E learning rate-and_speed
- 2. Rate ď‚›A comparison of physical quantities with time is called rate. ď‚› Rate describes how one quantity changes with respect to time.
- 3. Rate ď‚› Examples of rate are number of words typed per minute, number of heartbeats per minute and number of babies born per hour. ď‚› An important rate that you will be studying in this chapter is speed. ď‚› It is a comparison length with time.
- 4. Speed ď‚› Speed is defined as the rate of change of distance travelled. ď‚› The speed of an object depends on two quantities: 1. distance (length) moved and; 2. time taken ď‚› Therefore, speed is a derived quantity.
- 5. Speed ď‚› The SI unit for speed is metre per second (m/s). ď‚› Othercommon units are kilometres per hour (km/h) and centimetres per second (cm/s).
- 6. Speed ď‚› Typical speeds of different moving objects
- 7. Average Speed ď‚› An object does not always move at the same speed. ď‚› Sometimes it moves faster and sometimes slower. ď‚› For example, a bus starts from rest and moves faster. Then it slows down to a stop at a traffic light. ď‚› Therefore, it is more useful to measure the average speed than the speed at a particular instant.
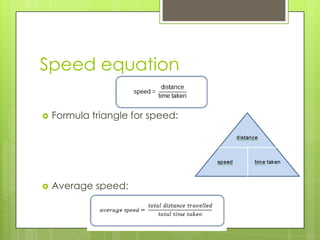
- 8. Speed equation ď‚› Formula triangle for speed: ď‚› Average speed: