Dw design 4_bus_architecture
- 1. DATA WAREHOUSING Multi Dimensional Data Modeling. DW Bus architecture and matrix
- 2. 2
- 3.  Obviously, building the enterprise’s data warehouse in one step is too daunting, yet building it as isolated pieces defeats the overriding goal of consistency.  For long-term data warehouse success, we need to use an architected, incremental approach to build the enterprise’s warehouse.  The approach we advocate is the data warehouse bus architecture. 3
- 4.  By defining a standard bus interface for the data warehouse environment, separate data marts can be implemented by different groups at different times.  The separate data marts can be plugged together and usefully coexist if they adhere to the standard 4
- 5.  During the limited duration architecture phase, the team designs a master suite of standardized dimensions and facts that have uniform interpretation across the enterprise. This establishes the data architecture framework 5
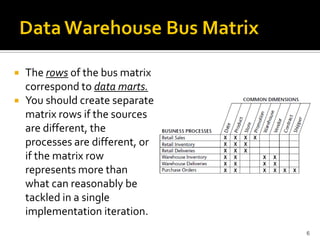
- 6.  The rows of the bus matrix correspond to data marts.  You should create separate matrix rows if the sources are different, the processes are different, or if the matrix row represents more than what can reasonably be tackled in a single implementation iteration. 6
- 7.  Common dimensions for different processes should be the same.  A dimension that has exactly the same meaning and content when being referred from different fact tables.  Where attributes apply, they should mean the same thing.  Roll-up dimensions conform to the base-level atomic dimension if they are a strict subset of that atomic dimension. (granularity) 7
- 8. 8
- 9.  Revenue, profit, standard prices, standard costs, measures of quality, measures of customer satisfaction, and other key performance indicators (KPIs) are facts that must be conformed. 9
- 10.  The Data Warehouse Toolkit.Second Edition.The Complete Guide to Dimensional Modeling.Ralph Kimball.Margy Ross 10