Eclipse
Download as PPT, PDF1 like2,583 views
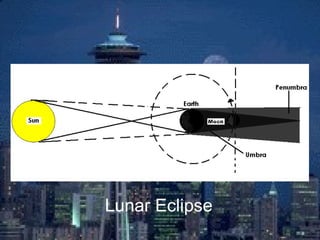
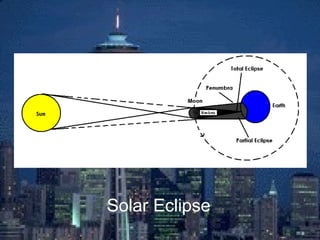
An eclipse occurs when one celestial body passes between the sun and another, blocking sunlight or moonlight. There are two main types of eclipses - lunar eclipses, where the moon passes into Earth's shadow, and solar eclipses, where the moon passes between Earth and the sun. During a lunar eclipse, the moon turns red as it is illuminated only by sunlight passing through Earth's atmosphere. A solar eclipse can be partial or total, where the moon completely blocks the sun's light over a small area. Total solar eclipses are rare as the moon's shadow is small and its orbit is tilted relative to Earth's.
1 of 20
Downloaded 95 times


















Recommended
Solar And Lunar



Solar And Lunarjlevs295
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one celestial body passes between a source of light and another, blocking the light. There are two types of eclipses: solar eclipses, where the moon passes between the earth and sun, and lunar eclipses, where the earth passes between the moon and sun. The moon's shadow during a solar eclipse has two parts - the penumbra, where a partial eclipse can be seen, and the umbra, where a total eclipse occurs.Solar and lunar eclipses 



Solar and lunar eclipses Victor F. Melitante Jr.
Ěý
A "lunar eclipse" and a "solar eclipse" refer to events involving three celestial bodies: the Sun ("solar"), the moon ("lunar"), and the Earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Moon and the Sun, and the Earth's shadow obscures the moon or a portion of it. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking all or a portion of the Sun. Different cases in the formation of shadows



Different cases in the formation of shadowsvedavamsikasangu
Ěý
This document discusses different types of shadows formed during lunar and solar eclipses. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon moves into Earth's shadow and is aligned with the sun and Earth. This can result in a blood moon that appears reddish. A solar eclipse happens when the moon is positioned between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow onto a portion of Earth. The document defines umbra, penumbra, and antumbra shadows and how they relate to complete or partial coverage of the moon or sun during different eclipse types. It also examines how the size of the light source and obstacle can impact shadow formation and characteristics.Solar and lunar_eclipses1



Solar and lunar_eclipses1Ravin Ravi
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses: solar and lunar. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes into the Earth's shadow, appearing red or dark. A solar eclipse happens when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on Earth. There are three types of each: total, partial, and penumbral/annular. Lunar eclipses are more common as anyone experiencing nighttime can see it, while only a small area experiences a solar eclipse due to the moon's small umbral shadow. Eclipses occur during eclipse seasons when the sun, Earth, and moon are directly aligned.Eclipse presentation[1]![Eclipse presentation[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/eclipsepresentation1-120104131043-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Eclipse presentation[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/eclipsepresentation1-120104131043-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Eclipse presentation[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/eclipsepresentation1-120104131043-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Eclipse presentation[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/eclipsepresentation1-120104131043-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Eclipse presentation[1]sciencenerd42 McCarthy
Ěý
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth's shadow. There are three types of lunar eclipses - total, partial, and penumbral - depending on how much of the Moon passes through the Earth's umbra or penumbra. During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon takes on a red color due to refraction of sunlight through the Earth's atmosphere. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. There are also three types of solar eclipses - total, partial, and annular - depending on the Moon's position and alignment with the Earth and Sun.Shadows and Solar-Lunar Eclipses



Shadows and Solar-Lunar EclipsesVal Bolislis
Ěý
This document discusses shadows, solar eclipses, and lunar eclipses. There are four types of solar eclipses: total, annular, hybrid, and partial. During a total solar eclipse, the moon completely obscures the sun, allowing the solar corona to be seen. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is not large enough to completely cover the sun, leaving a ring of sunlight visible. A hybrid eclipse shifts between total and annular. A partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon only partially obscures the sun. There are also three types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral.Eclipses



Eclipses06426345
Ěý
The document discusses eclipses and provides myths and legends about them from different cultures. It explains that solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on Earth. Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the sun and moon, and the Earth's shadow is cast on the moon. The document suggests doing a hands-on activity using balls and lamps to observe how eclipses are formed and includes links to NASA videos and worksheets on eclipses.Solar Eclipse of July 22, 2009



Solar Eclipse of July 22, 2009Siderence Chen
Ěý
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, blocking the sun's light. There are typically 2-5 solar eclipses per year. There are four types of solar eclipses: total, annular, partial, and hybrid. A total solar eclipse, where the moon completely blocks the sun's light, occurs on average every 18 months and can only be seen from a narrow path on Earth. The longest total solar eclipse of the 21st century occurred on July 22, 2009 and lasted over 6 minutes. Special care must be taken to safely observe a solar eclipse by using eclipse glasses or other filters to view the sun.Eclipses



Eclipsesmrcoyleteach
Ěý
The document discusses eclipses of the sun and moon through various quotes and descriptions. It provides background on solar eclipses, noting that there are three types - annular, partial and total - and details like their frequency and visibility. It also covers lunar eclipses and explains why the moon appears red during an eclipse due to atmospheric filtering of light. Upcoming eclipses are listed, though none will be fully visible from the location.Eclipses



