Embolism as a complication of trauma
- 2. Introduction Any trauma may complicate by 3 types of embolism according to its site & force If trauma was associated by long Bone fractures it may complicate by fat embolism If the neck or the thoracic cage were injured in the trauma it may complicate by systemic air embolism due to injury to blood vessel or a heart chamber their pressure is relatively negative Commonly with violent traumas which are associated with bone fractures & inability of walking for a while, Patients will have to lay in their beds in a certain position for long time, this prolonged recumbency in bed may lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) & if detachment occurs it may lead to pulmonary embolism In this research we will spotlight on these 3 types 1- Fat embolism Definition: A fat embolism is a type of embolism that is often (but not always) caused by physical trauma Presentation: Unlike emboli that arise from thrombi (blood clots), fat emboli are small and multiple, and so have widespread effects. Fat Embolism Syndrome (FES) is distinct from the presence of fat emboli. Symptoms usually occur 1-3 days after a traumatic injury and are predominantly: pulmonary (shortness of breath, hypoxemia), neurological (agitation, delirium, or coma), dermatological (petechial rash), and hematological (anemia, low platelets). The syndrome manifests more frequently in closed fractures of the pelvis or long bones. The petechial rash, which usually resolves in 5-7 days is said to be pathognomonic of the syndrome; however, it occurs in only 20-50% of cases. The risk of fat embolism syndrome is thought to be reduced by early immobilization of fractures, especially by early operative correction. There is also some evidence that steroid prophylaxis of high-risk patients reduces the incidence. The mortality rate of fat-embolism syndrome is approximately 10-20% Treatment: The most effective prophylactic measure is to reduce long bone fractures as soon as possible after the injury. Maintenance of intravascular volume is important because shock can exacerbate the lung injury caused by FES. Albumin has been recommended for volume resuscitation in addition to balanced electrolyte solution, because it not only restores blood volume but also binds fatty acids, and may decrease the extent of lung injury.
- 3. 2- Air embolism Definition: Small amounts of air often get into the blood circulation accidentally following a trauma Death may occur if a large bubble of gas becomes lodged in the heart; stopping blood from flowing from the right ventricle to the lungs (this is similar to vapor lock in engine fuel systems). Pathogenesis: Air embolism can occur whenever a blood vessel is open and a pressure gradient exists favoring entry of gas. Because the pressure in most arteries and veins is greater than atmospheric pressure, an air embolus does not always happen when a blood vessel is injured. In the veins above the heart, such as in the head and neck, the pressure is less than atmospheric and an injury may let air in. This is one reason why surgeons must be particularly careful when operating on the brain, and why the head of the bed is tilted down when inserting or removing a central venous catheter from the jugular or subclavian veins. When air enters the veins, it travels to the right side of the heart, and then to the lungs. This can cause the vessels of the lung to constrict, raising the pressure in the right side of the heart. If the pressure rises high enough in a patient who is one of the 20% to 30% of the population with a patent foramen ovale, the gas bubble can then travel to the left side of the heart, and on to the brain or coronary arteries. Such bubbles are responsible for the most serious of gas embolic symptoms. Trauma to the lung can also cause an air embolism. This may happen after a patient is placed on a ventilator and air is forced into an injured vein or artery, causing sudden death. N.B: Pulmonary barotrauma in divers: Air bubbles enter the bloodstream as a result of gross trauma to the lining of the lung following a rapid ascent while holding the breath; the air held within the lung expands to the point where the lungs burst (pulmonary barotrauma). This is easy to do as the lungs give little warning through pain until they do burst. The diver will arrive at the surface in pain and distress and may froth or spit blood Treatment: Recompression is the most effective treatment of an air embolism. Normally this is carried out in a recompression chamber. It is also important to promptly place the patient in left lateral decubitus position this positioning helps to trap air in the apex of the ventricle and prevent it from reaching the lung circulation.
