Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point
- 1. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point Correlates of the response to immunotherapy Daniel S. Chen & Ira Mellman Academia Sinica, MIB Chen group Nature , volume 541 , published:19 January 2017 Speaker : Ting-Wei Lin National Taiwan University, Genome and System Biology Lab Journal Reading 4th part
- 2. Zou, W., Wolchok, J. D., & Chen, L. (2016). PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Science Translational Medicine, 8(328), 328rv4. 10-40% anti-PD-L1/PD-1 antibodies Variation of the clinical response to the immunotherapy anti-CTLA4, IL-2 (even less response rate)
- 3. Predictive correlates of response with PD-L1 IHC staining IHC(Immunohistochemistry) Herbst, R. S., Soria, J.-C., Kowanetz, M., Fine, G. D., Hamid, O., Gordon, M. S., ŌĆ” Hodi, F. S. (2014). Predictive correlates of response to the anti- PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature, 515(7528), 563ŌĆō7. IC(Immune Cells) TC(Tumor Cell)
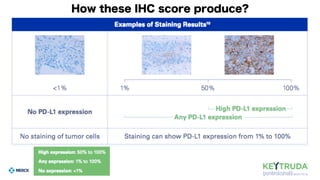
- 4. How these IHC score produce?
- 6. Tumeh, P. C., Harview, C. L., Yearley, J. H., Shintaku, I. P., Taylor, E. J. M., Robert, L., ŌĆ” Ribas, A. (2014). PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature, 515(7528), 568ŌĆō71. Requires Pre-existing CD8+ T cell mediated immune response Prembrolizumab Quantitative immunohistochemistry Multiplex quantitative immuno’¼éuorescence T cell receptor sequencing
- 7. non-small cell lung cancer metastatic urothelial carcinoma Strati’¼üed the patient survival with the level of cytokine and TC/IC score TC:tumor cell with PD-L1 expression, IC:in’¼ültrating immune cell Fehrenbacher, L., (2016). The Lancet, 387(10030), 1837ŌĆō1846. Rosenberg, J. E.,ŌĆ”(2016). The Lancet, 387(10031),
- 8. Three basic immune pro’¼üles correlating with responseCancer In’¼éamed tumour Immune-excluded tumour Immune-desert tumour 1. CD4/CD8 + T cell in Tumor Parenchyma 2. High expression of PD-L1 on TC or IC 3. Pro-in’¼éammatory and effector cytokine TC: Tumor cell, IC: In’¼ültrating immune cell 1. IC not penetrating the parenchyma 2. still abundant immune cells around tumor 1. few or no CD8+ T cell 2. Poor response
- 10. Immune-excluded tumour Joyce, J. A., & Fearon, D. T. (2015). T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy, 348(6230). 1 2 3
- 11. Immune-desert tumour Zou, W., Wolchok, J. D., & Chen, L. (2016). PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Science Translational Medicine, 8(328), 328rv4. 1 2 3
- 12. The tumor immunity spectrum and cycle Convert to in’¼éamed phenotype with combinationsRespond favorably to checkpoint inhibition Hegde, P. S., Karanikas, V., & Evers, S. (2016). The where, the when, and the how of immune monitoring for cancer immunotherapies in the era of checkpoint inhibition. Clinical Cancer Research, 22(8)
- 13. Predicting response with Personalized cancer immunotherapy paradigm Kim, J. M., & Chen, D. S. (2016). Immune escape to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade: Seven steps to success (or failure). Annals of Oncology, 27(8)