Economic analysis
- 1. ECONOMIC ANALYSIS - Cost Benefit Analysis - Cost Efficiency Analysis Presented By: Sujan Poudel MPH 2nd Sem, Nobel College
- 2. Cost Benefit Analysis • Cost Benefit analysis is used when a company wants to know the economic worth of a project or some type of investment. • This is accomplished by understanding the cost of the project and investment and making a comparison with benefits. • Both the costs and benefits are expressed in terms of a monetary value. • When the benefit are greater than the costs the investment or project is said to be worth pursuing.. 2
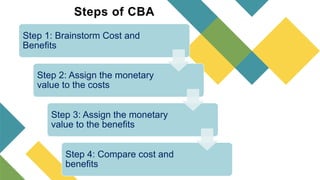
- 3. “ Step 1: Brainstorm Cost and Benefits Step 2: Assign the monetary value to the costs Step 3: Assign the monetary value to the benefits Step 4: Compare cost and benefits Steps of CBA
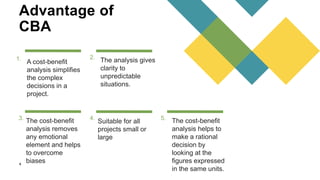
- 4. Advantage of CBA 1. A cost-benefit analysis simplifies the complex decisions in a project. 2. The analysis gives clarity to unpredictable situations. 3. The cost-benefit analysis removes any emotional element and helps to overcome biases 4. Suitable for all projects small or large 5. The cost-benefit analysis helps to make a rational decision by looking at the figures expressed in the same units. 4
- 5. Disadvantages of CBA 1. Potential Inaccuracies in Identifying and Quantifying Costs and Benefits 2. Increased Subjectivity for Intangible Costs and Benefits 3. Inaccurate Calculations of Present Value Resulting in Misleading Analyses 4. A Cost Benefit Analysis Might Turn in to a Project Budget 5
- 6. Cost Efficiency Analysis • The actual meaning of cost efficiency is minimum cost to produce maximum output • It ensure that profit are substantial enough by deciding the best way to bring with the least amount of financial investment. • Mainly used by firms to measure the worth cost and benefit of project investment. • Cost efficiency are of two types: • Cost benefit • cost effectiveness 6
- 7. Cost efficiency Vs Cost Effectiveness Cost Efficiency Analysis  Output  Cost Efficiency Analysis compares the costs of a program to the outputs it achieved (e.g. cost per latrine constructed, or cost per parental counseling), Cost Effectiveness Analysis  Outcome  Cost Effectiveness Analysis compares the costs of a program to the outcomes it achieved (e.g. cost per diarrheal incident avoided, cost per reduction in intra-family violence). Related but not same in all the circumstances 7
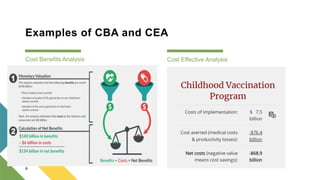
- 8. Examples of CBA and CEA Cost Benefits Analysis Cost Effective Analysis 8
- 9. Summary • Both Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) and Cost Efficiency Analysis (CEA) include health outcomes. However, CBA places a monetary value on health outcomes so that both costs and benefits are in monetary units. • CEA deals with performing or functioning in the best possible manner with the least waste of money, time and effort. 9
- 10. References • https://www.jaggaer.com/blog/what-cost- efficiency/#:~:text=Efficient%20(adj.),the%20best%20use%20of%20resource s. • https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/cost-benefit-analysis-for-projects-a- step-by-step-guide • https://www.cdc.gov/policy/polaris/economics/cost-effectiveness/index.html 10
- 11. Thank you !!! Sujan Poudel poudelsujan15@gmail.com
Editor's Notes
- Costs Direct costs Indirect costs Intangible costs Opportunity costs Costs of potential risks Benefits Direct Indirect Total benefits Net benefits
- Output- services produced in a specific time period Outcome: Consequences