EclipsesSimple ABbieC
Ěý
1) Eclipses occur when one celestial body blocks the light from another. Lunar eclipses happen during a full moon when the Earth casts its shadow on the moon. Solar eclipses occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the Earth and sun.
2) There are three types of lunar eclipses - total, partial, and penumbral - and three types of solar eclipses - total, partial, and annular.
3) Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to the Earth's orbit around the sun. Lunar eclipses are more frequent than solar eclipses.Solar and lunar eclipse



Solar and lunar eclipseKunal Yadav
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses - solar and lunar. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, while a lunar eclipse happens when the earth is between the sun and moon. Eclipses form when the three celestial bodies are aligned in a straight line. An eclipse can be total in the umbra region of complete shadow or partial in the penumbra region of partial shadow.Solar and Lunar eclipse



Solar and Lunar eclipseHemashree23
Ěý
This document discusses eclipses, including lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that eclipses occur when the sun, earth, and moon are aligned so that one celestial body casts a shadow on the other. A lunar eclipse can only happen during a full moon, while a solar eclipse can only happen during a new moon. The document outlines the different types of solar eclipses and provides safety precautions for viewing a solar eclipse directly.Solar and lunar eclipse



Solar and lunar eclipseHimeshRavi
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one astronomical object passes in front of another, temporarily obscuring it from view. There are two types of eclipses - solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between the earth and sun, and lunar eclipses, which occur when the earth passes between the sun and moon. The document provides instructions for safely viewing an eclipse using a pinhole projector or solar filter to project the sun's image without looking directly at it.Solar and lunar_eclipses



Solar and lunar_eclipsesMakati Science High School
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes into Earth's shadow, and solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun. Lunar eclipses can be total, partial, or penumbral depending on how far into Earth's shadow the moon passes. Solar eclipses can be total, partial, or annular depending on the moon's position in its orbit. Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the sun, so the three objects do not align perfectly except during eclipse seasons.September 27 Lunar Eclipse



September 27 Lunar EclipseSOCIEDAD JULIO GARAVITO
Ěý
The document discusses the total lunar eclipse that will occur on the evening of September 27, 2015 in North America. It will be visible across much of the western hemisphere and last over an hour. The eclipse will have five stages as the Moon passes through Earth's penumbra and umbra shadows. Observers are encouraged to time the moments when the umbra's edge crosses different lunar features to help scientists study variations in the size of Earth's shadow.Solar and lunar eclipses



Solar and lunar eclipsesmemuflo
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one celestial body blocks the light of another from an observer's perspective on Earth. There are two main types - solar eclipses where the moon passes in front of the sun, and lunar eclipses where the moon passes through the Earth's shadow. During a solar eclipse, the moon's shadow falls on parts of Earth and the sun appears darkened; there are three types depending on how much of the sun is covered. A lunar eclipse is visible over a larger area as the moon passes through the Earth's shadow and takes on a reddish hue. Eclipses can last up to seven minutes and a total solar eclipse occurs about every 1.5 years.Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipses



Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipsesdwinter1
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. For an eclipse to occur, the Sun, Moon and Earth must be aligned on the same plane. The document provides details on the conditions required to view lunar and solar eclipses and why the Moon appears red during a lunar eclipse.Eclipse



EclipseSyed Shah
Ěý
This document summarizes a presentation about solar eclipses, including:
1) It discusses the mythology and beliefs around eclipses in ancient cultures like China, India, and Egypt who saw them as omens. It also covers the mechanics of how eclipses occur.
2) It provides safety guidelines for viewing eclipses, emphasizing the importance of using approved solar filters.
3) It uses computer simulations to show the partial solar eclipse of March 29, 2006 as seen from different locations, and lists some important future eclipses between the present and 2030.Eclipses by WSTA412



Eclipses by WSTA412ferrazs
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when a celestial body passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, where the earth casts a shadow on the moon, and solar eclipses, where the moon casts a shadow on earth. During a lunar eclipse, the earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon, causing it to glow red. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes completely into the earth's shadow, while a partial lunar eclipse happens when it only partially enters the shadow.Eclipses



EclipsesSadia Zareen
Ěý
The document provides an overview of lunar phases, eclipses, and tides. It explains that the moon orbits at an angle relative to Earth's orbit and reflects sunlight, causing phases. Eclipses occur when the sun, earth, and moon align, sometimes blocking sunlight. Total lunar eclipses make the moon appear red due to atmospheric filtering of light. The moon's gravity also causes two high tides each day by pulling the side of Earth closest and farthest to it.Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipses



Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipsesdwinter1
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon. Solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. Eclipses only occur when the sun, Earth, and moon are aligned on the same plane. The document provides details on the conditions required to see each type of eclipse and diagrams demonstrating the geometry of lunar and solar eclipses.Moon Motions and Eclipses



Moon Motions and EclipsesShane Riordan
Ěý
The document summarizes the motions and phases of the Earth-Moon system. It explains that the moon orbits Earth over the course of about a month in an elliptical orbit, appearing larger when closer (perigee) and smaller when farther (apogee). The changing positions result in the phases of the moon as the illuminated side facing Earth waxes and wanes over the lunar cycle. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, causing the moon to block the sun during a solar eclipse or Earth to block the sun's light during a lunar eclipse.Eclipses



Eclipsesmrcoyleteach
Ěý
The document discusses different types of solar and lunar eclipses, including total, partial, and annular solar eclipses and penumbral, partial, and total lunar eclipses. It provides examples of quotes from historical accounts of eclipses dating back to 1375 BC and explanations of why the moon appears red during a lunar eclipse and the different parts of an eclipse shadow.The Great American Solar Eclipse



