E-CAB ADDA Power Point presentation
1 like344 views
E-CAB ADDA Power Point presentation
1 of 13
Downloaded 11 times







Ad
Recommended
Definition of enterprise Bangladesh contest
Definition of enterprise Bangladesh contest Shahin's Help Line
?
for more detail please visit www.facebook.com/helpline2012
??????? ????? ?????, ?????? ? ????_???????.pdf
??????? ????? ?????, ?????? ? ????_???????.pdfMdNajmusSakib
?
Pregnant Mother Care: Food and Nutrition. Bangla Parliamentary debate
Bangla Parliamentary debateWestern University
?
????? ????????? ??? ? ??????, ??????? ????? ???? ?????? ???? ???? ???? ???, ??????? ?????????? ???? ?? ??????? ???????Christian leadership for rohanpur
Christian leadership for rohanpurKomolpalma
?
This power point will teach us what is leadership in tribal community in Bangladesh.Bangladesh SME LOAN policy
Bangladesh SME LOAN policyShahin's Help Line
?
This document provides guidelines and procedures for microfinance (MF) loans in Bangladesh. It discusses Bangladesh Bank's role in developing the MF sector, including indicative targets for MF loans set for banks and financial institutions. It notes the employment generation and poverty reduction benefits of MF, especially for women. Guidelines include prioritizing loans for small and marginal farmers, setting loan amounts, and reserving a portion of loans for women borrowers.??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...
??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...Shahin's Help Line
?
??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ?????? ?? ??? ?????? ???? ? ???????????? ?? ???? ??????? ???? ??????????? More Related Content
What's hot (20)
??????? ????? ?????, ?????? ? ????_???????.pdf
??????? ????? ?????, ?????? ? ????_???????.pdfMdNajmusSakib
?
Pregnant Mother Care: Food and Nutrition. Bangla Parliamentary debate
Bangla Parliamentary debateWestern University
?
????? ????????? ??? ? ??????, ??????? ????? ???? ?????? ???? ???? ???? ???, ??????? ?????????? ???? ?? ??????? ???????Christian leadership for rohanpur
Christian leadership for rohanpurKomolpalma
?
This power point will teach us what is leadership in tribal community in Bangladesh.Viewers also liked (9)
Bangladesh SME LOAN policy
Bangladesh SME LOAN policyShahin's Help Line
?
This document provides guidelines and procedures for microfinance (MF) loans in Bangladesh. It discusses Bangladesh Bank's role in developing the MF sector, including indicative targets for MF loans set for banks and financial institutions. It notes the employment generation and poverty reduction benefits of MF, especially for women. Guidelines include prioritizing loans for small and marginal farmers, setting loan amounts, and reserving a portion of loans for women borrowers.??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...
??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...Shahin's Help Line
?
??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ?????? ?? ??? ?????? ???? ? ???????????? ?? ???? ??????? ???? ??????????? New trade licence gezzete ( recent price) in city corporation
New trade licence gezzete ( recent price) in city corporation Shahin's Help Line
?
New trade licence gezzete ( recent price) in city corporation Registration process of private limited company in Bangladesh
Registration process of private limited company in BangladeshMd. Rakibul Hasib
?
The document outlines the registration process for forming a private limited company in Bangladesh, emphasizing the role of the Registrar of Joint Stock Companies and Firms (RJSC) in approving registrations. It details the essential features of a company, including registration, legal personality, and limited liability, and explains the steps involved in company formation, such as name clearance, document submission, and applicable fees. Additionally, it covers obligations for annual returns and the procedures for winding up a company.Company law 1994 summary final
Company law 1994 summary finalMustafa Sagor
?
The document provides an overview of the Companies Act 1994 of Bangladesh. It discusses the background and history of company law in the region.
The executive summary outlines the 11 parts of the Companies Act 1994. It provides high-level descriptions of the key aspects covered in each part, including preliminary matters, company constitution/incorporation, share capital, management/administration, winding up procedures, registration office/fees, application to prior companies, registration of authorized companies, winding up of unregistered companies, foreign company registration, and supplemental legal matters.
Part II on company constitution/incorporation establishes the requirements for forming incorporated companies as public or private limited, or unlimited. It specifies the necessary contents of memorandumsThe Formation of a Company in Bangladesh
The Formation of a Company in BangladeshRafiqul Alam Khan
?
The document outlines the history and legal framework of company formation in Bangladesh, detailing the Companies Act of 1994, the types of companies, and the necessary steps for incorporation. It also discusses membership qualifications, legal documents required, and the processes involved in winding up a company. Furthermore, it addresses the safety regulations and welfare provisions under the factory acts, and the role of trade unions and collective bargaining in the context of industrial relations.Formation of companies
Formation of companiesNitin Patil
?
The document discusses the formation of companies, including the definition, stages, and required documents. It outlines the key stages of formation as promotion, name selection, incorporation by registering the Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association, and raising share capital. It also describes the key company documents - the Memorandum of Association, which defines the company objectives and rules, the Articles of Association, which outlines internal regulations, and the Prospectus, which provides details of share offerings.??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...
