DRILLING METHODS
- 2. 1. Definition 2. Objective of rock drilling 3. Classification of drilling 4. Brief description for each drilling methods 5. Drilling accessories
- 4. ïķ Exploration drilling for sample collected to estimate the quality and quantity of the mineral reserve ïķ Locates and defines economic mineralization ïķ Production drilling-in the mining cycle drilling performed for the placement of the explosives ïķ To generate under earth transportations and to allow locomotives ïķ In quarrying dimensions stone is freed by cutting channeling.
- 5. ï Auger drilling ï Reverse Circulation drilling ï Diamond core drilling ï Air core drilling ï Jumper bar drilling ï Jack hammer drilling ï Churn drilling ï Direct push rig ï Hydraulic rotary drilling ï Sonic drilling
- 6. ïķDrilling is done with the âhelical screwâ ïķHallow stem auger-softer ground ïķSolid fight auger-harder ground ïķGeo chemical sampling at un consolidated material ïķPortable ïķCheap & fast method ïķUncontaminated samples ïķBut poor penetration
- 8. ïķ Itâs similar to the air core drilling ïķ âHigh pressure fluid forced down outer pipe and returns chips to surface up inner pipeâ ïķ Geochemical sampling in hard and soft rocks ïķ Samples(rock chips) of fresh rock in large amount rock ïķ Moderately priced & relatively cheap ïķ Quick & un contaminated ïķ Sample will contaminate below the water table
- 10. ïķ Diamond drilling utilizes âdiamond impregnated drill bitsâ that attached in the end of the hallow drill rods. ïķ To get cylindrical core samples. ïķ It give whole rock sample and more geological information. ïķ Un contaminated high quality samples ïķ It can penetrate great depth. ïķ But expensive and slow method and small sample size water supply also required .
- 12. ïķ Hardened steel or tungsten blades are used to drill ïķ Three blades arranged around the drill bit ïķ The rods are hallow and contain inner tube ïķ That sits inside the hallow rod barrel ïķ Drill cuttings removed by injection of compressed air ïķ Geo chemical sampling into bed rock & it produce small chunks of cored rock ïķ More costly & slower than RAB method ïķ Minimal contamination but small sample size
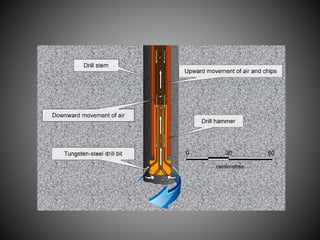
- 14. ïĻ There are manually operate drill used for making blast holes in stone and road material ïĻ The drill is consist of 1 -1.5 inch in diameter and length between 2ft to 4ft ïĻ Percussion is given by striking the drill manually by hammer ïĻ The sludge removed from the hole with a scoop periodically ïĻ The drill made of high carbon manganese steel bar
- 15. ïĻ In mechanized mining pneumatic drills are worked by compressed air ïĻ The principle involved is same that of manually operate jumper bar ïĻ A popular variation of compressed air drill is jack hammer ïĻ The air pressure of the drill is 800-1000 lbs per square inch
- 17. ïĻ A portable drill rig using a bit fashioned on a massive steel cylinder that is alternatively lifted and dropped to a hole in earth and rock ïĻ It used to drill into soft carbonate rocks of lead and zinc in hosted regions to extract bulk samples of ore ïĻ A large version of churn drill is used in oil drilling is known as cable tool drilling
- 19. ïķ This technology is pushing or hammering without rotating the drill string ïķ Itâs not mean the drilling but it achieves the same result âa bore hole ïķ Itâs limited and drilling in un consolidated rock ïķ & very soft material ïķ The speed and depth of penetration dependent on the soil type & weight of the power of rig ïķ It can produce a large number of high quality of samples quickly and cheaply ïķ Least penetration
- 21. ïķ Oil well drilling utilizes tri cone ;carbide embedded; fixed diamond impregnated drill bits ïķ âbentonite & bariteâ infused drilling muds to use to lubricate ;cool & clean the drill bit and control down hole pressure and stabilize the wall of the borehole ïķ it can pollute water and also causes dangerous fire risks ïķ So redundant safety systems & highly trained personnel are required to be implemented
- 23. ïķ Itâs works by sending high frequency resonant vibrations down the drill string to the drill bit ïķ Vibrations may also be generated within the drill head ïķ The frequency generated between 50 and 120 htz (cycle per second) ïķ Depend and varied by the operator ïķ Resonance magnifies the amplitude of the drill bit ïķ An internal spring system isolates these vibrational forces from the rest of the drill rig