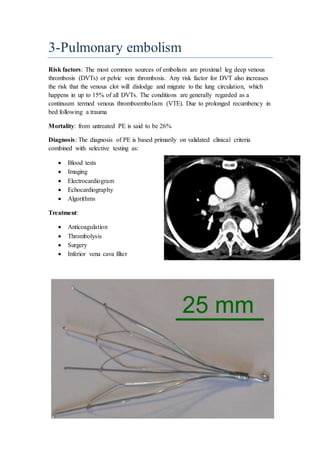
- 4. 3-Pulmonary embolism Risk factors: The most common sources of embolism are proximal leg deep venous thrombosis (DVTs) or pelvic vein thrombosis. Any risk factor for DVT also increases the risk that the venous clot will dislodge and migrate to the lung circulation, which happens in up to 15% of all DVTs. The conditions are generally regarded as a continuum termed venous thromboembolism (VTE). Due to prolonged recumbency in bed following a trauma Mortality: from untreated PE is said to be 26% Diagnosis: The diagnosis of PE is based primarily on validated clinical criteria combined with selective testing as: ´éÀ Blood tests ´éÀ Imaging ´éÀ Electrocardiogram ´éÀ Echocardiography ´éÀ Algorithms Treatment: ´éÀ Anticoagulation ´éÀ Thrombolysis ´éÀ Surgery ´éÀ Inferior vena cava filter
- 5. Contents Introduction 1- Fat embolism 1. A- Definition 1. B- Presentation 1. C- Treatment 2- Air embolism 2. A- Definition 2. B- Pathogenesis 2. C- Treatment 3- Pulmonary Embolism 3. A- Risk factors 3. B- Diagnosis 3. C- Treatment Contents By students: 264-Ôǽ┘àÏ¡┘àÏ»ÔǼ ÔǽϿ┘âÏ▒ÔǼ ÔǽÏÂÏ¡┘ëÔǼ 264-Ôǽ┘àϼϺ┘çÏ»ÔǼ ÔǽϺ┘äÏ▒Ï¡┘à┘åÔǼ ÔǽÏ╣Ï¿Ï»ÔǼ ÔǽÏÂÏ¡┘ëÔǼ 262-Ôǽ┘àÏ▒Ï╣┘èÔǼ ÔǽϺÏ│┘àϺÏ╣┘è┘äÔǼ Ôǽ┘àÏÁÏÀ┘ü┘ëÔǼ ÔǽÏÂ┘èϺÏíÔǼ 264-ÔǽϺ┘äÏ│┘êϺϡ┘ä┘èÔǼ ÔǽϺ┘äÏ¿┘åϻϺÏ▒┘èÔǼ Ôǽ┘àÏÁÏÀ┘ü┘ëÔǼ ÔǽÏÂ┘èϺÏíÔǼ 266-ÔǽϺ┘äÏ«┘ê┘ä┘ëÔǼ ÔǽϺ┘äÏ│┘èÏ»ÔǼ ÔǽÏÀϺÏ▒┘éÔǼ 264-ÔǽϺ┘ä┘äÏÀ┘è┘üÔǼ ÔǽÏ╣Ï¿Ï»ÔǼ ÔǽÏÀϺÏ▒┘éÔǼ 264-ÔǽÏ╣Ï▓ϬÔǼ ÔǽÏÀϺÏ▒┘éÔǼ 264-ÔǽϺ┘äÏ┤Ϻ┘üÏ╣┘èÔǼ ÔǽÏúÏ¡┘àÏ»ÔǼ ÔǽÏÀ┘çÔǼ 244-Ôǽ┘àÏ¡Ï│┘åÔǼ ÔǽϺ┘äÏ¡┘â┘è┘àÔǼ ÔǽÏ╣Ï¿Ï»ÔǼ 244-ÔǽϺ┘äϫϺ┘ä┘éÔǼ ÔǽÏ╣Ï¿Ï»ÔǼ