The Great American Solar EclipseDavid Hearn
Ěý
The document provides information about the upcoming August 21, 2017 total solar eclipse, including key times and locations to view it, safety tips for viewing, and what phenomena can be observed. The eclipse will be visible across the United States, with the path of totality stretching from Oregon to South Carolina. Key events along the path include first contact at 1:06 PM, totality beginning at 2:35 PM lasting 2 minutes 13 seconds, and fourth contact at 4:00 PM from Brasstown Bald in Georgia. Proper solar filters are required to safely observe the partial phases, while the corona can only be viewed without filters during the brief period of totality.Aug 21, 2017 solar eclipse



Aug 21, 2017 solar eclipseSteve Garretson
Ěý
The document discusses different types of solar eclipses: partial solar eclipses where only part of the sun is blocked by the moon; annular eclipses where the moon appears smaller allowing light to shine around the edges; and total lunar eclipses where the moon passes into the Earth's shadow. It provides information on the next solar eclipse over the US in 2024 and resources from NASA on visualizing and tracing the 2017 eclipse path. Safety tips are outlined for viewing a solar eclipse, including eye protection, layers of clothing, food, water, and first aid supplies.Moon phases



Moon phasesWoulf88JC
Ěý
The document discusses the eight phases of the moon, including the new moon phase where no part of the moon is illuminated, the waxing crescent phase where a small sliver of the moon is visible after sunset, and the first quarter phase where half of the moon is visible for the first half of the evening before setting. It concludes by stating that each month the moon passes through these eight phases, which are named based on how much of the illuminated part can be seen and whether that amount is increasing or decreasing each day.Solar and lunar_eclipses1



Solar and lunar_eclipses1helen de la cruz
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that a lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. There are three types of each: total, partial, and penumbral/annular. Eclipses do not occur daily because the Moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the Sun, but there are seasons when eclipses are more likely to occur.G7 science student modules 3rd & 4th qrtr



G7 science student modules 3rd & 4th qrtrMakati Science High School
Ěý
This document is the second part of the Grade 7 Science Learner's Material published by the Department of Education of the Philippines. It contains 6 units on topics of energy in motion, waves, sound, light, heat, electricity, the Philippine environment, solar energy and the atmosphere, and seasons and eclipses. Each unit includes multiple student activities to explain and explore the concepts covered in that unit through hands-on learning experiences. The material is intended for use by students and teachers in learning and teaching the Grade 7 science curriculum in Philippine schools.Shadow Activity



Shadow Activityguest37e850
Ěý
This document provides instructions for an activity to teach students about shadows. It explains how shadows are formed when an object blocks light and includes a hands-on activity where students will trace each other's shadows using a flashlight on black paper. The activity is meant to demonstrate that shadows are longer in the morning and evening when the sun is lower, and shorter at noon when the sun is highest. Students are asked questions to check their understanding of how shadows change at different times of day.Shadows by Lucy AR



Shadows by Lucy ARisamadero79
Ěý
Light rays travel in straight lines from a light source. If an opaque object blocks these rays, a shadow is formed where the light cannot reach. Moving the light source closer to an object causes it to block more light, resulting in a larger shadow, while moving it farther away blocks less light and produces a smaller shadow.More Related Content
What's hot (19)
Eclipses



Eclipsesmrcoyleteach
Ěý
The document discusses eclipses of the sun and moon through various quotes and descriptions. It provides background on solar eclipses, noting that there are three types - annular, partial and total - and details like their frequency and visibility. It also covers lunar eclipses and explains why the moon appears red during an eclipse due to atmospheric filtering of light. Upcoming eclipses are listed, though none will be fully visible from the location.Eclipses



EclipsesSimple ABbieC
Ěý
1) Eclipses occur when one celestial body blocks the light from another. Lunar eclipses happen during a full moon when the Earth casts its shadow on the moon. Solar eclipses occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the Earth and sun.
2) There are three types of lunar eclipses - total, partial, and penumbral - and three types of solar eclipses - total, partial, and annular.
3) Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to the Earth's orbit around the sun. Lunar eclipses are more frequent than solar eclipses.Solar and lunar eclipse



Solar and lunar eclipseKunal Yadav
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses - solar and lunar. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, while a lunar eclipse happens when the earth is between the sun and moon. Eclipses form when the three celestial bodies are aligned in a straight line. An eclipse can be total in the umbra region of complete shadow or partial in the penumbra region of partial shadow.Solar and Lunar eclipse



Solar and Lunar eclipseHemashree23
Ěý
This document discusses eclipses, including lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that eclipses occur when the sun, earth, and moon are aligned so that one celestial body casts a shadow on the other. A lunar eclipse can only happen during a full moon, while a solar eclipse can only happen during a new moon. The document outlines the different types of solar eclipses and provides safety precautions for viewing a solar eclipse directly.Solar and lunar eclipse



Solar and lunar eclipseHimeshRavi
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one astronomical object passes in front of another, temporarily obscuring it from view. There are two types of eclipses - solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between the earth and sun, and lunar eclipses, which occur when the earth passes between the sun and moon. The document provides instructions for safely viewing an eclipse using a pinhole projector or solar filter to project the sun's image without looking directly at it.Solar and lunar_eclipses



Solar and lunar_eclipsesMakati Science High School
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes into Earth's shadow, and solar eclipses, which occur when the moon passes between Earth and the sun. Lunar eclipses can be total, partial, or penumbral depending on how far into Earth's shadow the moon passes. Solar eclipses can be total, partial, or annular depending on the moon's position in its orbit. Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the sun, so the three objects do not align perfectly except during eclipse seasons.September 27 Lunar Eclipse



