Electrostatics(Elecro-magnetic field)
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes188 views
1. Electrostatics describes static electricity and the forces between electric charges at rest. 2. Electric charge is a fundamental property that comes in discrete quantities and is conserved, meaning it can be transferred but not created or destroyed. 3. There are several ways charges can be transferred, including through friction, conduction, or induction. Rubbing materials like silk and glass leads to a transfer of electrons that leaves one material positively charged and the other negatively charged.
1 of 18
Download to read offline

















Recommended
Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
The document defines static electricity as the imbalance of positive and negative charges that occurs when electrons are transferred between objects by rubbing them together. It distinguishes static electricity from current electricity by describing how static charges do not involve a continuous flow of electrons. The document also defines conductors as materials that allow electrons to move freely, creating static shocks, while insulators do not allow electron movement.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
The document discusses static electricity and current electricity. It provides an agenda for a lesson that includes discussing the difference between static and current electricity. It defines static electricity as the imbalance and buildup of electric charges on objects at rest, whereas current electricity involves the flow of electric charges. It describes how rubbing objects can cause the transfer of electrons and creation of static charges.electrostatics;part 1 by vandana mishra



electrostatics;part 1 by vandana mishravandanamishra46
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation discusses electricity and covers several topics:
- The discovery of static electricity by Thales of Miletus in 600 BC and the naming of positive and negative charges by Benjamin Franklin.
- The historical treatment of electricity and magnetism as separate subjects and the later theory of electromagnetism by Lorentz.
- The definitions and key differences between charge, mass, electrostatics, and electrodynamics.
- Examples of charging by induction versus contact and the quantization of electric charge on macroscopic versus microscopic scales.
- Numerical problems involving calculating total charge on a system and the net charge on a metal sphere after removing electrons.
- Recommendations for additional learning resources on electricity including onlineStatic Electricity



Static ElectricityShafie Sofian
Ěý
1. Charging by friction is demonstrated using a plastic straw and tissue paper. Rubbing the straw with tissue gives it a static charge, causing small bits of paper to be attracted.
2. There are two types of electrical charges: positive and negative. Charge is measured in coulombs. Unlike charges attract and like charges repel according to Coulomb's law.
3. An electric field is a region where an electric charge would experience force. It is represented by electric field lines originating from positive charges and terminating on negative charges.Static Electricity



Static ElectricityTerri
Ěý
The document discusses static electricity and Coulomb's law. It explains that Benjamin Franklin established the convention of calling the two types of electric charges "positive" and "negative". It also explains that Coulomb's law states that the electric force between two point charges depends on the magnitudes of the charges and the distance between them, and is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance. The document provides an example calculation of the electric force between two charges using Coulomb's law.Electrostatics



Electrostaticsfourangela
Ěý
1. Electrostatics involves electric charges at rest, which arise from the particles that make up atoms. Atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons, giving them a net neutral charge.
2. Objects can become charged through friction, induction, or conduction. Friction charging involves the transfer of electrons between two objects in contact. Induction charging uses a charged object to polarize a neutral object without direct contact.
3. The amount and type of charge on an object depends on whether it has an excess or deficit of electrons compared to protons. Coulomb's law describes the relationship between charged objects based on their relative charges and distance.Electric charge and static electricity fisica



Electric charge and static electricity fisicaLucii Artigas Viramontt
Ěý
Electric charge is a property that causes subatomic particles like protons and electrons to attract or repel each other. A net electric charge is produced by an excess or shortage of electrons, and electric forces are the attraction or repulsion between charged objects. Static electricity refers to the transfer of electric charge through friction, contact, or induction, which can cause hair to stand up or sparks to fly.electric potential



electric potentialSHIVAMPILANIA
Ěý
The document discusses electric charge and its properties. It states that electric charge is an intrinsic property of protons and electrons, with protons having a positive charge and electrons having a negative charge. The magnitude of the charge on a proton equals the magnitude of the charge on an electron. Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract. Charge is quantized and can only occur in integer multiples of the elementary charge e. The document also discusses how objects can become charged through rubbing, contact, or induction, and introduces Coulomb's law which describes the electric force between two point charges.Electric charge



Electric chargeVeena Vs
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of electricity and electric charge. It describes how Greeks first discovered the attractive properties of amber in 600 BC and key discoveries throughout history that helped define positive and negative electric charge. The document explains how rubbing certain materials like glass and silk can cause the transfer of electrons, leaving one material with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit. It summarizes that electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that can be either positive or negative, and like charges repel while opposite charges attract.Exp SPA - Chp 16 Static Electricity



Exp SPA - Chp 16 Static Electricityharrywwh
Ěý
The document discusses static electricity and electrostatics. It explains that:
- Charged objects can be charged through friction or induction. Friction charging involves the transfer of electrons, while induction charging uses the redistribution of existing electrons in a conductor.
- Like charges repel and unlike charges attract, following Coulomb's law. The direction and strength of electric fields can be represented by field lines.
- Applications include photocopiers, which use photoconductivity and electrostatic attraction/repulsion to transfer toner images to paper. Hazards include lightning and electrostatic discharge damaging electronics.Static electricity U6L2 Notes



