Embryology 1st year mbbs
- 2. MORULA •As the cleavage proceeds the ovum comes to have 16 cells. •It looks like a mulberry. •It is still surrounded by the zona pellucida. •It has inner cell mass and outer layer of cells giving rise to future trophoblast. •The inner cell mass give rise to embryo proper so called embryoblast.
- 3. * Fluid accumulation starts. •Inner cell mass and trophoblast are well defined. •Zona pellucida disappears.
- 4. BLASTOCYST •Know the morula becomes the blastocyst. •The cavity – blastocoele. •The side of the blastocyst to which inner cell mass is attached is known as embryonic /animal pole and the opp side- aembryonic pole.
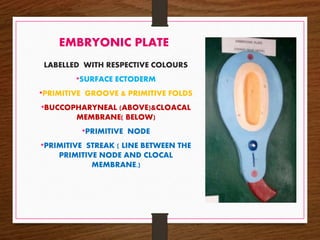
- 5. EMBRYONIC PLATE LABELLED WITH RESPECTIVE COLOURS •SURFACE ECTODERM •PRIMITIVE GROOVE & PRIMITIVE FOLDS •BUCCOPHARYNEAL (ABOVE)&CLOACAL MEMBRANE( BELOW) •PRIMITIVE NODE •PRIMITIVE STREAK ( LINE BETWEEN THE PRIMITIVE NODE AND CLOCAL MEMBRANE.)
- 6. EMBRYONIC PLATE SHOWING GERM LAYERS •SURFACE ECTODERM •NOTOCHORD •NEURAL GROOVE •ENDODERM •MESODERM(paraxial,intermedi ate and lateral plate mesoderm) •Curves on sides are EXTRA EMBRYONIC MESODERM.
- 7. SURFACE ECTODERM DERIVATIVES: 1. Epidermis of skin 2.sweat glands and sebaceous glands 3. mammary glands 4. hair ,nails, enamel of teeth 5. epithelium of lip, cheeks, gums 6. lens of eye 7. anterior pitutary 8. internal ear 9. epithelium of cornea, conjunctiva,ciliary body and iris 10. outer layer of tympanic membrane.
- 8. FROM NEURAL CREST CELLS : •MEDULLA & SUPRA RENAL GLAND •PIGMENT CELLS( melanocytes) •SCHWANN CELLS •DORSAL ROOT GANGLIA •SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA •DENTINE OF TEETH •BONES OF HEAD •BULBAR AND CONJUNCTIVAL RIDGES IN THE HEART.
- 9. FROM NEURAL TUBE: •BRAIN & SPINAL CORD • RETINA •PINEAL BODY •POSTERIOR PITUITARY
- 14. PHARYNGEAL ARCHES. 1st arch-mandibular nerve-medial and lateral pterygoid,temporalis, massestor,mylohyoid, ant belly of digastric muscles,tensor tympani and tensor palati. 2nd arch-facial nerve- facial muscles, occipitofrontalis, platysma,stylohyoid,posterior belly of digastric,stapedius, auricular musles 3rd arch-glossopharyngeal nerve- stylopharyngeus 4th arch- superior laryngeal nerve- muscles of larynx and pharynx 5th-glossopharyngeal nerve
- 15. ENDODERMAL POUCHES 1ST POUCH-ventral part forms the tongue,dorsal part along with dorsal part of the second pouch forms a diverticulum along the developing ears,called tubo tympanic recess.Proximal part called auditory tube and distal part called middle ear cavity. 2nd pouch- epithelium of the ventral part of this pouch contributes to the formation of the tonsil. 3rd- inferior parathyroid glands and the thymus 4 th pouch- superior parathyroid glands and thyroid gland. 5th pouch or ultimobrachial pouch. Generally incorporated with the 4 th pouch forming caudal pharyngeal complex. The superior parathyroid arises from this and also the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland.
- 16. ECTODERMAL CLEFTS FIRST cleft- develops into the epitheal lining of the External acoustic meatus, the pinna is formed from a series of swellings or hillocks, that arise on the first and second arches,where they adjoin the first cleft. The ventral part of this arch is obliterated. Cerival sinus present between the second arch and remaining arches.