EDLC-EMBEDDED PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE
- 2. ’āś Introduction ’āś What is EDLC ’āś Why EDLC ’āś Objectives of EDLC ’āś Different phases of EDLC ’āś EDLC approaches ’āś References
- 3. Software development company - SDLC Product development company - EDLC Example ŌĆō Preparation of any food dish ’āś Dish selection and Ingredient list ’āś Procurement of the items in the list ’āś Preparation and initial taste testing ’āś Serving and final taste testing Embedded Product development view ’āś Father - Overall management ’āś Mother - Developing and testing ’āś We - End user /client
- 4. ’āś EDLC is an Analysis-Design-Implementation based problem solving approach for the product development. ’é¦Analysis ŌĆō What product need to be developed ’é¦Design ŌĆō Good approach for building it ’é¦Implementation ŌĆō To develop it
- 5. ’āś Essential in understanding the scope and complexities involved in any Embedded product development. ’āś Defines interaction and activities among Various groups of product development sector. ’āś Project management ’āś System design and development ’āś System testing ’āś Release management and quality assurance
- 6. ’āś Aim of any product development is the Marginal benefit ’āś Marginal benefit = Return on investment ’āś Product needs to be acceptable by the end user i.e. it has to meet the requirements of the end user in terms of quality, reliability & functionality. ’āś EDLC helps in ensuring all these requirements by following three objective ’āś Ensuring that high quality products are delivered to user ’āś Risk minimization and defect prevention in product development through project management ’āś Maximize productivity
- 7. ’āś The primary definition of quality in any embedded product development is return on investment achieved by the product. ’āś In order to survive in market, quality is very important factor to be taken care of while developing the product. ’āś Qualitative attributes depends on the budget of the product so budget allocation is very important. ’āś Budget allocation might have done after studying the market, trends & requirements of product, competition .etc.
- 8. ’āś Project management (PM) ’āś Adds an extra cost on budget ’āś But essential for ensuring the development process is going in right direction ’āś Projects in EDLC requires Loose project management or tight project management. ’āś PM is required for ’āś Predictability ’āś Analyze the time to finish the product (PDS = no of person days ) ’āś Co-ordination ’āś Resources (developers) needed to do the job ’āś Risk management ’āś Backup of resources to overcome critical situation ’āś Ensuring defective product is not developed
- 9. ’āś Measure of efficiency as well as ROI Different ways to improve the productivity are ’āś Saving the manpower ’āś X members ŌĆō X period ’āś X/2 members ŌĆō X period ’āś Use of automated tools where ever is required ’āś Re-usable effort ŌĆō work which has been done for the previous product can be used if similarities present b/w previous and present product. ’āś Use of resources with specific set of skills which exactly matches the requirements of the product, which reduces the time in training the resource
- 10. ’āś A life cycle of product development is commonly referred as the ŌĆ£modelŌĆØ ’āś A simple model contains five phases ’āś Requirement analysis ’āś Design ’āś Development and test ’āś Deployment and maintenance ’āś The no of phases involved in EDLC model depends on the complexity of the product Classic Embedded product development life cycle model
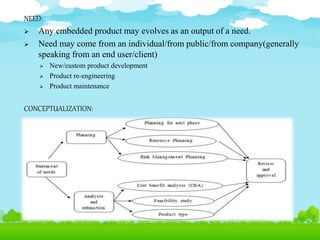
- 11. NEED: ’āś Any embedded product may evolves as an output of a need. ’āś Need may come from an individual/from public/from company(generally speaking from an end user/client) ’āś New/custom product development ’āś Product re-engineering ’āś Product maintenance CONCEPTUALIZATION:
- 12. ANALYSIS: Analyze and document functional and non-functional requirements Interface definition and documentation Define test plan and procedure Requirement specification document Document review Rework on requirements and documents
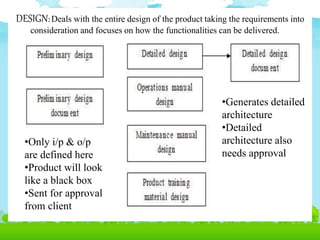
- 13. DESIGN:Deals with the entire design of the product taking the requirements into consideration and focuses on how the functionalities can be delivered. ŌĆóOnly i/p & o/p are defined here ŌĆóProduct will look like a black box ŌĆóSent for approval from client ŌĆóGenerates detailed architecture ŌĆóDetailed architecture also needs approval
- 14. DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING: ’āś Development phase transforms the design into realizable product ’āś Design is transformed into hardware and firmware ’āś Look and feel of the device is very important Testing phase can be divided into ’āś Unit testing ŌĆō independent testing of hardware and firmware ’āś Integration testing ŌĆō testing after integrating hardware and firmware ’āś System testing ŌĆō testing of whole system on functionality and non-functionality basis ’āś User acceptance testing ŌĆō testing of the product against the criteria mentioned by the end-user/client ’āś Test reports
- 15. DEPLOYMENT: ’āś A process of launching fully functional model into the market SUPPORT: ’āś Deals with the operation and maintenance of the product ’āś Support should be provide to the end user/client to fix the bugs of the product UPGRADES: ’āś Releasing of new version for the product which is already exists in the market ’āś Releasing of major bug fixes. RETIREMENT/DISPOSAL: ’āś Everything changes, the technology you feel as the most advanced and best today may not be the same tomorrow ’āś Due to this the product cannot sustain in the market for long ’āś It has to be disposed on right time before it causes the loss.
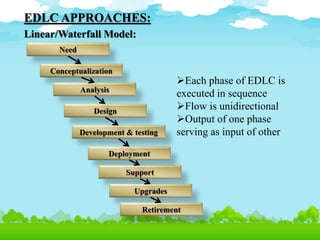
- 16. EDLC APPROACHES: Linear/Waterfall Model: Conceptualization Need Analysis Design Development & testing Deployment Support Upgrades Retirement ’āśEach phase of EDLC is executed in sequence ’āśFlow is unidirectional ’āśOutput of one phase serving as input of other
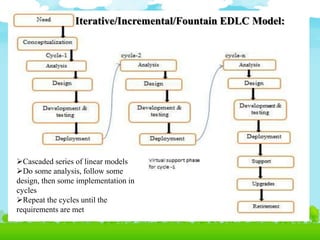
- 17. Iterative/Incremental/Fountain EDLC Model: ’āśCascaded series of linear models ’āśDo some analysis, follow some design, then some implementation in cycles ’āśRepeat the cycles until the requirements are met
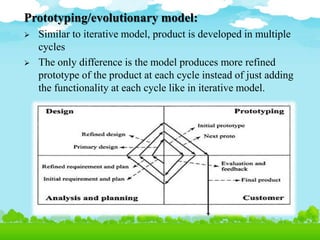
- 18. Prototyping/evolutionary model: ’āś Similar to iterative model, product is developed in multiple cycles ’āś The only difference is the model produces more refined prototype of the product at each cycle instead of just adding the functionality at each cycle like in iterative model.
- 19. Spiral model: ’āś Spiral model is best suited for the development of complex embedded products and situations where the requirements are changing from customer side. ’āś Risk evaluation in each stage helps in reducing risk
- 20. Conclusion In order to make best profit out of product what you do, development life cycle is very important. To build a reliable product, of best quality, functionality and to release your product in right time. EDLC will make things easy for sure!!.
- 21. REFERENCES: ’āś Introduction to Embedded System by Shibu K.V ’āś http://www.luxoft.com/embedded-systems- development/product-life-cycle/ ’āś http://geny-agile.blogspot.in/2010/09/product-development- life-cycle-of.html