September 27 Lunar EclipseSOCIEDAD JULIO GARAVITO
Ěý
The document discusses the total lunar eclipse that will occur on the evening of September 27, 2015 in North America. It will be visible across much of the western hemisphere and last over an hour. The eclipse will have five stages as the Moon passes through Earth's penumbra and umbra shadows. Observers are encouraged to time the moments when the umbra's edge crosses different lunar features to help scientists study variations in the size of Earth's shadow.Solar and lunar eclipses



Solar and lunar eclipsesmemuflo
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one celestial body blocks the light of another from an observer's perspective on Earth. There are two main types - solar eclipses where the moon passes in front of the sun, and lunar eclipses where the moon passes through the Earth's shadow. During a solar eclipse, the moon's shadow falls on parts of Earth and the sun appears darkened; there are three types depending on how much of the sun is covered. A lunar eclipse is visible over a larger area as the moon passes through the Earth's shadow and takes on a reddish hue. Eclipses can last up to seven minutes and a total solar eclipse occurs about every 1.5 years.Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipses



Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipsesdwinter1
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. For an eclipse to occur, the Sun, Moon and Earth must be aligned on the same plane. The document provides details on the conditions required to view lunar and solar eclipses and why the Moon appears red during a lunar eclipse.Eclipse



EclipseSyed Shah
Ěý
This document summarizes a presentation about solar eclipses, including:
1) It discusses the mythology and beliefs around eclipses in ancient cultures like China, India, and Egypt who saw them as omens. It also covers the mechanics of how eclipses occur.
2) It provides safety guidelines for viewing eclipses, emphasizing the importance of using approved solar filters.
3) It uses computer simulations to show the partial solar eclipse of March 29, 2006 as seen from different locations, and lists some important future eclipses between the present and 2030.Eclipses by WSTA412



Eclipses by WSTA412ferrazs
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when a celestial body passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. There are two types of eclipses: lunar eclipses, where the earth casts a shadow on the moon, and solar eclipses, where the moon casts a shadow on earth. During a lunar eclipse, the earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon, causing it to glow red. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes completely into the earth's shadow, while a partial lunar eclipse happens when it only partially enters the shadow.Eclipses



EclipsesSadia Zareen
Ěý
The document provides an overview of lunar phases, eclipses, and tides. It explains that the moon orbits at an angle relative to Earth's orbit and reflects sunlight, causing phases. Eclipses occur when the sun, earth, and moon align, sometimes blocking sunlight. Total lunar eclipses make the moon appear red due to atmospheric filtering of light. The moon's gravity also causes two high tides each day by pulling the side of Earth closest and farthest to it.Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipses



Eclipses - Solar and Lunar Eclipsesdwinter1
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon. Solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. Eclipses only occur when the sun, Earth, and moon are aligned on the same plane. The document provides details on the conditions required to see each type of eclipse and diagrams demonstrating the geometry of lunar and solar eclipses.Moon Motions and Eclipses



Moon Motions and EclipsesShane Riordan
Ěý
The document summarizes the motions and phases of the Earth-Moon system. It explains that the moon orbits Earth over the course of about a month in an elliptical orbit, appearing larger when closer (perigee) and smaller when farther (apogee). The changing positions result in the phases of the moon as the illuminated side facing Earth waxes and wanes over the lunar cycle. Eclipses occur when the sun, Earth, and moon align, causing the moon to block the sun during a solar eclipse or Earth to block the sun's light during a lunar eclipse.Eclipses



Eclipsesmrcoyleteach
Ěý
The document discusses different types of solar and lunar eclipses, including total, partial, and annular solar eclipses and penumbral, partial, and total lunar eclipses. It provides examples of quotes from historical accounts of eclipses dating back to 1375 BC and explanations of why the moon appears red during a lunar eclipse and the different parts of an eclipse shadow.The Great American Solar Eclipse



The Great American Solar EclipseDavid Hearn
Ěý
The document provides information about the upcoming August 21, 2017 total solar eclipse, including key times and locations to view it, safety tips for viewing, and what phenomena can be observed. The eclipse will be visible across the United States, with the path of totality stretching from Oregon to South Carolina. Key events along the path include first contact at 1:06 PM, totality beginning at 2:35 PM lasting 2 minutes 13 seconds, and fourth contact at 4:00 PM from Brasstown Bald in Georgia. Proper solar filters are required to safely observe the partial phases, while the corona can only be viewed without filters during the brief period of totality.Aug 21, 2017 solar eclipse



Aug 21, 2017 solar eclipseSteve Garretson
Ěý
The document discusses different types of solar eclipses: partial solar eclipses where only part of the sun is blocked by the moon; annular eclipses where the moon appears smaller allowing light to shine around the edges; and total lunar eclipses where the moon passes into the Earth's shadow. It provides information on the next solar eclipse over the US in 2024 and resources from NASA on visualizing and tracing the 2017 eclipse path. Safety tips are outlined for viewing a solar eclipse, including eye protection, layers of clothing, food, water, and first aid supplies.Moon phases



Moon phasesWoulf88JC
Ěý
The document discusses the eight phases of the moon, including the new moon phase where no part of the moon is illuminated, the waxing crescent phase where a small sliver of the moon is visible after sunset, and the first quarter phase where half of the moon is visible for the first half of the evening before setting. It concludes by stating that each month the moon passes through these eight phases, which are named based on how much of the illuminated part can be seen and whether that amount is increasing or decreasing each day.Solar and lunar_eclipses1



