Effective thinking
- 3. These words of the Philosopher Rene Descartes illustrate the importance of thinking. We exist because we think.
- 4. ’é© Thinking may be described as mental processing of information. ’é© Thinking is done voluntarily or involuntarily. ’é© Thinking may be in forms of fantasizing, daydreaming, reasoning and problem-solving. ’é© Systemic thinking acts as a filter & helps in separating the important from the unimportant.
- 5. According to Psychologist Robert Sternberg, people acquire their thinking styles through socialization. However, it is also possible to teach thinking styles.
- 6. SternbergŌĆÖs conceptions of thinking style are based on following hypothesis: 1) Thinking styles are preferences in the use of abilities, & not the abilities themselves. 2) A match between styles & abilities creates a synergy which is more than mere sum of its parts. 3) The life choices we make should fit styles as well as abilities. 4) People have profiles of styles, not just a single style.
- 7. 5) Styles vary across tasks, situations as well as across the life span. 6) People differ in the strength of their preferences and in their stylistic flexibility. 7) Styles are socialized, measurable & teachable. 8) The value of styles may change. 9) Styles are not good or bad ŌĆō itŌĆÖs a question of suitability
- 9. Our thinking styles help us to carry out three functions. 1) Legislative Style: ’é© People with legislative style of thinking like doing things their own way. ’é© The legislative style of thinking favors creativity. ’é© Individuals with this style like activities such as creative writing, inventing new things, starting new businesses, etc.
- 10. 2) Executive Thinking ’é¦ Here people prefer the need of guidelines that WHAT to do and HOW to do. ’é¦ This type of thinking is valued in schools and organizations. ’é¦ Individuals with this style like activities such as solving well- defined mathematical problem, applying rules, giving lessons on others peopleŌĆÖs ideas, etc.
- 11. 3) Judicial Thinking:- ’é¦ This type of thinking prefers evaluating rules & procedures & judging situations. They favor problems which can be analyzed & evaluated. ’é¦ This style of thinking is often not given importance it deserves. ’é¦ Individuals with this style like activities such as giving opinions, writing critiques, judging people and their work, etc.
- 13. Sternberg also distinguished between four different forms of thinking styles & they are :- 1) Monarchic Form, 2) Hierarchic Form, 3) Oligarchic Form, 4) Anarchic Form.
- 15. Sternberg identified 2 levels thinking Styles :- 1.Global thinking Styles 2.Local thinking Styles
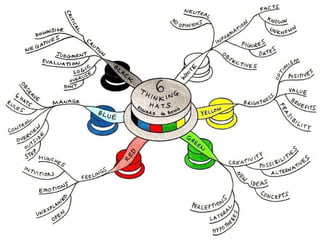
- 18. ’ā╝ The de Bono Hats system (also known as "Six Hats" or "Six Thinking Hats") is a thinking tool for group discussion and individual thinking. Combined with the idea of parallel thinking which is associated with it, it provides a means for groups to think together more effectively, and a means to plan thinking processes in a detailed and cohesive way. The method is attributed to Dr. Edward de Bono and is the subject of his book, Six Thinking Hats.
- 19. 1)Information: (White) - considering purely what information is available, what are the facts? 2)Emotions (Red) - instinctive gut reaction or statements of emotional feeling (but not any justification) 3)Bad points judgment (Black) - logic applied to identifying flaws or barriers, seeking mismatch 4)Good points judgment (Yellow) - logic applied to identifying benefits, seeking harmony 5)Creativity (Green) - statements of provocation and investigation, seeing where a thought goes 6)Thinking (Blue) - thinking about thinking