) on, "Rational Use of Blood".
Date: 07-12-2004Similar to Donor selection ppt (20)
Blood bank



Blood bankWasanaRuchi Heiyanthuduwa
╠²
This is a very short ppt about blood bank created by Wasana Heiyanthuduwa. I hope this will be useful to you especially for nursing students. 2016 education at recruitment



2016 education at recruitmentMagda Silva
╠²
This document provides information about joining the Be The Match bone marrow registry. It summarizes that individuals between 18-44 can join by committing to donate marrow to any patient in need and reviewing health guidelines. It notes that thousands of patients with blood cancers need marrow transplants to survive and most do not have a matched donor in their family, so they rely on the Be The Match registry. If selected as a match, committing to join means being willing to donate marrow through a surgical procedure or blood stem cells through a non-surgical procedure, which takes 4-6 weeks.donor selection criteria



donor selection criteriaMLT LECTURES BY TANVEER TARA
╠²
This document outlines donor selection criteria and policies for blood donation. It discusses the types of blood donors, including voluntary, replacement, autologous, and apheresis donors. Professional donors who are paid are not preferred due to risks. Guidelines are provided for donor recruitment, selection, counseling, and care before, during and after donation to ensure donor and recipient safety. Proper donor selection involves evaluating medical history and screening for risks of transfusion-transmitted infections.Journal club



Journal clubSowmya Srinivas
╠²
JOURNAL - Blood donor selection and deferral pattern as an important tool for blood safety in a tertiary care hospital.donor selection criteria



donor selection criteriaMLT LECTURES BY TANVEER TARA
╠²
This document discusses donor selection criteria and donor care policies. It outlines different types of blood donors, including voluntary, replacement, autologous, and apheresis donors. Professional donors who are paid are not preferred due to risks. Selection criteria aim to protect both donors and recipients by ensuring donors are healthy and low risk. The donor selection process involves registration, consent, medical screening, and testing. Policies cover donor recruitment, retention, counseling, and ensuring a safe donation experience.DONOR SELECTION AND DONOR DEFERRAL.pptx



DONOR SELECTION AND DONOR DEFERRAL.pptxDrmustafa Ali
╠²
This document discusses blood donor types and blood donation safety. There are four main types of blood donors: voluntary non-remunerated donors who donate without payment; replacement donors who donate for a specific patient; professional donors who are paid; and autologous donors who donate for their own planned procedures. Ensuring donor safety involves screening donors through medical history questionnaires and health checks before acceptance. Certain medical conditions and high risk behaviors require deferral periods before a donor can be accepted. Maintaining the safety of both donors and recipients is crucial.Legal and ethical aspect 0f transplant



Legal and ethical aspect 0f transplantdr vipin Drvipinsharma3
╠²
The document discusses the ethical and legal aspects of organ transplantation in India. It outlines the key laws governing transplantation, including the Transplantation of Human Organs Act (1994) and subsequent amendments. It describes regulations around living and deceased organ donation, and the roles of the Authorization Committee and Appropriate Authority in overseeing donations. Guidelines are provided around donor-recipient relationships, consent processes, and evaluating proposed donations.legalandethicalissueintransplantautosaved-180305131337.pdf



legalandethicalissueintransplantautosaved-180305131337.pdfDrYogeshMundra1
╠²
The document discusses the ethical and legal aspects of organ transplantation in India. It outlines the key laws governing transplantation, including the Transplantation of Human Organs Act (1994) and subsequent amendments. It describes the roles of the Authorization Committee and Appropriate Authority in regulating transplantation and overseeing hospitals. Guidelines are provided for living donation, donor-recipient relationships, and preventing commercial sale of organs. Overall consent processes, counseling requirements, and principles of justice and equity in organ allocation are addressed.Blood donor selection



Blood donor selectiontareq chowdhury
╠²
how to select a healthy donor & care of donor .A healthy donor is one of the most vital part of transfusion medicine for safe transfusion of blood & blood product Programs aimed at ensuring Sanyam (self-control) and Swasthya (health) focus ...