Solar and lunar_eclipses1helen de la cruz
Ěý
The document discusses lunar and solar eclipses. It explains that a lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. There are three types of each: total, partial, and penumbral/annular. Eclipses do not occur daily because the Moon's orbit is tilted relative to Earth's orbit around the Sun, but there are seasons when eclipses are more likely to occur.Viewers also liked (20)
G7 science student modules 3rd & 4th qrtr



G7 science student modules 3rd & 4th qrtrMakati Science High School
Ěý
This document is the second part of the Grade 7 Science Learner's Material published by the Department of Education of the Philippines. It contains 6 units on topics of energy in motion, waves, sound, light, heat, electricity, the Philippine environment, solar energy and the atmosphere, and seasons and eclipses. Each unit includes multiple student activities to explain and explore the concepts covered in that unit through hands-on learning experiences. The material is intended for use by students and teachers in learning and teaching the Grade 7 science curriculum in Philippine schools.Shadow Activity



Shadow Activityguest37e850
Ěý
This document provides instructions for an activity to teach students about shadows. It explains how shadows are formed when an object blocks light and includes a hands-on activity where students will trace each other's shadows using a flashlight on black paper. The activity is meant to demonstrate that shadows are longer in the morning and evening when the sun is lower, and shorter at noon when the sun is highest. Students are asked questions to check their understanding of how shadows change at different times of day.Shadows by Lucy AR



Shadows by Lucy ARisamadero79
Ěý
Light rays travel in straight lines from a light source. If an opaque object blocks these rays, a shadow is formed where the light cannot reach. Moving the light source closer to an object causes it to block more light, resulting in a larger shadow, while moving it farther away blocks less light and produces a smaller shadow.Eclipses



EclipsesAngelica Villegas
Ěý
There are three distinct parts of a shadow: the umbra, penumbra, and antumbra. The document discusses the two primary types of eclipses, solar and lunar, and defines the different types of each including total, partial, annular, hybrid, and penumbral. It provides the dates for the next solar and lunar eclipses occurring in 2015 and 2016.Seasons and weather james



Seasons and weather jamesroom04
Ěý
The document discusses the reasons for seasons on Earth. It explains that as the Earth revolves around the sun, the seasons change, with summer having longer days than winter due to the Earth's tilt. Some animals hibernate in winter because the days are shorter.Watching the seasons change



Watching the seasons changelauttasaari
Ěý
This document provides instructions for a study observing seasonal changes that will inform a workshop in Helsinki in May 2016. Students will keep a monthly diary recording length of day, sunshine, rainfall, temperature, and other weather data. They will also take one picture per month from June 2015 to April 2016 to document changes in views and species migration. The individual school observations will be compiled into a presentation to be sent to the workshop organizers by April 15th, 2016.Science presentation



Science presentationsh2610
Ěý
The document discusses the causes of day and night, seasons, the length of a year, and the phases of the moon. It explains that day and night are caused by the Earth's rotation, seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis, and it takes approximately 365.25 days for the Earth to orbit the sun. It also notes that the phases of the moon are due to its monthly orbit around Earth and its positioning relative to the Earth and sun, which determines how much of its illuminated side is visible to observers on Earth.the seasons change



the seasons changeliuhanxiang
Ěý
The document discusses the four seasons and their causes. It mentions winter, autumn, summer, and spring but only provides details about spring, suggesting the document focuses on explaining what causes that particular season.09 Feb 19 Blackbody, Sun



09 Feb 19 Blackbody, SunSteve Koch
Ěý
The document discusses various topics related to light and the sun, including:
1) Light carries both energy and momentum even though it has no mass. Light phenomena can be understood by treating light as both a particle and wave.
2) Shadows and eclipses are discussed. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon.
3) All objects emit radiation called blackbody radiation whose spectrum depends on the object's temperature, with higher temperatures emitting light with shorter wavelengths. Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipses



Sp11 -notes--moon and eclipsesdolandese
Ěý
1) The Earth, Sun and Moon exist in a complex system of orbits where the Moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth revolves around the Sun.
2) As the Moon orbits the Earth, the illuminated portion that we see from Earth changes in a cycle called phases, ranging from new moon to full moon and back over about two weeks.
3) Lunar and solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, casting its shadow on either the Moon or Earth, and can be total or partial depending on the alignment of the three bodies.Cassandra Summit 2015 - A Change of Seasons



Cassandra Summit 2015 - A Change of SeasonsEiti Kimura
Ěý
The document summarizes Movile's big move to Apache Cassandra from relational databases for three key systems:
1) The subscription and billing system to improve performance, availability, and scalability.
2) The Kiwi user platform to reduce costs and improve throughput.
3) Distributing shared resources across a Cassandra cluster to improve scalability and reduce hardware costs.
The moves resulted in significant cost savings, throughput increases, and more scalable architectures.Seasons



SeasonsRAISSA RO
Ěý
The document discusses four seasons of loneliness created by Raissa. It is a musical composition divided into four parts representing different seasons. Each season portrays feelings of loneliness through the music.Formation of shadows



Formation of shadowsharila78
Ěý
The document discusses how the rotation of the Earth causes the position and length of shadows to change throughout the day. It notes that in the morning shadows are long and point west, becoming shorter until reaching their shortest at noon, then lengthening and pointing east in the afternoon as the sun sets in the west.Seasons