Static electricity U6L2 NotesGena Barnhardt
Ěý
Static electricity is the build-up of electric charge on an object. It occurs when electrons are transferred from one object to another, leaving an imbalance of charges. This can cause sparks or shocks when charges are equalized. Static cling and lightning are both examples of static electricity. Safety tips to prevent shocks or fires from static electricity include grounding oneself before pumping gas and staying inside during thunderstorms.Static electricity



Static electricityVIGYANPRASAR
Ěý
Static electricity occurs when there is a build up of electric charge on the surface of a material without the flow of electric current. It results from the transfer of electrons between two materials during friction like rubbing a balloon on hair. This can cause attraction between materials with opposite charges like a negatively charged balloon and positively charged hair. Common examples are rubbing a plastic ruler to attract paper or walking on carpet and touching a doorknob to discharge. Different materials have different tendencies to gain or lose electrons through friction based on their electron affinity.Electrostatics



ElectrostaticsSeyid Kadher
Ěý
1. The document discusses electrostatic force and electric charge. It explains that when certain materials are rubbed together, they acquire a property called electricity that allows them to attract small pieces of paper.
2. Electric charge is a property of objects that causes electrical and electromagnetic effects. Charge can be positive, negative, or neutral. Charge is quantized and can only occur in discrete integer multiples of the elementary charge.
3. An electric field is the region of space around a charged object where other charged objects will feel an electrostatic force. The electric field strength is defined as the force on a small test charge placed in the field.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of positive or negative charges on the surface of objects, caused by electrons moving between objects during physical contact like rubbing. It differs from current electricity which involves the controlled flow of electrons through conductors. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Static charges are created by the imbalance and redistribution of electrons on and between objects, and can cause static shocks when excess electrons jump between two charged objects and their charges equalize.1 ELECTROSTATICS



1 ELECTROSTATICSSheeba vinilan
Ěý
This document discusses the fundamental concepts of electromagnetism. It explains that electromagnetism underlies most of the forces we experience in everyday life, with the exception of gravity. Examples given include pushing an object, standing on the Earth's surface, and static/kinetic friction. The document then provides a brief history of the discovery of electromagnetism dating back to Thales' observation of static electricity in amber. It defines key terms like electrification and static electricity. Finally, it outlines some basic properties of electric charges like the constant total charge in the universe and quantization of charge in integer multiples of the elementary charge.Static electricity



Static electricityTekZeno
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on the surface of objects. It was discovered in 600 BC by Thales of Miletos who observed that rubbing amber with fur caused the amber to attract feathers due to static charge. Benjamin Franklin's kite experiment in the 1740s demonstrated that lightning is a form of electricity. Static charge is generated through friction, conduction, or induction. Objects can become positively or negatively charged by gaining or losing electrons. Coulomb's Law from 1785 describes the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges, directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.4 intro electrostatics



4 intro electrostaticsCyrus Trance
Ěý
Benjamin Franklin conducted experiments with electricity in the 1700s using simple apparatus. Through his experiments, he developed the concepts of positive and negative charges and proposed demonstrating the connection between lightning and electricity by flying a kite during a storm. In 1752, Franklin performed his famous kite experiment during a storm and was able to draw sparks from a key attached to the kite string, providing evidence that lightning is a form of electricity. Franklin's experiments made him famous and helped establish the field of electrostatics.Unit 1 Static Electricity



Unit 1 Static ElectricityBruce Coulter
Ěý
The document summarizes static electricity and different models that were proposed to explain it. It discusses the two-fluid model proposed by Charles Dufay involving vitreous and resinous fluids. It then discusses Benjamin Franklin's one-fluid model involving positive and negative charges. Finally, it introduces the modern particle model involving electrons, protons and neutrons to explain how objects become charged through the gain or loss of electrons.Introduction to Electrostatics



Introduction to ElectrostaticsNatasia Gouws
Ěý
This document discusses how objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons, and defines positive and negative charges. It explains that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Methods for charging objects include friction, touch, and induction. The key rules are that charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred, and that when two charged objects touch, their total charge is distributed equally between them. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the new charges and number of electrons transferred when two charged spheres touch.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
This document defines static electricity and current electricity. It explains that static electricity is caused by an imbalance of electric charges, usually through rubbing materials together, while current electricity involves the controlled flow of electrons. It distinguishes conductors that allow electron flow from insulators that do not, and describes how static charges build up and arc in lightning.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is caused by an imbalance of electric charges, usually between electrons and protons. It occurs when two objects are rubbed together, causing electrons to transfer between them leaving one object positively charged and one negatively charged. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Current electricity differs in that it involves the controlled, one-directional flow of electrons through conductors, powered by an external voltage source.Electricity