??? ????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ???????????? ??????? ???? ? ??? ?????? ??????...Shahin's Help Line
?
Ad
More from Shahin's Help Line (20)
Bsti product list
Bsti product list Shahin's Help Line
?
This document lists 155 products across various categories that have been brought under the mandatory certification marks scheme in Bangladesh. The products are divided into 4 main categories: A) 64 food and agricultural products, B) 40 chemical products, C) 11 jute and textile products, and D) 25 electronics and electrical products. It provides the name and corresponding Bangladesh standard number for each listed product.Review of ?????????? ? ?, ? ?
Review of ?????????? ? ?, ? ?Shahin's Help Line
?
^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄ ????? ????? ????? ????? ??????? , ???? ?????? ?? ???? ??????? ????? ???????? ???? ??? ??? ????? ???? ???????? ????? ???? ????? ???? , ?????? ????? ?????? ???????? ?????? ???? ?????? ???? ? ???????????? ???? ^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄
???????????? ???? ^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄Shahin's Help Line
?
?????¨? ????? ???? ?? ???? ???? ???????? ????? ????? !
?????¨? ????? ???? ???? ???????????? ???? ?????? ????? ^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄
.^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄ ???? ????? ???????? ??? ???? ???? ????????? ???? ????????? ?????? ???? ???? ??? ?? ???? ?????? ????? ?????? ? ????? ???? ???????????? ???? ???? ???????? ?? ? ???? ????? ? ?? ???? ???? ??????????? ???? ??? ??? ????, ?????? ???????? ???? ???? ?????? ??? ??, ???? ?????? ???????????? ???????? ??? ???? ?? ?? ????????? ?????? ????? ????? ? ?? ?????? ????? ???????? ?? ?????? ?? ?????? ???? ????? ?????? ??? ????? ? ????? ???? ?? ????? ???? ????? ????, ?????? ???? ???? ?? ????? ???????? ???? ??? ? ?????? ????? ???, ?????? ???????? ??? ?? ?? ???? ????? ????? ??? ??????? ?????????? ?? ?????? ???? ?? ?? ??????? ???????? ??? ????? ??? ??? ????? ^?????????? ? ?, ? ? ̄ ???? ?????? ????????? ????? ??? ?????? ??? ??? ???? ??? ?????? ??? ???????? ????? ???? ???? ????????? /?????? ???? ???? ???? ????? ???? ? ??? ???? ??? ????? ????? ?? ??? ?? ?????? ??? ???? ???? ?????? ????? ????? ???? ????? ??? ???????? ???? ???? ? ?????? ???? ???? ???? ?? ????? ????? ???? ? ????? ????? ??? ???? ? ?????, ??? ????? ????? ?????? ?? ????? ????????? ? ????? ?
?? ????? ?????? ?? ????? ????????? ? ????? ?Shahin's Help Line
?
?? ????? ?????? ?? ????? ????????? ? ????? ?An entrepreneurs vs one commercial address
An entrepreneurs vs one commercial addressShahin's Help Line
?
An entrepreneurs vs one commercial addressCompany registration guideline rjsc
Company registration guideline rjscShahin's Help Line
?
The document provides guidelines for registering a joint stock company online, including instructions on filling out registration applications, uploading documents, editing submissions, and printing documents. Applicants select the company type and fill in general information, details on corporate and individual subscribers, memorandum and articles of association. They can upload soft copies of required documents and submit the application for payment processing. Editing is allowed before final submission.Re financing scheme FOR Bangladeshi women entrepreneurs
Re financing scheme FOR Bangladeshi women entrepreneursShahin's Help Line
?
This document summarizes the Re-Financing Scheme of Bangladesh Bank, which provides financial assistance to support the business activities of only female borrowers. Some key points of this scheme are that only women can receive loans under it, up to 10% of the loan amount is provided at a lower interest rate, loans up to 25 thousand BDT are available for working capital needs, and personal guarantees are considered as collateral. This scheme partners with 29 commercial banks and 10 non-bank financial institutions to provide advice to women entrepreneurs on obtaining bank loans.Export & import certificate process in Bangladesh
Export & import certificate process in BangladeshShahin's Help Line
?
1) Importers and exporters can now import and export any permissible goods without restrictions on value or quantity by obtaining an Import Registration Certificate (IRC) or Export Registration Certificate (ERC).
2) Obtaining an IRC or ERC has a simplified process requiring only documents like a trade license, membership in a trade organization, tax ID, and bank certificate.
3) Certificates are issued within 3 hours of applying, and importers are classified into 6 categories based on annual import value with different registration and renewal fees listed.Checklist for bank loan
Checklist for bank loanShahin's Help Line
?
The document lists the key documents and information that are typically required by banks and financial institutions when applying for a loan. This includes documents like trade license, bank statements, national ID, tax certificates, partnership agreements, resumes, references and more. It mentions that a checklist has been prepared by banks summarizing these common requirements to help loan applicants. Applicants can contact the bank's SME department if they need any clarification or advice regarding the application process.Handbook of entrepreneurship development
Handbook of entrepreneurship developmentShahin's Help Line
?
