Building a Graph of Names and Contextual Patterns for Named Entity ClassificationEcir09 poster
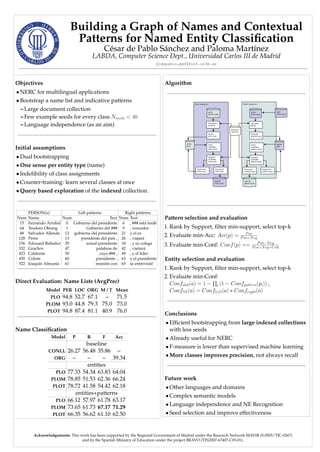
- 1. Building a Graph of Names and Contextual Patterns for Named Entity Classi’¼ücation C┬┤esar de Pablo S┬┤anchez and Paloma Mart┬┤─▒nez LABDA, Computer Science Dept., Universidad Carlos III de Madrid {cdepablo,pmf}@inf.uc3m.es Objectives ŌĆó NERC for multilingual applications ŌĆó Bootstrap a name list and indicative patterns ŌĆō Large document collection ŌĆō Few example seeds for every class Nseeds < 40 ŌĆō Language independence (as an aim) Initial assumptions ŌĆó Dual bootstrapping ŌĆó One sense per entity type (name) ŌĆó Indelibility of class assignments ŌĆó Counter-training: learn several classes at once ŌĆó Query based exploration of the indexed collection. PERSON(x) Left patterns Right patterns Num Name Num Text Num Text 15 Fernando Arrabal 0 Gobierno del presidente 6 , ### esta tarde 64 Teodoro Obiang 1 Gobierno del ### 9 , vencedor 68 Salvador Allende 12 gobierno del presidente 21 y el ex 128 Peres 13 presidente del pa┬┤─▒s , 26 , viajar┬┤a 156 Edouard Balladur 29 actual presidente 34 , y su colega 332 Grachov 47 palabras de 42 , visitar┬┤a 423 Calder┬┤on 50 cuyo ### , 49 , y el l┬┤─▒der 450 Colom 60 presidente , 63 y el presidente 522 Joaqu┬┤─▒n Almunia 61 reuni┬┤on con 65 se entrevist┬┤oŌĆÖ Direct Evaluation: Name Lists (AvgPrec) Model PER LOC ORG M / T Mean PLO 94.8 52.7 67.1 ŌĆō 71.5 PLOM 93.0 44.8 79.3 75.0 73.0 PLOT 94.8 87.4 81.1 40.9 76.0 Name Classi’¼ücation Model P R F Acc baseline CONLL 26.27 56.48 35.86 ŌĆō ORG ŌĆō ŌĆō ŌĆō 39.34 entities PLO 77.33 54.34 63.83 64.04 PLOM 78.85 51.53 62.36 66.24 PLOT 78.72 41.58 54.42 62.18 entities+patterns PLO 66.12 57.97 61.78 63.17 PLOM 73.65 61.73 67.17 71.29 PLOT 66.35 56.62 61.10 62.50 Algorithm Pattern selection and evaluation 1. Rank by Support, ’¼ülter min-support, select top-k 2. Evaluate min-Acc: Acc(p) = Pos Pos+Neg 3. Evaluate min-Conf: Conf(p) == PosŌłÆNeg Pos+Neg+Unk Entity selection and evaluation 1. Rank by Support, ’¼ülter min-support, select top-k 2. Evaluate min-Conf: Confslot(a) = 1 ŌłÆ i (1 ŌłÆ Confpattern(pi)) , ConfNE(a) = Confleft(a) ŌłŚ Confright(a) Conclusions ŌĆó Ef’¼ücient bootstrapping from large indexed collections with less seeds ŌĆó Already useful for NERC ŌĆó F-measure is lower than supervised machine learning ŌĆó More classes improves precision, not always recall Future work ŌĆó Other languages and domains ŌĆó Complex semantic models ŌĆó Language independence and NE Recognition ŌĆó Seed selection and improve effectiveness Acknowledgements: This work has been supported by the Regional Government of Madrid under the Research Network MAVIR (S-0505/TIC-0267) and by the Spanish Ministry of Education under the project BRAVO (TIN2007-67407-C03-01).