ElectricityPaul Comitz
Ěý
This document outlines the agenda and content for Module 4 of a physics course on electromagnetism. The module will cover electric charge, Coulomb's law, the electric field, Ohm's law, and include labs on electricity and electromagnetism. Key concepts that will be discussed include the relationship between positive and negative charges, Coulomb's inverse square law relating electric force to charge and distance, electric fields and potential differences, and Ohm's law relating voltage, current, and resistance in circuits.Electrostatics 



Electrostatics Shriyesh Gautam
Ěý
Electrostatics covers the properties of electric charges, electrostatic force, and electric fields. Key points include:
- There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
- Charge is quantized and conserved. It exists in integer multiples of the fundamental unit, e.
- Coulomb's law describes the electrostatic force between two point charges. The force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Electric fields are vector fields that exist around charged objects. The electric field strength is defined as the force per unit charge. Field lines are used to represent electric fields graphically.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of positive or negative charges on the surface of objects, caused by electrons moving between objects during physical contact like rubbing. It differs from current electricity which involves the controlled flow of electrons through conductors. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Static charges are created by the imbalance and redistribution of electrons on and between objects, and can cause static shocks when excess electrons jump between two charged objects and their charges equalize.Lesson 1_electrostatics_12



Lesson 1_electrostatics_12sujameryll
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the basics of electrostatics, including that static electricity occurs when charges build up on the surface of materials without moving, and that rubbing certain materials like polythene and perspex with cloth results in one becoming negatively charged and the other positively charged due to the transfer of electrons. It also explains that a rubbed balloon sticks to the ceiling due to opposite charges attracting, with the balloon becoming negatively charged and repelling electrons in the wall, leaving it positively charged.Static Electricity



Static ElectricityOhMiss
Ěý
Static electricity occurs when objects become electrically charged through the transfer of electrons. Charging occurs when two materials are rubbed together, causing electrons to move from one material to the other. This leaves one material with an excess of electrons and a negative charge, and the other material with a deficit of electrons and a positive charge. The electric charges remain on the surface of the objects until they are given a path to ground or neutralize each other through contact or discharge.Charge and Its Property



Charge and Its PropertyAnkur Patel
Ěý
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes electromagnetic attraction and repulsion. The electric charge is quantized, meaning it occurs in discrete integer multiples of the elementary charge carried by a single electron or proton. Robert Millikan's oil drop experiment directly demonstrated the quantization of charge by measuring the electric charges on tiny oil droplets, finding they were always integer multiples of approximately 1.6Ă—10^-19 coulombs. Coulomb's law describes the electric force between two charged particles, stating it is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.Electric charge



Electric chargeVeena Vs
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of electricity and electric charge. It traces the key discoveries around electricity from ancient Greeks observing amber's attractive properties when rubbed in 600 BC to J.J. Thompson's discovery of the electron in 1890. When certain materials like glass are rubbed against other materials like silk, electrons are transferred, leaving one material with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract based on the inverse square law discovered by Coulomb in 1770. Electric charge is quantized and comes in positive or negative units of the elementary charge of an electron.electrostatics_and_history.ppt



electrostatics_and_history.pptTwinkleStar53
Ěý
Electrostatics is the study of stationary electric charges and the forces between them. Key discoveries include:
- Otto van Guericke invented the first electric generator using friction in 1663.
- Stephen Gray discovered electricity can flow through wires in 1729, leading to telegraphs.
- E.G. von Kleist and Pieter van Musschenbroek independently discovered the Leyden jar capacitor in the mid-1700s.
- Benjamin Franklin proposed the theory of one electric fluid (electricity) and that oppositely charged objects attract in the 1700s.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Electric charge



Electric chargeVeena Vs
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of electricity and electric charge. It describes how Greeks first discovered the attractive properties of amber in 600 BC and key discoveries throughout history that helped define positive and negative electric charge. The document explains how rubbing certain materials like glass and silk can cause the transfer of electrons, leaving one material with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit. It summarizes that electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that can be either positive or negative, and like charges repel while opposite charges attract.Exp SPA - Chp 16 Static Electricity



Exp SPA - Chp 16 Static Electricityharrywwh
Ěý
The document discusses static electricity and electrostatics. It explains that:
- Charged objects can be charged through friction or induction. Friction charging involves the transfer of electrons, while induction charging uses the redistribution of existing electrons in a conductor.
- Like charges repel and unlike charges attract, following Coulomb's law. The direction and strength of electric fields can be represented by field lines.
- Applications include photocopiers, which use photoconductivity and electrostatic attraction/repulsion to transfer toner images to paper. Hazards include lightning and electrostatic discharge damaging electronics.Static electricity U6L2 Notes



Static electricity U6L2 NotesGena Barnhardt
Ěý
Static electricity is the build-up of electric charge on an object. It occurs when electrons are transferred from one object to another, leaving an imbalance of charges. This can cause sparks or shocks when charges are equalized. Static cling and lightning are both examples of static electricity. Safety tips to prevent shocks or fires from static electricity include grounding oneself before pumping gas and staying inside during thunderstorms.Static electricity



Static electricityVIGYANPRASAR
Ěý
Static electricity occurs when there is a build up of electric charge on the surface of a material without the flow of electric current. It results from the transfer of electrons between two materials during friction like rubbing a balloon on hair. This can cause attraction between materials with opposite charges like a negatively charged balloon and positively charged hair. Common examples are rubbing a plastic ruler to attract paper or walking on carpet and touching a doorknob to discharge. Different materials have different tendencies to gain or lose electrons through friction based on their electron affinity.Electrostatics



ElectrostaticsSeyid Kadher
Ěý
1. The document discusses electrostatic force and electric charge. It explains that when certain materials are rubbed together, they acquire a property called electricity that allows them to attract small pieces of paper.
2. Electric charge is a property of objects that causes electrical and electromagnetic effects. Charge can be positive, negative, or neutral. Charge is quantized and can only occur in discrete integer multiples of the elementary charge.
3. An electric field is the region of space around a charged object where other charged objects will feel an electrostatic force. The electric field strength is defined as the force on a small test charge placed in the field.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of positive or negative charges on the surface of objects, caused by electrons moving between objects during physical contact like rubbing. It differs from current electricity which involves the controlled flow of electrons through conductors. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Static charges are created by the imbalance and redistribution of electrons on and between objects, and can cause static shocks when excess electrons jump between two charged objects and their charges equalize.1 ELECTROSTATICS



1 ELECTROSTATICSSheeba vinilan
Ěý
This document discusses the fundamental concepts of electromagnetism. It explains that electromagnetism underlies most of the forces we experience in everyday life, with the exception of gravity. Examples given include pushing an object, standing on the Earth's surface, and static/kinetic friction. The document then provides a brief history of the discovery of electromagnetism dating back to Thales' observation of static electricity in amber. It defines key terms like electrification and static electricity. Finally, it outlines some basic properties of electric charges like the constant total charge in the universe and quantization of charge in integer multiples of the elementary charge.Static electricity



Static electricityTekZeno
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on the surface of objects. It was discovered in 600 BC by Thales of Miletos who observed that rubbing amber with fur caused the amber to attract feathers due to static charge. Benjamin Franklin's kite experiment in the 1740s demonstrated that lightning is a form of electricity. Static charge is generated through friction, conduction, or induction. Objects can become positively or negatively charged by gaining or losing electrons. Coulomb's Law from 1785 describes the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges, directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.4 intro electrostatics



4 intro electrostaticsCyrus Trance
Ěý
Benjamin Franklin conducted experiments with electricity in the 1700s using simple apparatus. Through his experiments, he developed the concepts of positive and negative charges and proposed demonstrating the connection between lightning and electricity by flying a kite during a storm. In 1752, Franklin performed his famous kite experiment during a storm and was able to draw sparks from a key attached to the kite string, providing evidence that lightning is a form of electricity. Franklin's experiments made him famous and helped establish the field of electrostatics.Unit 1 Static Electricity



Unit 1 Static ElectricityBruce Coulter
Ěý
The document summarizes static electricity and different models that were proposed to explain it. It discusses the two-fluid model proposed by Charles Dufay involving vitreous and resinous fluids. It then discusses Benjamin Franklin's one-fluid model involving positive and negative charges. Finally, it introduces the modern particle model involving electrons, protons and neutrons to explain how objects become charged through the gain or loss of electrons.Introduction to Electrostatics



Introduction to ElectrostaticsNatasia Gouws
Ěý
This document discusses how objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons, and defines positive and negative charges. It explains that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Methods for charging objects include friction, touch, and induction. The key rules are that charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred, and that when two charged objects touch, their total charge is distributed equally between them. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the new charges and number of electrons transferred when two charged spheres touch.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
This document defines static electricity and current electricity. It explains that static electricity is caused by an imbalance of electric charges, usually through rubbing materials together, while current electricity involves the controlled flow of electrons. It distinguishes conductors that allow electron flow from insulators that do not, and describes how static charges build up and arc in lightning.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is caused by an imbalance of electric charges, usually between electrons and protons. It occurs when two objects are rubbed together, causing electrons to transfer between them leaving one object positively charged and one negatively charged. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Current electricity differs in that it involves the controlled, one-directional flow of electrons through conductors, powered by an external voltage source.Electricity



ElectricityPaul Comitz
Ěý
This document outlines the agenda and content for Module 4 of a physics course on electromagnetism. The module will cover electric charge, Coulomb's law, the electric field, Ohm's law, and include labs on electricity and electromagnetism. Key concepts that will be discussed include the relationship between positive and negative charges, Coulomb's inverse square law relating electric force to charge and distance, electric fields and potential differences, and Ohm's law relating voltage, current, and resistance in circuits.Electrostatics 



Electrostatics Shriyesh Gautam
Ěý
Electrostatics covers the properties of electric charges, electrostatic force, and electric fields. Key points include:
- There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
- Charge is quantized and conserved. It exists in integer multiples of the fundamental unit, e.
- Coulomb's law describes the electrostatic force between two point charges. The force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Electric fields are vector fields that exist around charged objects. The electric field strength is defined as the force per unit charge. Field lines are used to represent electric fields graphically.Static electricity and electrical currants



Static electricity and electrical currantssbarkanic
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of positive or negative charges on the surface of objects, caused by electrons moving between objects during physical contact like rubbing. It differs from current electricity which involves the controlled flow of electrons through conductors. Conductors allow electron flow while insulators do not. Static charges are created by the imbalance and redistribution of electrons on and between objects, and can cause static shocks when excess electrons jump between two charged objects and their charges equalize.Lesson 1_electrostatics_12



Lesson 1_electrostatics_12sujameryll
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the basics of electrostatics, including that static electricity occurs when charges build up on the surface of materials without moving, and that rubbing certain materials like polythene and perspex with cloth results in one becoming negatively charged and the other positively charged due to the transfer of electrons. It also explains that a rubbed balloon sticks to the ceiling due to opposite charges attracting, with the balloon becoming negatively charged and repelling electrons in the wall, leaving it positively charged.Static Electricity



Static ElectricityOhMiss
Ěý
Static electricity occurs when objects become electrically charged through the transfer of electrons. Charging occurs when two materials are rubbed together, causing electrons to move from one material to the other. This leaves one material with an excess of electrons and a negative charge, and the other material with a deficit of electrons and a positive charge. The electric charges remain on the surface of the objects until they are given a path to ground or neutralize each other through contact or discharge.Charge and Its Property



Charge and Its PropertyAnkur Patel
Ěý
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes electromagnetic attraction and repulsion. The electric charge is quantized, meaning it occurs in discrete integer multiples of the elementary charge carried by a single electron or proton. Robert Millikan's oil drop experiment directly demonstrated the quantization of charge by measuring the electric charges on tiny oil droplets, finding they were always integer multiples of approximately 1.6Ă—10^-19 coulombs. Coulomb's law describes the electric force between two charged particles, stating it is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.Similar to Electrostatics(Elecro-magnetic field) (20)
Electric charge



Electric chargeVeena Vs
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of electricity and electric charge. It traces the key discoveries around electricity from ancient Greeks observing amber's attractive properties when rubbed in 600 BC to J.J. Thompson's discovery of the electron in 1890. When certain materials like glass are rubbed against other materials like silk, electrons are transferred, leaving one material with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract based on the inverse square law discovered by Coulomb in 1770. Electric charge is quantized and comes in positive or negative units of the elementary charge of an electron.electrostatics_and_history.ppt



electrostatics_and_history.pptTwinkleStar53
Ěý
Electrostatics is the study of stationary electric charges and the forces between them. Key discoveries include:
- Otto van Guericke invented the first electric generator using friction in 1663.
- Stephen Gray discovered electricity can flow through wires in 1729, leading to telegraphs.
- E.G. von Kleist and Pieter van Musschenbroek independently discovered the Leyden jar capacitor in the mid-1700s.
- Benjamin Franklin proposed the theory of one electric fluid (electricity) and that oppositely charged objects attract in the 1700s.Electricity website



Electricity websitestephm32
Ěý
This document discusses electricity and electric charge. It defines the basic properties of electric charge including that there are two types - positive and negative. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Charge is conserved and cannot be created or destroyed. The key particles - proton, electron, and neutron - and their charges are identified. Conductors allow charge to move through them while insulators restrict charge movement. Triboelectric series shows how charge transfers during friction. Induction can charge objects without contact by redistributing protons and electrons. Devices like electroscopes and Van de Graaff generators are used to study electric charge.1 Electrostatics jwjwjwjwjjwjwkwjwjwjwkwkwkwkwkwkwk



1 Electrostatics jwjwjwjwjjwjwkwjwjwjwkwkwkwkwkwkwkhijazi123sara
Ěý
1. The document discusses the topic of electrostatics, which is the study of electric charges at rest. It defines key terms like electrification and covers concepts like Coulomb's law.
2. Methods of electrification include charging by friction, contact, and induction. Friction charging involves the transfer of electrons between two objects in contact. Contact charging occurs when a charged object transfers charge to a neutral one. Induction charging causes redistribution of charges without direct contact.
3. Examples demonstrate different charging scenarios and calculate things like final charge amounts. The law of conservation of electric charge and Coulomb's law are also explained through examples.Elec mag2



Elec mag2er_eljunrionel
Ěý
The document discusses the history and properties of electricity and magnetism. It covers how electricity was first observed in amber, the development of theories on positive and negative charges by scientists like Du Fay and Franklin, and how static electricity works. It also explains concepts like conductors, insulators, charging and grounding objects, and Coulomb's law governing the electric force between charges.Electric charges and fields are ok .pptx



Electric charges and fields are ok .pptxokbie584
Ěý
Hi what are the number is prime False and give questions 1 electrostatic 09