This document discusses the importance of empowering entrepreneurship in Bangladesh to achieve its goal of becoming a middle-income country by 2021. Unemployment, especially among educated youth, is a major issue that needs to be addressed to avoid social crisis. Creating more entrepreneurs is seen as the easiest way to generate more employment and solve this crisis. The country's youth have the energy and boldness to take up the challenge of becoming successful entrepreneurs if provided with the necessary skills and support.Nice classification for trade mark
Nice classification for trade markShahin's Help Line
?
This document outlines the International Classification of Goods and Services (Nice Classification) which provides a common system for classifying goods and services for the purposes of registering trademarks. It establishes a Special Union of countries that have adopted the Nice Classification and discusses the Committee of Experts that oversees revisions to the Classification. The document also specifies that the Classification consists of a list of classes and an alphabetical list of goods and services with their corresponding classes.Ad
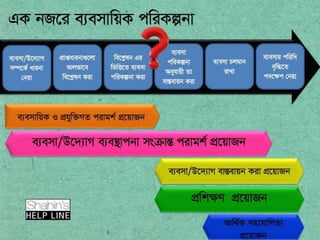
E-CAB ADDA Power Point presentation
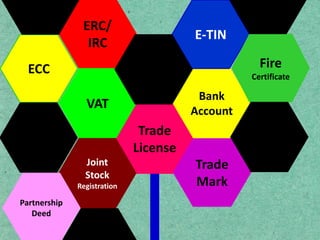
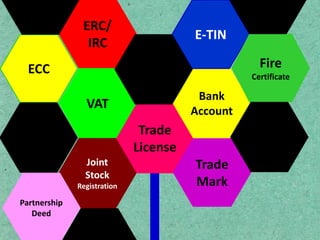
- 6. Trade License ? ?U?W jvB?m? wK Ges ?Kb c??qvRb ? ? ?Kvb c?wZ?vb ?_?K ?U?W jvB?m? Ki?Z nq ? ? wKfv?e ?U?W jvB?m? Ki?Z nq ? ? ?U?W jvB?m? Ki?Z K?Zv UvKv jv?M ? ? GKwU ?U?W jvB?m? wK GKvwaK e:emvq e:envi Kiv hvq ? ? GKwU ?U?W jvB?m? wK GKvwaK e:w? Ki?Z cvi?eb? ? ?U?W jvB?m? wK bevqb Ki?Z nq ? e:emvwqK wVKvbv gvwjKvbvi aib e:emvi aib
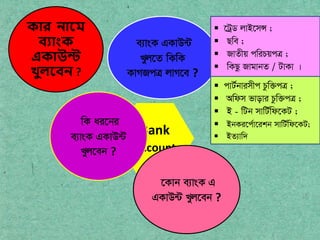
- 7. Bank Account ??? ???? ?????? ??????? ?????? ? wK ai?bi e:vsK GKvD?U Lyj?eb ? e:vsK GKvD?U Lyj?Z wKwK KvMRc? jvM?e ? ? ?U?W jvB?m? ; ? Qwe ; ? RvZxq cwiPqc? ; ? wKQz RvgvbZ / UvKv | ? cvU?bvimxc Pzw?c? ; ? Awdm fvovi Pzw?c? ; ? B - wUb mvwU?wd?KU ; ? BbKi?c?v?ikb mvwU?wd?KU; ? BZ:vw` ?Kvb e:vsK G GKvD?U Lyj?eb ?
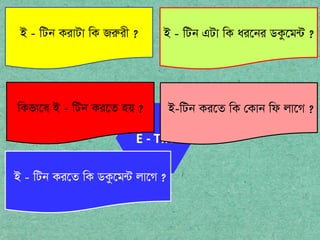
- 8. E - TIN B - wUb KivUv wK Ri?ix ? B - wUb GUv wK ai?bi WKz?g?U ? wKfv?e B - wUb Ki?Z nq ? B-wUb Ki?Z wK ?Kvb wd jv?M ? B - wUb Ki?Z wK WKz?g?U jv?M ?
- 9. Trade Mark ?U?W gvK? wK Ges ?Kb c??qvRb ? ?U?W gvK? ?Kv_v ?_?K Ki?Z nq ? ?U?W gvK? Gi Rb: wK wd jv?M ? ?U?W gvK? Gi wK WKz?g?U jv?M ?
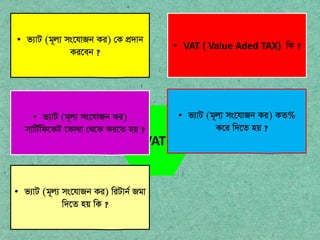
- 10. VAT ? VAT ( Value Aded TAX) wK ? ? f:vU (g~j: ms?hvRb Ki) ?K c?`vb Ki?eb ? ? f:vU (g~j: ms?hvRb Ki) mvwU?wd?KU ?Kv_v ?_?K Ki?Z nq ? ? f:vU (g~j: ms?hvRb Ki) KZ% K?i w`?Z nq ? ? f:vU (g~j: ms?hvRb Ki) wiUvb? Rgv w`?Z nq wK ?