SeasonsBrandi
Ěý
The seasons are caused by the 23.5 degree tilt of the Earth's axis as it revolves around the sun, resulting in different parts of the Earth receiving more or less direct sunlight over the course of a year. Summer occurs in the northern hemisphere when its axis is tilted toward the sun, producing longer days, and winter happens when the axis is tilted away from the sun for shorter days. The changing position of the Earth relative to the sun's rays is responsible for seasonal variations in weather patterns and daylight hours around the world.What causes seasons on earth



What causes seasons on earthnmsouthern
Ěý
The document summarizes what causes seasons on Earth. It explains that seasons result from the tilt of Earth's axis relative to its orbit around the sun. This causes variations in the intensity of sunlight and day length throughout the year. Specifically, summer occurs in the Northern Hemisphere when it is tilted toward the sun, and winter occurs when it is tilted away. Spring and fall seasons experience nearly equal amounts of daylight and nighttime.Journal poupée Paris mai 2015



Journal poupée Paris mai 2015massillonprimaire
Ěý
1) The document is a diary from a student's week-long trip to Paris, France for an exchange program with students from other European countries.
2) Each day provides details of the activities the student participated in, including visiting landmarks like Notre Dame, riding a bateaux-mouches boat tour, workshops on architecture, and saying goodbye to friends at the end of the week.
3) The student enjoyed learning about Paris and spending time with friends from Turkey, Greece, Poland, Finland, and other countries, but was sad to see most of them leave at the end of the week after building models of landmarks together.Q3 q4 teachers guide v1.0



Q3 q4 teachers guide v1.00709198907231987
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a 7th grade science unit on energy and motion. The unit covers key topics like uniform and accelerated motion, waves, sound, light, heat, and electricity. For each topic, specific concepts are introduced and example focus questions are provided. The unit aims to help students understand that energy exists in different forms, can transfer between objects, and that motion demonstrates the possession of energy. It focuses on sources of different energy forms and how energy transfers. Motion is the first topic as it concretely demonstrates energy, and its concepts aid understanding of waves, sound, and light. The unit utilizes hands-on activities to reinforce concepts and develop student thinking and skills.Light and Shadow



Light and ShadowYoshy Faweta
Ěý
Light travels in straight lines and can be reflected or refracted. There are three types of materials: transparent, translucent, and opaque. Shadows are formed when an object blocks light. The length and shape of a shadow depends on the position of the light source and object. An experiment was conducted to determine which material - transparent plastic, tissue paper, or black paper - makes the darkest shadow. Black paper produced the darkest shadow because it is opaque and does not let any light pass through.şÝşÝߣshare ppt



şÝşÝߣshare pptMandy Suzanne
Ěý
Miss goodheart created a PowerPoint to test out the şÝşÝߣshare tool, which was introduced to her by Sharon Tonner on January 20th, 2011.Similar to Eclipse (20)
pdf_20230618_191133_0000.pdf



pdf_20230618_191133_0000.pdfBrixdavidTumbaga1
Ěý
The document discusses solar and lunar eclipses. It explains that a solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, casting its shadow on parts of Earth. A lunar eclipse happens when Earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon. There are three types of solar eclipses: partial, annular, and total, depending on the alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth. During a solar or lunar eclipse, the moon's shadow on Earth or Earth's shadow on the moon can include the umbra, antumbra, or penumbra regions.ECLIPSES.pptx



ECLIPSES.pptxEDWARDMAYA16
Ěý
An eclipse occurs when one heavenly body passes in front of another, blocking its light. There are two types of eclipses on Earth: solar and lunar. A solar eclipse happens when the moon passes between the earth and sun, casting its shadow on earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon. Eclipses can be partial or total depending on how much of the sun or moon is blocked.SCIENCE-5-WEEK-6-Q4-1.pptx



SCIENCE-5-WEEK-6-Q4-1.pptxSmileyDeSmilling
Ěý
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and was formed from debris after a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized body. It orbits Earth every 27.3 days and rotates at the same rate, so the same side always faces Earth. Its phases are caused by the varying illumination of its surface as it orbits our planet. The Moon causes Earth's tides and has geological features like maria and craters.Eclipses And Tides



Eclipses And Tidesshas595
Ěý
The document discusses different types of eclipses including solar and lunar eclipses. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, blocking the sun from view. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting the moon in earth's shadow. The document provides details on the different types of solar and lunar eclipses as well as explanations for why eclipses do not occur every month and why the moon appears red during a lunar eclipse.Total Eclipse



Total Eclipsesengul1
Ěý
The document discusses solar eclipses, including their cultural significance, types of eclipses, and how to safely observe them. It provides details on total solar eclipses, explaining the geometry of the sun, earth and moon during an eclipse. It also describes a total solar eclipse observed in Turkey on March 29, 2006, noting the path of totality passed through various regions with over 4 minutes of totality in Antalya.Astronomy 1 Ppt



Astronomy 1 Pptshas595
Ěý
The document summarizes key concepts about sunlight and its travel from the sun to earth. It explains that sunlight takes approximately 8 minutes to reach earth from the sun, traveling at 300,000 km per second. It also describes how shadows are formed when light is blocked, and how the earth's rotation causes day and night and influences the seasons.By Sheena MOON-PHASES-AND-ECLIPSE-1.pptx