1 electrostatic 09GODARAMANGERAM
Ěý
1. Electrostatics is the study of electric charge at rest. Friction electricity was discovered in 600 BC when amber was rubbed with fur. In 1600, Sir William Gilbert named the phenomenon "electricity" from the Greek word for amber.
2. When two bodies are rubbed together, electrons are transferred leading one body to become positively charged and the other negatively charged. According to Coulomb's law, the electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
3. The dielectric constant of a medium is the ratio of the electrostatic force between charges in air to the force between the same charges in that medium.GenPhysics 2.pptx



GenPhysics 2.pptxChristyJoyRetanal
Ěý
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on the surface of objects. It occurs through three main processes: friction, conduction, and induction. When certain materials are rubbed together, electrons are transferred, leaving one material with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit. This separation of charges causes a static electric force. No new charges are created in this process - electrons simply move between objects. Conductors allow charge to flow easily while insulators do not, making insulators prone to charging. Grounding neutralizes charge by providing a path to earth. Lightning is a large-scale example of static discharge.Electricity



Electricityphysics101
Ěý
This document covers key concepts in electricity including electric charge, Coulomb's law, electric fields, potential difference, and capacitors. It describes three experiments showing that like charges repel and unlike charges attract. It defines the coulomb as the unit of electric charge and explains that electric charge is found in protons, electrons, and neutrons in atoms. It also summarizes that the electric field is the "alteration of space" caused by a charge, conductors allow electric charge to flow easily, capacitors store energy in an electric field between charges, and capacitance depends on the geometry and materials of a capacitor.Electrostatics 2-Shahjahan notes



Electrostatics 2-Shahjahan notesShahjahan Physics
Ěý
This document provides notes on electrostatics. It defines key terms like electrostatics, electric charge, conductors, insulators, semiconductors. It describes properties of electric charge including additivity, quantization, and conservation. Coulomb's law is explained, relating the electrostatic force between two point charges to the product of their charges and the inverse square of the distance between them. The document also compares electrostatic force and gravitational force.Electric Forces



Electric ForcesPaula Mills
Ěý
1. Electrostatic forces are caused by the attraction and repulsion of electric charges, such as when objects are rubbed together.
2. Atoms become charged when they gain or lose electrons, forming ions. The structure of the atom is such that electrons orbit a small, dense nucleus at relatively large distances.
3. Charged objects interact through electric fields and can attract or repel one another depending on whether their charges are opposite or the same. Applications of electrostatic forces include photocopiers, spray painting, and identifying atoms through spectroscopy.Static Electricity.ppt



Static Electricity.pptMathandScienced
Ěý
This document provides information about static electricity and electrostatics. It defines key terms like electrostatic, charges, protons, electrons, and ions. It discusses historical figures like Benjamin Franklin and his contributions. It explains how charging occurs through friction, conduction, and induction. Rules of attraction and repulsion between charged objects are covered. The document also discusses lightning, electric fields, and Coulomb's Law.electric charges and fields class 12 study material pdf download



electric charges and fields class 12 study material pdf downloadVivekanand Anglo Vedic Academy
Ěý
Have you ever experienced a crackling sound or witnessed a spark while removing synthetic clothes or a sweater, especially in dry weather? This phenomenon occurs due to the discharge of electric charges accumulated through the rubbing of insulating surfaces. Another example of electric discharge is lightning observed during thunderstorms. These occurrences result from static electricity generation. NCERT Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 1 on Electric Charges and Fields delves into these phenomena extensively. Electrostatics is the branch of physics that investigates forces, fields, and potentials arising from static charges.
For more information, visit- www.vavaclasses.comElectrostatics



Electrostaticsapwazap777
Ěý
This document discusses various topics in electrostatics including:
1) Electric charge can be positive or negative and like charges repel while unlike charges attract.
2) Charge is conserved meaning the total amount of charge in a system remains constant during interactions and transformations.
3) The coulomb is the SI unit for electric charge and small amounts are measured in microcoulombs. The elementary charge is the smallest unit of charge possible.
4) Materials can be conductors, insulators or semiconductors depending on how freely charge can flow through them.Physics 2 electrostatics



Physics 2 electrostaticsedmar alonzo
Ěý
1. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that can be either positive or negative. Charges interact via the inverse square law, where like charges repel and unlike charges attract.
2. When a glass rod is rubbed against silk, electrons are transferred from the glass onto the silk, leaving the rod positively charged and the silk negatively charged. Insulators like glass and silk hold their charges without allowing further transfer.
3. The document discusses the history of electrostatics and discoveries about electric charge. It also covers topics like Coulomb's law, quantization of charge, and the relative strengths of electric and gravitational forces.PHY2-11_12-Q3-0101-FD.pptx hshdjhdhehheheheh



PHY2-11_12-Q3-0101-FD.pptx hshdjhdhehhehehehHilchenHeruela
Ěý
The way to get the latest version of the way do it short The nature of electricity



The nature of electricityJohn Paul Fabricante
Ěý
Electricity powers many aspects of modern life - it provides power for lighting, heating, cooling, and transportation, as well as entertainment devices, appliances, and more. Electricity is distributed through power grids and used in homes, businesses, and industries worldwide. Advanced technologies have integrated electricity into areas like communication, medicine, manufacturing, and more. Electricity's versatile and widespread applications have transformed society and fueled economic growth.312_Physics_Eng_Lesson15.pdf



312_Physics_Eng_Lesson15.pdfVishalTiwari506825
Ěý
- The document discusses electric charge and the electric field. It begins by describing humans' dependence on electricity in daily life.
- It then discusses two types of electric charges (positive and negative), and how like charges repel and unlike charges attract based on experiments using a glass rod and rubber rod. Charge is also quantized and conserved.
- Coulomb's law is introduced, which states that the electrical force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.Electric Fields



Electric FieldsPaula Mills
Ěý
This document discusses electric fields and forces. It explains that electric charge comes from electrons and protons in atoms, and that rubbing materials together can transfer electrons, creating a separation of positive and negative charges. It also describes how conductors, insulators, and semiconductors differ in how easily they allow charge to flow through or remain separated.Recently uploaded (20)
Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profile



Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profilezebcoeng
Ěý
We’re excited to share our product profile, showcasing our expertise in Industrial Valves, Instrumentation, and Hydraulic & Pneumatic Solutions.
We also supply API-approved valves from globally trusted brands, ensuring top-notch quality and internationally certified solutions. Let’s explore valuable business opportunities together!
We specialize in:
• Industrial Valves (Gate, Globe, Ball, Butterfly, Check)
• Instrumentation (Pressure Gauges, Transmitters, Flow Meters)
• Pneumatic Products (Cylinders, Solenoid Valves, Fittings)
As authorized partners of trusted global brands, we deliver high-quality solutions tailored to meet your industrial needs with seamless support.Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
Ěý
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACgoogle_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPT



google_developer_group_ramdeobaba_university_EXPLORE_PPTJayeshShete1
Ěý
EXPLORE 6 EXCITING DOMAINS:
1. Machine Learning: Discover the world of AI and ML!
2. App Development: Build innovative mobile apps!
3. Competitive Programming: Enhance your coding skills!
4. Web Development: Create stunning web applications!
5. Blockchain: Uncover the power of decentralized tech!
6. Cloud Computing: Explore the world of cloud infrastructure!
Join us to unravel the unexplored, network with like-minded individuals, and dive into the world of tech!Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...



Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...slayshadow705
Ěý
This presentation provides an in-depth analysis of structural quality control in the KRP 401600 section of the Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3) in Uzbekistan. As a Structural QA/QC Inspector, I have identified critical welding defects, alignment issues, bolting problems, and joint fit-up concerns.
Key topics covered:
✔ Common Structural Defects – Welding porosity, misalignment, bolting errors, and more.
✔ Root Cause Analysis – Understanding why these defects occur.
✔ Corrective & Preventive Actions – Effective solutions to improve quality.
✔ Team Responsibilities – Roles of supervisors, welders, fitters, and QC inspectors.
✔ Inspection & Quality Control Enhancements – Advanced techniques for defect detection.
📌 Applicable Standards: GOST, KMK, SNK – Ensuring compliance with international quality benchmarks.
🚀 This presentation is a must-watch for:
âś… QA/QC Inspectors, Structural Engineers, Welding Inspectors, and Project Managers in the construction & oil & gas industries.
âś… Professionals looking to improve quality control processes in large-scale industrial projects.
📢 Download & share your thoughts! Let's discuss best practices for enhancing structural integrity in industrial projects.
Categories:
Engineering
Construction
Quality Control
Welding Inspection
Project Management
Tags:
#QAQC #StructuralInspection #WeldingDefects #BoltingIssues #ConstructionQuality #Engineering #GOSTStandards #WeldingInspection #QualityControl #ProjectManagement #MOF3 #CopperProcessing #StructuralEngineering #NDT #OilAndGasMathematics behind machine learning INT255 INT255__Unit 3__PPT-1.pptx



Mathematics behind machine learning INT255 INT255__Unit 3__PPT-1.pptxppkmurthy2006
Ěý
Mathematics behind machine learning INT255 Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ěý
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionLessons learned when managing MySQL in the Cloud



Lessons learned when managing MySQL in the CloudIgor Donchovski
Ěý
Managing MySQL in the cloud introduces a new set of challenges compared to traditional on-premises setups, from ensuring optimal performance to handling unexpected outages. In this article, we delve into covering topics such as performance tuning, cost-effective scalability, and maintaining high availability. We also explore the importance of monitoring, automation, and best practices for disaster recovery to minimize downtime.Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
Ěý
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...



Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...dhanashree78
Ěý
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Outdoor and indoor air pollution cause respiratory and other diseases and are important sources of morbidity and mortality.
WHO data show that almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants, with low- and middle-income countries suffering from the highest exposures.
Air quality is closely linked to the earth’s climate and ecosystems globally. Many of the drivers of air pollution (i.e. combustion of fossil fuels) are also sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Policies to reduce air pollution, therefore, offer a win-win strategy for both climate and health, lowering the burden of disease attributable to air pollution, as well as contributing to the near- and long-term mitigation of climate change.
AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge Graphs



AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge GraphsMax De Marzi
Ěý
How tarrifs, supply chains and knowledge graphs combine.How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using Arduino



How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using ArduinoCircuitDigest
Ěý
Learn how to build an RFID-based door lock system using Arduino to enhance security with contactless access control.Taykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
Ěý
Kalite Politikamız
Taykon Çelik için kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle paylaştığınız an başlar. Proje çiziminden detayların çözümüne, detayların çözümünden üretime, üretimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin gerçekleştiğini gördüğünüz ana kadar geçen tüm aşamaları, çalışanları, tüm teknik donanım ve çevreyi içine alır KALİTE.Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ěý
Electrostatics(Elecro-magnetic field)
- 2. Electrostatics GIRL SAFELY CHARGED TO SEVERAL HUNDRED THOUSAND VOLTS GIRL IN GREAT DANGER AT SEVERAL THOUSAND VOLTS
- 3. Electrostatic Charges A New Fundamental Physics Quantity The charge of an electron (qe) is -1.6 x 10-19 C The SI unit for charge is called the coulomb (C). Common electrostatic charges are small: millicoulomb = mC = 10-3 C microcoulomb = µC = 10-6 C nanocoulomb = nC = 10-9 C Electrostatic charge is a fundamental quantity like length, mass, and time. The symbol for charge is q. ATTRACTION AND REPULSION The charge of an proton (qp) is 1.6 x 10-19 C
- 4. The Nature of Electric Charge The Greeks first noticed electric charged by rubbing amber with fur, then picking up bits of matter. The Greek word for amber is elektron. Charge is conserved, meaning it cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one location to another. Benjamin Franklin arbitrarily called the two kinds of charge positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. In all atoms, electrons (qe) have negative charge and protons (qp) have positive charge. Discovery of charge Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract. Properties of charge Charge is quantized, meaning it comes in discrete amounts (like money). total charge = integer x fundamental unit of charge
- 5. Electric Charge The Transfer of Charge SILK Glass Rod Some materials attract electrons more than others.
- 6. ElEctric chargE thE transfEr of chargE silK glass rod -+ as thE glass rod is rubbEd against silK, ElEctrons arE pullEd off thE glass onto thE silK.
- 7. Electric Charge The Transfer of Charge SILK Glass Rod - -+ + Usually matter is charge neutral, because the number of electrons and protons are equal. But here the silk has an excess of electrons and the rod a deficit.
- 8. The Transfer of Charge SILK Glass Rod - + + + + + Glass and silk are insulators: charges stuck on them stay put. --- -
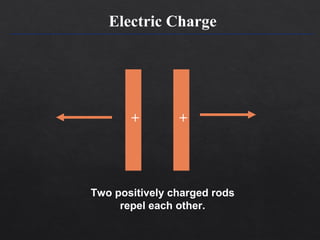
- 9. Electric Charge + + Two positively charged rods repel each other.
- 10. History 600 BC Greeks first discover attractive properties of amber when rubbed. 1600 AD Electric bodies repel as well as attract
- 11. Electric Forces and Electric Fields CHARLES COULOMB (1736-1806) MICHAEL FARADAY (1791-1867)
- 13. •Electric charges at rest (static electricity) •Involves electric charges, the forces between them, and their behavior in materials Electrostatic s
- 14. • Arise from the particles in atoms • Alone: Billions and billions of times as strong as the force of gravity • In Pairs: Cancel each other out and have no noticeable effect Electric Forces
- 15. Conservation of Charge •No case of the creation or destruction of net electric charge has ever been found •Electrons are always transferred in whole – they cannot be divided into fractions of electrons Electrons are never created nor destroyed, but are simply transferred from one material to another
- 16. Charging by Friction Materials have different affinities for electrons. When insulators are rubbed together, one gives up electrons and becomes positively charged, while the other gains electrons and becomes negatively charged. • plastic foodwrap that sticks to a container • sweater pulled over your head that sparks • laundry from the dryer that clings Common examples of charging by friction: A material will give up electrons to another material below it on a triboelectric series. • small shocks from a doorknob after walking on carpet with rubber-soled shoes • balloon rubbed with hair sticks that to a wall
- 17. Charging by Conduction When a charged conductor makes contact with a neutral conductor there is a transfer of charge. Electrons are transferred from the rod to the ball, leaving them both negatively charged. Electrons are transferred from the ball to the rod, leaving them both positively charged. Remember, only electrons are free to move in solids. CHARGING NEGATIVELY CHARGING POSITIVELY Notice that the original charged object loses some charge.
- 18. Charging by Induction Step 1. A charged rod is brought near an isolated conductor. The influence of the charge object polarizes the conductor but does not yet charge it. Step 2. The conductor is grounded to the Earth, allowing charge to flow out between it and the Earth. Induction uses the influence of one charged object to “coerce” charge flow.