Programs aimed at ensuring Sanyam (self-control) and Swasthya (health) focus ...kannadigamysure
╠²
Programs aimed at ensuring Sanyam (self-control) and Swasthya (health) focus on the holistic well-being of individuals by integrating physical, mental, and emotional health practices. Here are key components and strategies derived from the search results:Unit 7 referral system part 2



Unit 7 referral system part 2rohini harikrishnan
╠²
This document discusses India's 3-tier referral system for healthcare and the nurse's role within it. It describes the levels from village to tertiary care and the purposes of referrals for early treatment, cost-effectiveness, and education. The referral process involves selecting cases based on severity, preparing documentation, informing the receiving unit, transporting the patient, and providing feedback. Nurses are responsible for communication, monitoring patients during transfer, collecting records, and properly handing off care. The system aims to efficiently direct patients to the appropriate level of specialized treatment.SGBV Algorithm used in healthcare facilities



SGBV Algorithm used in healthcare facilitiesaketchveronica064
╠²
This is the guide on how to go about cases of SGBV that are reported at various health facilities so as to ensure safetyBonor selection criteria 1



Bonor selection criteria 1Asif Zeb
╠²
1. Donor management in blood banks involves strict donor selection through screening, eligibility criteria, and deferral criteria to ensure blood safety.
2. The blood donation procedure includes pre-donation screening, a medical examination, blood collection, and post-donation care and advice.
3. All donated blood is tested for transfusion transmissible infections like HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, and malaria to maintain the highest safety standards.Blood donation ss



Blood donation ssDr Shahida Baloch
╠²
Blood is essential for life but in short supply. Regular blood donation is needed to meet the increasing demand from hospitals. Donating blood is safe and helps save lives by providing blood for transfusions to patients with injuries, cancers, or blood disorders. All donated blood is tested for infections to ensure the safety of donors and recipients.Betsy session 3.pptx



Betsy session 3.pptxpamduker
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation about identifying potential living kidney donors through one's social network. It discusses who to approach within a social network like family, friends, coworkers, and religious or community groups. It provides tips for utilizing social networks like planning ahead, asking group leaders for help, and brainstorming the best way to approach people. Sample language is given for writing a story to share about one's need for a living donor transplant. The document also summarizes challenges in transplantation like infectious risk donors, HBV positive donors, and evaluating organ quality.Blood Donation awareness and motivation presentation by ME.ppt



Blood Donation awareness and motivation presentation by ME.pptDrSanjitChatterjee
╠²
blood donation awareness Blood donation & selection of donor



Blood donation & selection of donorHussein Al-tameemi
╠²
1. Blood donation involves voluntarily donating blood or blood components which are then used for transfusions or to create medications. Donations can be of whole blood or specific components.
2. There are several types of donations including voluntary unpaid donations, donations from friends/family of patients, and paid donations. Donors can also donate for their own future planned medical procedures.
3. Prior to donation, potential donors undergo screening including testing for transmissible diseases and a medical history/physical exam to ensure the donation is safe. Donors must wait specified periods between donations depending on what they donate.Betsy session#1



Betsy session#1pamduker
╠²
This document summarizes an educational session on kidney transplantation and live donation. It discusses the program's mission to increase awareness and identify potential live donors. An overview is provided on renal failure and its treatment options. Live donation is outlined as the best treatment, with benefits like immediate transplant and longer kidney function. The evaluation, surgical, and recovery processes for live donors are described. Common myths are addressed, such as risks to donors. The session aims to educate attendees to feel more comfortable discussing live donation with potential donor candidates.BLOOD DONATION ppt For medical students..pptx



BLOOD DONATION ppt For medical students..pptxdarshitam0310
╠²
Mention safety measures and potential side effects. Provide tips on how to prepare for donations such as staying hydrated and eating well.This concise format covers the essential aspects of blood donation.Recently uploaded (20)
Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025



Presentaci├│ "Projecte Benestar". MWC 2025Badalona Serveis Assistencials
╠²
Presentaci├│ que va acompanyar la demostraci├│ pr├Āctica de metge d'Innovaci├│ Jos├® Ferrer sobre el projecte Benestar de BSA, nom d'IDIAP Pere Gol, el 5 de mar├¦ de 2025 a l'estand de XarSMART al Mobible Word Congress. DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTER



DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTERdaminipatel37
╠²
Diagnosis of all three trimester of pregnancy Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
╠²
A complete information of Inflammation, it includes types of Inflammation, purpose of Inflammation, pathogenesis of acute inflammation, chemical mediators in inflammation, types of chronic inflammation, wound healing and Inflammation in skin repair, phases of wound healing, factors influencing wound healing and types of wound healing.SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025



SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025Dr. Anindya
╠²
Final Round of SAPIENT Medi-trivia quiz
Part of TRI-ORTA 2025
Venue: GLT, Medical College Kolkata
Date: 25-02-2025MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....



MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....maheenmazhar021
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed exploration of the morphological and microscopic features of pneumonia, covering its histopathology, classification, and clinical significance. Designed for medical students, pathologists, and healthcare professionals, this lecture differentiates bacterial vs. viral pneumonia, explains lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia, and discusses diagnostic imaging patterns.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ģ Normal lung histology vs. pneumonia-affected lung
Ō£ģ Morphological changes in lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
Ō£ģ Microscopic features: Fibroblastic plugs, alveolar septal thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration
Ō£ģ Stages of lobar pneumonia: Congestion, Red hepatization, Gray hepatization, Resolution
Ō£ģ Common causative pathogens (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycoplasma, etc.)
Ō£ģ Clinical case study with diagnostic approach and differentials
¤ö¼ Who Should Watch?
This is an essential resource for medical students, pathology trainees, and respiratory health professionals looking to enhance their understanding of pneumoniaŌĆÖs morphological aspects.The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcome



The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcomeLokesh Kumar Sharma
╠²
this content related to birth companionship, role of birth companion in care of mother and neonatal Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
╠²
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
╠²
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & Applications



Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & ApplicationsKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of optimization in pharmaceutical formulations. It explains the concept of optimization, different types of optimization problems (constrained and unconstrained), and the mathematical principles behind formulation development. Key topics include:
Methods for optimization (Sequential Simplex Method, Classical Mathematical Methods)
Statistical analysis in optimization (Mean, Standard Deviation, Regression, Hypothesis Testing)
Factorial Design & Quality by Design (QbD) for process improvement
Applications of optimization in drug formulation
This resource is beneficial for pharmaceutical scientists, R&D professionals, regulatory experts, and students looking to understand pharmaceutical process optimization and quality by design approaches.Local Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable Patients



Local Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable PatientsReza Aminnejad
╠²
Local anesthetics are a cornerstone of pain management, but their use requires special consideration in vulnerable groups such as pediatric, elderly, diabetic, or obese patients. In this presentation, weŌĆÖll explore how factors like age and physiology influence local anesthetics' selection, dosing, and safety. By understanding these differences, we can optimize patient care and minimize risks.
Macafem Reviews 2024 - Macafem for Menopause Symptoms



Macafem Reviews 2024 - Macafem for Menopause SymptomsMacafem Supplement
╠²
At Macafem, we provide 100% natural support for women navigating menopause. For over 20 years, we've helped women manage symptoms, and in 2024, we're proud to share their heartfelt experiences.psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy management



psychosomaticdisorder and it's physiotherapy managementDr Shiksha Verma (PT)
╠²
Psychosomatic disorder PRODUCTION OF HB VACCINE AND INTERFERONS BY rDNA - Copy.pptx



