Driver Genius 24 Crack 2025 License Key Free Download
- 1. 1 Submitted By: Diya Dixit University Roll Number- 2370110015 SEED PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY OF MAIZE WELCOME PRINCIPLES OF SEED TECHNOLOGY- BAGC0125 Submitted To: Dr. Vineeta Pandey Assistant Professor Faculty of Agricultural Sciences GLA University
- 2. 2 CONTENT - ï Introduction ï Types of Corn ï Brief Cultural Practices ï Variety ï Isolation ï Field Standard ï Nutrient Management ï Irrigation ï Intercultural Operations ï Field Inspection ï Roughing ï Harvesting and Yield ï Seed Standard
- 3. 3 Botanical Name: Zea mays Chromosome Number: 2n=20, Family: Poaceae âĒ Origin â Southern Mexico âĒ Maize is common cereal crop of India with wider industrial and household utility. âĒ It is used a feed, food and raw material in soft drink industry. âĒ The maize is rich in riboflavin, phosphorus, potash, iron, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B and also has a high amount of vitamin A (carotenoids). INTRODUCTION-
- 4. 4 Type of Corn ïž Dent Corn - Dent corn, also known as field corn, has kernels containing a hard form of starch at the sides and a soft type in the center. ïž Flint Corn -Flint corn, also known as Indian corn, has kernels with a hard outer layer to protect the soft endosperm inside the kernels. ïž Flour Corn - Flour corn is one of the oldest types of corn and was used by Indians and Americans to grind the kernels into flour. It has soft starch throughout the kernel and has no hard layer. ïž Baby Corn - Baby corn, as the name suggests, are young finger-like unfertilized cobs with 1 to 3 centimeters emerged silk. ïž Sweet Corn -Sweet corn is one of the trending vegetables in different developing and developed countries. The reason behind its growing popularity is its delicious taste and vitamins A and C. The sugary genes present in sweet corn naturally prevent the conversion of sugar into starch. ïž Waxy Corn -Waxy corn originates from China and is largely used in the USA. Due to its wax-like appearance, it is named as waxy corn . It is also used in the manufacturing and paper industries. ïž Pop Corn - Popcorn is among the oldest surviving varieties of maize. It contains only a small portion of soft starch, with the kernels being either pointed or round.
- 5. 5 . âĒ Land Requirement - Maize needs well pulverized, fine and smooth field for seed emergence and root growth . Also free from seed borne disease, voluntary plants and crop residues. âĒ Source of Seedâ It should be collected from authentic sources of appropriate class. âĒ Seed rate - About 20-25 kg/ha of seed should be used. âĒ Seed treatment - Bavistin + Captan in 1:1 ratio @2g/kg seed for Banded leaf and sheath blight, Maydis leaf blight etc. Imidachlorpit @4g/kg seed for termite and shoot fly. Brief Cultural Practices-
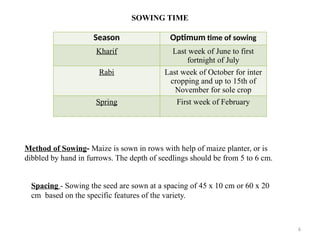
- 6. 6 SOWING TIME Season Optimum time of sowing Kharif Last week of June to first fortnight of July Rabi Last week of October for inter cropping and up to 15th of November for sole crop Spring First week of February Spacing - Sowing the seed are sown at a spacing of 45 x 10 cm or 60 x 20 cm based on the specific features of the variety. Method of Sowing- Maize is sown in rows with help of maize planter, or is dibbled by hand in furrows. The depth of seedlings should be from 5 to 6 cm.