By Sheena MOON-PHASES-AND-ECLIPSE-1.pptxRogelioSibulan
Ěý
Moon Phases:
The moon's phases refer to the different appearances of the moon as observed from Earth during its orbit around our planet. These phases are primarily determined by the relative positions of the Earth, the moon, and the sun. As the moon orbits the Earth, different portions of its surface are illuminated by sunlight, resulting in the various phases we observe.
1. New Moon:
The new moon occurs when the moon is positioned between the Earth and the sun, with its illuminated side facing away from Earth. From our perspective, the moon appears dark and invisible in the night sky. This marks the beginning of a new lunar cycle.
2. Waxing Crescent:
Following the new moon, a small sliver of the moon becomes visible as sunlight gradually illuminates its surface. This phase is known as the waxing crescent. It appears as a thin crescent shape in the western sky after sunset.
3. First Quarter:
During the first quarter phase, the moon has completed approximately one-quarter of its orbit around the Earth. Half of the moon's surface is illuminated by sunlight, creating a half-moon shape. This phase is often referred to as the waxing half or the half moon.
4. Waxing Gibbous:
As the moon continues to orbit, more of its surface becomes illuminated by sunlight. The waxing gibbous phase occurs when the illuminated portion of the moon is greater than half but not yet full. It appears as a bulging, almost full moon in the night sky.
5. Full Moon:
The full moon occurs when the Earth is positioned directly between the sun and the moon, with the moon's entire illuminated side facing Earth. This phase marks the midpoint of the lunar cycle and is characterized by a fully illuminated, round shape. The full moon is often associated with cultural and religious significance and is the brightest phase of the lunar cycle.
6. Waning Gibbous:
Following the full moon, the moon begins to wane or decrease in illumination. The waning gibbous phase occurs when the illuminated portion of the moon is greater than half but gradually diminishing. It appears as a shrinking, nearly full moon in the night sky.
7. Third Quarter:
During the third quarter phase, the moon has completed approximately three-quarters of its orbit around the Earth. Half of the moon's surface is illuminated, but this time, the opposite half compared to the first quarter phase. It is often referred to as the waning half or the half moon.
8. Waning Crescent:
The waning crescent phase marks the final stage of the lunar cycle before the new moon. Only a small portion of the moon's surface is illuminated by sunlight, appearing as a thin crescent shape in the eastern sky before sunrise. This phase gradually transitions into the new moon, completing the lunar cycle.
These phases repeat in a continuous cycle, with each complete cycle lasting approximately 29.5 days, known as a synodic month. The moon's phases have significant cultural, religious, and scientific importance, The SUN and MOON in GEOGRAPHY 



The SUN and MOON in GEOGRAPHY Lyn Gile Facebook
Ěý
PRESENTED BY: ESTHER BAILON
PRESENTED TO: Ms. JELEN L. DOLOSA
INSTRUCTOR
MULTIMEDIA
PRESENTATION
in
GEOGRAPHY
Revision



RevisionEdTechonGC Mallett
Ěý
The document discusses the relationship between the Earth, moon, and sun. It explains that the Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun cause the seasons to change. As the Earth orbits, different hemispheres are tilted toward or away from the sun, resulting in summer and winter. It also describes how the gravitational pull of the moon causes ocean tides, with the highest tides occurring during full moons and new moons. Additionally, it explains lunar and solar eclipses, noting that a solar eclipse can only occur during a new moon when the moon passes between the Earth and sun.Space sunlight



Space sunlightimadamir
Ěý
Light from the sun reaches Earth in just 8 minutes. It takes over 3,000 hours, or 140 days, to drive to the moon at 70 mph. The earth's rotation causes day and night, and its tilt relative to the sun causes seasons; it is warmer when the sun's rays hit the earth at a more direct angle in summer. Eclipses occur when the moon blocks the sun's light from reaching parts of Earth.D. the moon



D. the moonJan Crisides Corrado
Ěý
There were several theories proposed to explain the origin of the Moon throughout history. The first was the fission theory from the 19th century, which suggested that the Moon formed when a chunk of Earth was pulled away by the Sun's gravity as Earth rapidly spun. Later theories included the capture theory, where the Moon was a wandering planet captured by Earth, and the coaccretion theory where the Moon and Earth formed together from the same material. Currently, the giant impact theory is favored, where a Mars-sized body collided with Earth, ejecting debris that coalesced to form the Moon. This theory best explains the compositional similarities and differences between Earth and the Moon.Ch. 17 l.s. 2



Ch. 17 l.s. 2Jawahir al riyadh int school
Ěý
The document discusses patterns that can be seen in the night sky and provides details about the moon phases and eclipses. It explains that the moon revolves around the Earth and rotates on its axis, causing the shapes and illumination that we see over the course of a month. The phases include the new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent. Eclipses occur when the moon or Earth pass through each other's shadows. There are lunar and solar eclipses. The document also briefly discusses stars and constellations visible in the night sky.Origin of the solar system



Origin of the solar systemjomer09ful
Ěý
The document provides an overview of eclipses, which occur when one astronomical body passes in front of another, temporarily obscuring it from view. It notes that solar eclipses occur when the moon passes between the Earth and sun, while lunar eclipses occur when the moon passes into the Earth's shadow. Eclipses only happen during eclipse seasons when the moon's orbit aligns with the Earth's orbit around the sun. The type of solar eclipse depends on the relative sizes of the sun and moon as seen from Earth.Tapping prior knowledge and building schema on tides and eclipsespdf



Tapping prior knowledge and building schema on tides and eclipsespdfGina Obierna
Ěý
1. Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun on the Earth's oceans, with approximately two high tides and two low tides every 48 hours.
2. Spring tides occur at New and Full Moons, producing very high high tides and low low tides, while neap tides at First and Last Quarters have lower tides.
3. Solar eclipses occur during New Moons when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun, while lunar eclipses happen at Full Moons as the Moon passes through the Earth's shadow.CLASS 5 Moon and Artificial Satellites.pptx



