Efficiency and equity
- 2. Self Interest, Social Interest ÔÇõ Make a choice to get out most of scarce resources ÔÇõ Social Interest has two dimensions Efficiency Fairess
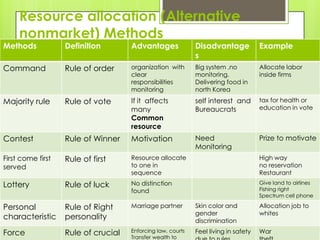
- 3. Resource allocation (Alternative nonmarket) Methods Methods Definition Advantages Disadvantage Example s Command Rule of order organization with Big system ,no Allocate labor clear monitoring. inside firms responsibilities Delivering food in monitoring north Korea Majority rule Rule of vote If it affects self interest and tax for health or many Bureaucrats education in vote Common resource Contest Rule of Winner Motivation Need Prize to motivate Monitoring First come first Rule of first Resource allocate High way served to one in no reservation sequence Restaurant Lottery Rule of luck No distinction Give land to airlines Fishing right found Spectrum cell phone Personal Rule of Right Marriage partner Skin color and Allocation job to gender whites characteristic personality discrimination Force Rule of crucial Enforcing law, courts Transfer wealth to Feel living in safety War
- 4. Demand and Marginal Benefit  Demand= Value the seller get=Price the buyer pay=Marginal benefit  D=MB  ∑(individual demand)=Social demand market demand curve=economy’s marginal benefit curve MSB=Market Demand Price=#of $ you pay to lose other goods or services to obtain this good or service
- 5. Consumer Surplus Value or Marginal benefit of good minus the price paid ,summed over quan
- 6. Supply and Marginal Cost  Supply=Marginal cost=Minimum supply price  S=MC  ∑(individual Supply)=Market demand market supply curve=economy’s marginal social cost curve MSC=Market Supply
- 7. Producer Surplus Price received minus its minimum supply price or marginal cost, summed over q
- 10. Efficiency and invisible hand
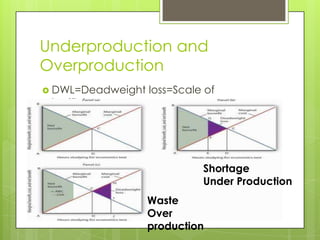
- 11. Underproduction and Overproduction ÔÇõ DWL=Deadweight loss=Scale of inefficiency: Inefficiency in production decrease the surplus Shortage Under Production Waste Over production
- 12. Obstacle to Efficiency Market Failure Cause Underproduction or Shortage and Overproduction or Waste: ÔÇõ Price and Quantity regulation ÔÇõ Taxes and subsidies ÔÇõ Externalities ÔÇõ Public goods and Common resources ÔÇõ Monopoly ÔÇõ High Transaction Costs
- 13. method Price and Limitation By Underproducti Minimum Wage regulation Rent Cap, ceiling Quantity on Limit permission of regulation Production Tax Increase the price Underproducti to pay decrease the price to on receive subsidies Decrease the Underproducti Government price to pay payment to ,increase the price on producers to receive Cost for other than Overproductio Contamination, buyer and seller phone in public n Externalities Benefit for other Underproducti Smoke detector, than buyer or seller on Public good Consumer same Underproducti National defense, time no pay Law enforcement Free_RIDER on common No owner, everyone use and put the cost Overproductio Atlantic Salmon Majority rule resources on others n Tragedy of Commons Monopoly Sole provider of a Underproducti good ,price maker on
- 14. ÔÇõ Under Production cause: 1. Long line or Queue 2. Wasting time 3. Black Market 4. rubbery ÔÇõ Over production cause: 1. Waste 2. Destruction 3. Illnesses
- 15. Fairness of Market ÔÇõ Victim of natural disaster ÔÇõ Low skilled workers under living wage ÔÇõ Principals of fairness is universally vague ÔÇõ Make the economic pie greater in lowest cost ÔÇõ No equity
- 16. Games have rules and result Utilitarian Same desire and capacity Fair result The wealthier the lesser MB Economy as a game Both better off The big tradeoff …Symmetry Fair rules Principal
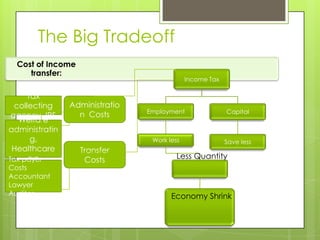
- 17. The Big Tradeoff Cost of Income transfer: Income Tax Tax collecting Administratio Employment Capital agency, IRS n Costs Welfare administratin g, Work less Save less Healthcare Transfer sys Tax payer Costs Less Quantity Costs Accountant Lawyer Auditor Economy Shrink
- 18. Modified version of Utilitarian ÔÇõ Theory of Justice : 1. Lowe tax 2. Consider all transfer and administration cost Symmetry Principal: 1. Behave toward others same as you expect them behave toward you (religion) 2. Equality in opportunity (economy) Nozick Principals 1.Protect Private Property by enforcing law =every thing has an owner, theft is prevented ,strong will not prevail 2.Private Property can only exchange voluntary=no theft
- 19. ÔÇõ In Competitive Market, respect to private property right and voluntary exchange without 6 obstacle, resources would be fair and efficient.