PRODUCTION OF HB VACCINE AND INTERFERONS BY rDNA - Copy.pptxkarishmaduhijod1
╠²
APPLICATION of RECOMBINANAT DNA TECHNOLOGY : IN THE PRODUCTION OF HEPATITIS B VACCINE ,INSULIN and INTERFERONMLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
The course covers the steps undertaken from tissue collection, reception, fixation,
sectioning, tissue processing and staining. It covers all the general and special
techniques in histo/cytology laboratory. This course will provide the student with the
basic knowledge of the theory and practical aspect in the diagnosis of tumour cells
and non-malignant conditions in body tissues and for cytology focusing on
gynaecological and non-gynaecological samples.Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
╠²
Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Viable air & surface sampling best practices
Ō£ö’ĖÅ USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
Ō£ö’ĖÅ How to analyze & trend viable sample data
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
¤Äź Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
¤ōó Stay informedŌĆöfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptxamralmohammady27
╠²
┘ä┘ł ž╣┘åž»┘ā ┘䞦ž© ž¬┘łž© žŻ┘ł ž¬ž¦ž©┘䞬 ┘üž¦┘ä
power point show
┘ć┘Ŗ┘å┘üž╣┘ā ž¼ž»ž¦ ┘ü┘Ŗ ┘ģž▒ž¦ž¼ž╣ž® ž│ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž® ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äž® ž¦┘䞦┘ģž¬žŁž¦┘å
┘łž¦┘ä┘ä┘Ŗ ┘Ŗ┘éž»ž▒ ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä žŁž¦ž¼ž® ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä┘枦
┘łž┤┘āž▒ž¦ ┘ä┘äž»┘āž¬┘łž▒ž® ┘å┘łž¦┘ä ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¬ž¼┘ģ┘Ŗž╣ž® žŻž│ž”┘äž® ž¦┘äž©┘Ŗ┘łAcute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
╠²
MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
Donor selection ppt
- 1. Donor Selection Presented by:- Hemani. N M.Sc 2 nd
- 2. objectives ŌĆó Donor selection ŌĆó Types of blood donors ŌĆó Donor registration ŌĆó Medical and physical examination ŌĆó Lab investigations ŌĆó Donor record register
- 3. Donor Selection Criteria Donor selection determines the eligibility of a donor to donate blood and blood components. Protect the donor ŌĆó Ensures that it is safe for the donor to donate Protect the recipient ŌĆó Ensures that any risk of transfusion transmitted ŌĆó Infection or other adverse effect is minimized. Introduction
- 4. Types of blood donors ŌĆóVoluntary Donors ŌĆōDonate Blood on their own. ŌĆóReplacement Donors : from within the patientŌĆÖs own family or community.
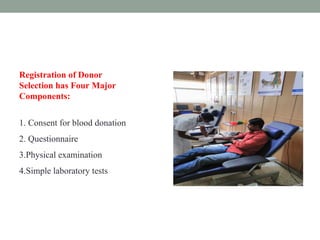
- 5. Registration of Donor Selection has Four Major Components: 1. Consent for blood donation 2. Questionnaire 3.Physical examination 4.Simple laboratory tests
- 6. Donor registration should include ŌĆóDonation date and time. ŌĆóLast and first name (middle initial if available). ŌĆóAddress. ŌĆóTelephone number. ŌĆóGender. ŌĆóAge (or DOB). ŌĆóPrevious deferral record must be consulted. Deferral
- 7. Medical history ŌĆóMedical history should be taken by trained health care professional person ŌĆóIt must be assured that the confidentiality of the donor should be maintained ŌĆóDirect questions or leading questions are allowed in the interview
- 8. Medical history ŌĆó The standard medical information questionnaire which helps to collect same information systematically from each donor. ŌĆó This questionnaire can give information, which make quick assessment whether to accept, Temporary defer or permanently reject the donor.
- 10. Major conditions for donor deferral Period of deferralConditions for deferral
- 12. Physical Examination ŌĆóGeneral appearance of donor: Donor should be fit n healthy. ŌĆóPulse:- 60-120 beats per minute. ŌĆóBlood pressure o Diastolic 60-100 mm Hg o Systolic 100-160 mm Hg Temperature: Maximum 37.5 0 C Donor weight: Minimum 45 Kgs Amount of blood to be drawn o Ōēź 55 Kg - 450ml o 45- 54 Kg - 350ml
- 13. Lab investigation Determination of hemoglobin and hematocrit:- ŌĆó Donors:- Hb 12.5-18 g/dl Hct 38-52 ŌĆóPlatelet count >1.5 lakh (plateletpheresis) ŌĆóComplete blood count
- 15. Donation interval The minimum time gap between the blood donations should be 3 months Interval between two Plateletphersis is 48- 72hrs. Not more than two procedures to be done in a week Whole blood donation must be take for at least 1 weak after can be donate the plateletpheresis In case of re-infusion failure after pheresis procedure, donor should not donate whole blood for 3 months
- 16. ŌĆó That the donor has under stood all the donor information presented, and have all his questions been answered? ŌĆó That his blood would be tested for Transfusion Transmitted Infections(TTI). ŌĆó That if the screening tests are reactive, he/she may transmit TTI. ŌĆó Whether the donor wants to be informed about abnormal test results? SIGNATURE____________________ DATED________________________ Informed consent
- 17. Donor Record Register ’é¦ Registration Number ’é¦ Tube segment Number ’é¦ Name of Donor ’é¦ FatherŌĆÖs Name ’é¦ Age/Sex ’é¦ Address ’é¦ Date of Collection ’é¦ Date of Expiry ’é¦ Blood Group ’é¦ Signature of Doctor ’é¦ Signature of Phlebotomist ’é¦ Weight ’é¦ Blood Pressure ’é¦ Hemoglobin ’é¦ Type of Donation VD/RD ’é¦ Type of Bag ’é¦ Volume of collection ’é¦ Time of collection ’é¦ Duration of collection
- 19. Post-Donation care ŌĆó Drink more fluid in next 24 hours. ŌĆó Do not smoke for ┬Į hour after donation. ŌĆó Avoid strenuous exercise eg:- weight lifting for 24 hours. ŌĆó Do not drive for at least half an hour. ŌĆó Report to blood bank in case of any adverse reaction occur.
- 20. Donor satisfaction ŌĆóCongenial atmosphere ŌĆóTrained staff ŌĆóCare & comfort ŌĆóConfidentiality ŌĆóConstant feed back
- 21. Summary
- 22. References 1. Blood Banking and Transfusion Medicine 2nd Edition Basic Principles and Practice Authors: Christopher Hillyer Leslie Silberstein Paul Ness Kenneth Anderson John Roback 2. Essentials Of Blood Banking (A Handbook For Students Of Blood Banking And Clinical Residents) 3. Human Blood Components & Functions ŌĆō Biology Notes for SSC, Banking & Railways in PDF
- 23. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- #7: Outcomes Of Donor Screening-Acceptance,Temporary deferral,Permanent deferral