CLASS 5 Moon and Artificial Satellites.pptxNancyNarang2
Ěý
mjhgjhfgnfhgfjgvjhgkjhvgkjgjkfkjfkjfkhffhjfhjfhjgjhgkhgkugkugkhgjkjkhkjhhhhhkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkYear 6 - Eclipses.pptx



Year 6 - Eclipses.pptxNor Amryina Mat Nor
Ěý
There are two types of eclipses: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and sun, blocking the sun's light. A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and moon, casting its shadow on the moon. Both occur when the three celestial bodies are aligned in a straight line. A solar eclipse can last only a few minutes, while a lunar eclipse can last for several hours. Total eclipses block the entire sun or moon, while partial eclipses only block part of the sun or moon.The moon and tides



The moon and tidesNicole Cammylle Beltran
Ěý
The document discusses various lunar phenomena such as micro moons, blue moons, blood moons, eclipses, and tides. A micro moon occurs when the full moon coincides with the moon's farthest point from Earth. There are three types of lunar eclipses defined as penumbral, partial, and total. Eclipses happen when the sun, moon, and Earth are aligned. Tides are influenced by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, and there are two types of tides called spring tides and neap tides.Eclips es 2010 rvf



Eclips es 2010 rvfRory Van Fossen
Ěý
Eclipses occur when one celestial body blocks the sunlight from reaching another. A solar eclipse happens during a new moon when the moon passes between the earth and sun, casting its shadow on earth. A lunar eclipse occurs during a full moon when the earth blocks the sunlight from reaching the moon, casting its shadow on the moon. Eclipses only occur when the sun, moon, and earth are precisely aligned in a straight line, which does not happen every month due to the tilt of the moon's orbit.Eclipse 5



Eclipse 5sarslan
Ěý
- Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow on Earth's surface.
- Eclipses can be partial, total, or annular depending on the Moon's alignment with the Sun and Earth. A total solar eclipse can only be seen within the narrow path of the Moon's umbral shadow.
- While eclipses are now understood scientifically, many ancient cultures viewed solar eclipses as ominous events, believing they disrupted the natural order. Some people still react fearfully during an eclipse today.COT 2.pptx



COT 2.pptxApril Rose Garcia
Ěý
The document discusses different types of eclipses. It explains that a solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun, casting its shadow on Earth. There are three types of solar eclipses: total, annular, and partial. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through Earth's shadow. The moon's shadow consists of the umbra, where the sun is completely covered, the penumbra where it is only partially covered, and the antumbra. Students are assigned group projects to diagram and present the alignments of celestial bodies during eclipses, compare solar and lunar eclipses, and provide safety guidelines for viewing a solar eclipse.Eclipse
- 1. Eclipse
- 2. Celestial bodies in space such as the moon and Earth cast shadows. They casts shadow because the are opaque bodies. Earth and the moon cast conelike shadows. This occurrence is observed from the Earth as an Eclipse .
- 3. Why Are There Eclipses? Both the moon and the Earth do not produce their own light. They borrow their light from the sun. Being both opaque, they do not allow light to pass through.
- 4. When the moon, the earth, and the sun are in one straight line, shadow may fall on either the moon or the Earth. An eclipse occurs when a celestial body blocks light from reaching another celestial body.
- 6. Lunar Eclipse During the full moon, the Earth is between the sun and the moon. When the sun shines on the side of the Earth, the light does not pass through. The shadow of the Earth is formed. The Earth’s shadow may fall on the face of the moon.
- 7. When the face of the moon is covered with the Earth’s shadow, the moon cannot reflect the sun’s light. It will be dark even during full moon. This is Lunar Eclipse. A lunar eclipse may be partial or total.
- 9. If the moon is in the dark part of Earth’s shadow (umbra), there is a total lunar eclipse . If it is in the light part of the shadow (penumbra) there is a partial lunar eclipse . A total lunar eclipse can last for more than an hour
- 10. Solar Eclipse During the new moon, the moon is between the sun and the Earth. The moon passes over the same place twice a day, one at night one during the day, because the Earth rotate.
- 11. If the moon passes over the Earth as the sun shines on one side of the Earth, the moon blocs the sunlight and a shadow of the moon is formed. This shadow falls on the surface of the Earth. The part of the earth that receives this shadow of the moon will be darkened. The people will experience darkness (like night) even during daytime. This is called solar eclipse.
- 12. Solar Eclipse
- 13. Total Solar Eclipse During a solar eclipse, the moon moves between the sun and the earth. The light from the outer part of the sun’s atmosphere, called the corona, became visible during a total solar eclipse on July 11, 1991, in La Paz, Baja California, Mexico. The moon’s shadow on earth appeared only as a thin band not more than 269 km (167 mi) wide.
- 14. During a solar eclipse, the moon casts shadow of the earth, with a dark region called umbra and the lighter region called penumbra. If the Earth is inside the umbra, Earth experience a total solar eclipse. If the earth is inside the penumbra, it will experience only a partial solar eclipse.
- 15. Ěý
- 16. An annular eclipse occurs when the tip o the umbra does not reach the earth. You can only see a bright ring around the sun, which is called an annulus . This only happens in an eclipse of the sun, never in an eclipse of the moon.
- 17. Ěý
- 18. Why a Total Solar Eclipse Seldom Happens? There are two reasons for this. First, the moon’s orbit is tilted five degrees to Earth’s orbit. Second, the moon is so small that its dark shadow can barely touch the earth’s surface.
- 19. During a total solar eclipse, a small place can be totally dark, like nighttime. The longest may be seven and a half minutes. But this darkness is confined only to a small place, the place where the dark shadow if the moon falls. The other places are bright and sunny.
- 20. Ěý
