Dynamic compaction
- 1. Presented by:- Gaurav Verma IIT Roorkee
- 2. ï― Method invented and developed by Menard Company in Late 1960âs ï― Dynamic Compaction has been used on the numerous sites all over the world for various soil conditions and for a variety of applications such as: roads, airports, large halls
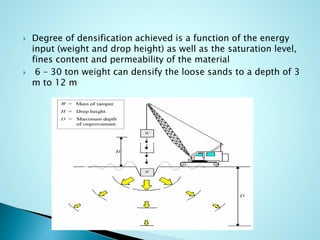
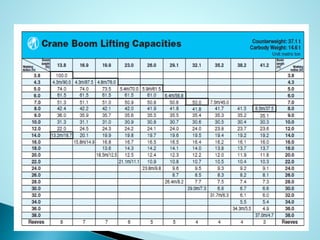
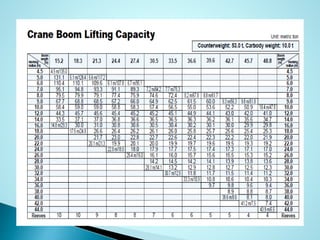
- 3. ï― Technique involves repeatedly dropping a large weight from a crane ï― Weight may range from 6 to 172 tons ï― Drop height typically varies from 10 m to 40m
- 4. ï― Degree of densification achieved is a function of the energy input (weight and drop height) as well as the saturation level, fines content and permeability of the material ï― 6 â 30 ton weight can densify the loose sands to a depth of 3 m to 12 m
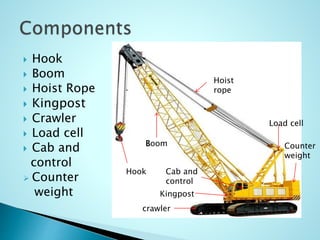
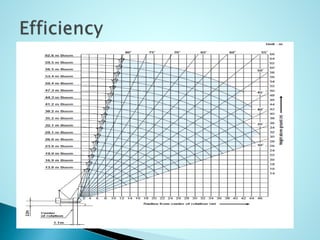
- 5. ï― Hook ï― Boom ï― Hoist Rope ï― Kingpost ï― Crawler ï― Load cell ï― Cab and control ï Counter weight Hook Hoist rope Boom Kingpost crawler Load cell Cab and control Counter weight
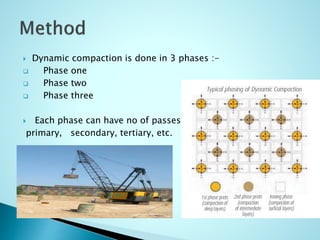
- 6. ï― Dynamic compaction is done in 3 phases :- ïą Phase one ïą Phase two ïą Phase three ï― Each phase can have no of passes primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.
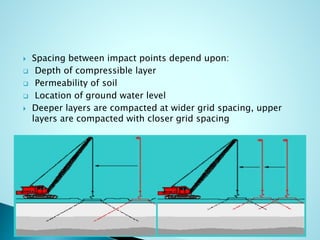
- 7. ï― Spacing between impact points depend upon: ïą Depth of compressible layer ïą Permeability of soil ïą Location of ground water level ï― Deeper layers are compacted at wider grid spacing, upper layers are compacted with closer grid spacing
- 8. ï― Deep craters are formed by tamping ï― Craters may be filled with sand after each pass ï― Heave around craters is generally small
- 9. ï― Applicable for all type of granular soil ï― This technique is particularly well adapted to non-organic, non-homogeneous fill and reclamation areas with variable characteristics ï― It is effective in both saturated and un-saturated soils. ï― The depth of the compaction most often varies between 3.0 and 7.0 m.
- 10. ï― Expensive and time consuming ï― Shock waves affect underground utilities in developed areas ï― The soil can be treated as close as 3 m from underground services and can be treated 6 m from the sound structures ï― Causes environmental pollution by making noise, gusts of air, vibrations