EMG
- 1. VELTECH DEPARTMENT OF ECE Electromyography- EMG Prepared By, V.Mahalakshmi, Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Veltech
- 3. What is EMG? • The study of electrical activity of muscles is called electromyography. • The instrument used to measure the electrical activity of muscles is called electromyogram. • The recorded pattern of the electrical activity of muscles is called electromyograph. • Recording the action potential of peripheral nerve is known as Electro neurography.
- 4. Electrodes used for EMG Types of electrodes are used for recording EMG. • Surface electrodes are used when signals are recorded on the surface and it cannot detect deep potential from within the cell. • Needle electrodes are inserted deep into the tissue, which records the muscle potential. • Microelectrode is used to record action potential from single nerve.
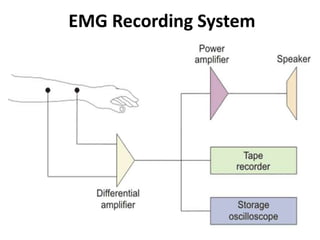
- 7. EMG Recording System • Electrodes record EMG potentials from the tissue. • Disc shaped surface electrodes made of Ag/AgCl are used to pick the signals. • The skin surface is cleaned and electrode gel is applied on the skin surface. • Elastic bands are used to attach the electrodes to the skin. • When electrodes are affixed tight on the skin, it reduces the skin contact impedance to below 10kΩ.
- 8. EMG Recording System The amplitude of EMG signal depends on various factors like • Type of electrode used • Placement of electrode on the muscle and • The degree of muscular exertions. • When surface electrodes are used, it picks signals from nearby spikes. Therefore, it produces average voltage value from the muscles ad motor units. • The needle electrodes pick signal from single nerve fiber and it produces one voltage value.
- 9. EMG Recording System • The voltage value of EMG signals varies between 0.1 to 0.5 mV. • The frequency of the EMG signal is the range of 20 Hz to 10 KHz, which lies in the audio range. • The normal frequency of EMG is 60 Hz. • The differential amplifier has high gain and frequency range between 10 Hz to 10 KHz. The amplified output is given to the power amplifier that helps to amplify the signal to a higher level. • The amplified signal is given to the loudspeaker, tape recorder and CRO.
- 10. Applications of Electromyography • To study neuromuscular functions. • To know the neuromuscular condition. • To study reflex responses. • To know about the extent of nerve lesions. • Helps to diagnose the muscular diseases.
- 11. Measurement of Conduction Velocity in Motor Nerves
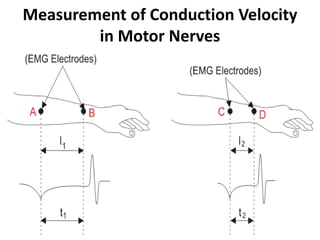
- 12. Measurement of Conduction Velocity in Motor Nerves • In the motor nerves, to indicate the location and type of nerve lesions, conduction velocity is measured. • An electric shock of duration 0.2 – 0.5 ms is stimulated on the nerves. • Conduction velocity along the peripheral nerve is measured to calculate the latency. • Latency is defined as difference in time between stimulating impulse and action potential of the muscle.
- 13. Measurement of Conduction Velocity in Motor Nerves • The conduction velocity is calculated using the below formula. • Normally the value of conduction velocity is 50 m/s.