- 7. 7 Fig. Varieties ï§ Others varieties-K1,Jawahar,CO1
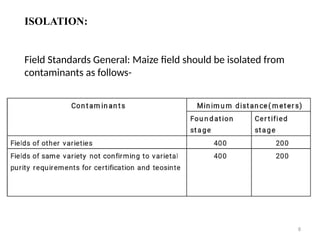
- 8. 8 ISOLATION: Field Standards General: Maize field should be isolated from contaminants as follows-
- 9. 9 SPECIFIC STANDARD: Of maize of maize crop:
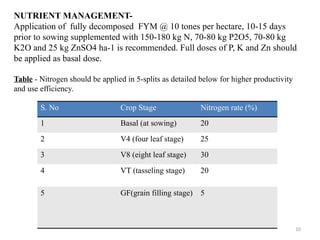
- 10. 10 NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT- Application of fully decomposed FYM @ 10 tones per hectare, 10-15 days prior to sowing supplemented with 150-180 kg N, 70-80 kg P2O5, 70-80 kg K2O and 25 kg ZnSO4 ha-1 is recommended. Full doses of P, K and Zn should be applied as basal dose. Table - Nitrogen should be applied in 5-splits as detailed below for higher productivity and use efficiency. S. No Crop Stage Nitrogen rate (%) 1 Basal (at sowing) 20 2 V4 (four leaf stage) 25 3 V8 (eight leaf stage) 30 4 VT (tasseling stage) 20 5 GF(grain filling stage) 5
- 11. 11 IRRIGATION- The crop should be irrigated once in 10-15 days for enhanced seed set and formation of bolder grains. The critical stages of irrigation are primordial initiation stage, vegetative stage , flowering, milky and maturation stage. If the irrigation is withheld in these stages seed set will be poor and seed size will be reduced.
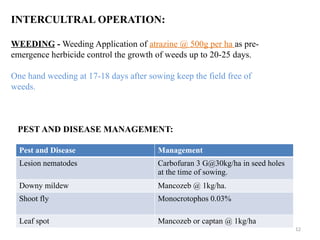
- 12. 12 INTERCULTRAL OPERATION: WEEDING - Weeding Application of atrazine @ 500g per ha as pre- emergence herbicide control the growth of weeds up to 20-25 days. One hand weeding at 17-18 days after sowing keep the field free of weeds. PEST AND DISEASE MANAGEMENT: Pest and Disease Management Lesion nematodes Carbofuran 3 G@30kg/ha in seed holes at the time of sowing. Downy mildew Mancozeb @ 1kg/ha. Shoot fly Monocrotophos 0.03% Leaf spot Mancozeb or captan @ 1kg/ha
- 13. 13 FIELD INSPECTION: A minimum of two inspections shall be made . Stages of crop inspection- ï At the time of sowing: to monitor the land, isolation distance, proper sowing time, seed treatment . ï During pre-flowering/vegetative stage: to verify the rouging and removal of off type plants. ï During flowering stage: to check disease and pest infestation. ï During post-flowering and pre-harvest stage: to remove the late and diseased plants Differential type of tassel/silk plants. ï Harvesting time: to see the proper time of harvesting.
- 14. 14 Rouging: The practice of identifying and removing plants with undesirable characteristics ,off types or disease plants. Off types can be identified through stem colour , plant structure , number of leaves , auricles, nodal colour , tassel colour , sheath colour , grain colour etc. i) After 12-15 days of sowing: Off-type and excess plants should be removed. Proper plant to plant distance should be maintained ii) At knee high stage: All the dissimilar plants should be removed. iii) At flowering stage: Remove dissimilar tassel bearing plant before anthesis from the male.
- 15. 15 HARVESTING: The crop attains physiological maturity 30-35 days after 50% flowering and the seed moisture at this stage will be around 25-30%. The crop is harvested as cob harvesting when the sheath of cob dries and attains straw yellow color. YIELD: 3 to 4 tones per hectare
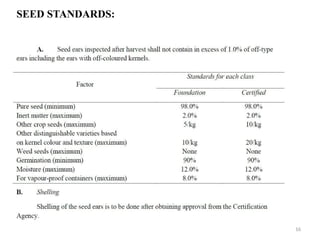
- 17. 17 THANK YOU