Emotional Intelligence
- 1. EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE key to stress management
- 2. EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE Emotional intelligence (EI) commonly known as EQ has become a wide spread interest to psychological research It was Salovey and Mayer, who first introduced the term emotional intelligence. But it was popularized by Goleman with the publication of his influential book Emotional Intelligence in 1995 which appeared in the cover page of TIME magazine.
- 3. IQ and EQ Earlier it was believed that people with high IQ could alone become successful in personal, academic, family and professional life. Many people with high IQ may be productive and ambitious but found to be cold and detached. People with EQ, even with average IQ have found to be more successful because they are social, empathetic and cheerful’. IQ is mostly determined by genetics and so it can not be changed drastically. But EQ is mostly learned and people can be trained.
- 4. One of the definition of EI “ An interrelated set of abilities that allow an individual to recognize use and regulate emotion in an efficient and productive manner, thereby allowing effective dealing with the environment”
- 5. Approaches Salovey & Mayer Identifying emotions Using emotions Understanding emotions Managing emotions Salovey & Mayer: “We define emotional intelligence as the subset of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one's own and others' feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide one's thinking and actions.”
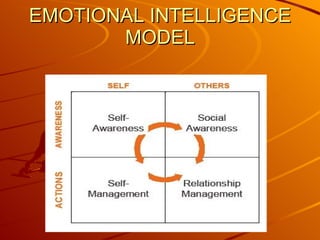
- 6. Approaches Goleman Self-awareness - Knowing our own emotions Self-management - Managing our own emotions Self-motivation - Motivating ourselves Social awareness (empathy)- Recognizing other’s emotions Social skills - Handling relationships
- 8. Approaches Bar-on Intrapersonal skills Interpersonal skills Adaptability Stress management General mood "People in good moods are better at inductive reasoning and creative problem solving."
- 9. Self - Intrapersonal Self-awareness - feelings, values and goals etc Self-confidence - overcoming self doubt, assertivenes etc Self-control - dealing with stress, emotion etc
- 10. Social - Inter personal Empathy - active listening, understanding others point of view, reading non-verbal cues Motivation -taking initiative, inspiriting others, creative, persistant and commitment Social competence -rapport building, minimizing conflict, influencing others, integirity
- 11. Self management Mood management Self-motivation Dealing with setbacks Dealing with stress Managing your time, energy, work Avoid unwanted addictive behaviour
- 12. Managing others Maintain close relationships Motivating others Leading others Developing others Confronting others Collaborating with others
- 13. Elements of EI Emotion perception identify one’s own emotional experiences, emotional experiences of others, and value attributed to objects Emotional assimilation know how to use emotion to help shape judgment and behaviour. Hence emotion influencing information processing
- 14. Elements of EI Emotion understanding rich emotion knowledge base such as cause, bodily sensation, expressive modes and how the emotion functions interpersonally Emotion regulation monitor and manage emotion in self and others to produce the desired out come in a given situation
- 15. Emotion regulation Emotional regulation involves persons attempts to influence which emotions they have, how they experience and express these emotion "What really matters for success, character, happiness and life long achievements is a definite set of emotional skills - your EQ - not just purely cognitive abilities that are measured by conventional IQ tests." -Daniel Goleman, Ph.D.
- 16. Emotion regulation Situation selection approaching or avoiding certain people, places or objects in order to influence one’s emotions Situation modification selected situation may be tailored so as to modify its emotional impact
- 17. Emotion regulation 3. Attentional deployment select and modify imagined situation 4. Cognitive change selecting many possible meanings will be attached to given situation 5. Response modulation influencing these response tendencies once they have been elicited
- 18. Life is a series of experiences, each one of which makes us bigger, even though it is hard to realize this. For the world was built to develop character and we must learn that the setbacks and griefs which we endure help us out in marching onward. – Henry Ford
- 19. Beginning today, treat everyone you meet as if they were going to be dead by midnight. Extend them all the care, kindness and understanding you can muster. Your life will never be the same again. - Og Mandino
- 20. Smile at each other, smile at your wife, smile at your husband, smile at your children, smile at each other - it doesn't matter who it is - and that will help you to grow up in greater love for each other. - Mother Teresa
- 21. “ When you listen with empathy to another person, you give that person psychological air.”  - Stephen R. Covey Tenderness and kindness are not signs of weakness and despair, but manifestations of strength and resolution. - Kahlil Gibran
- 22. Freedman et al.: "Emotional Intelligence is a way of recognizing, understanding, and choosing how we think, feel, and act. It shapes our interactions with others and our understanding of ourselves. It defines how and what we learn; it allows us to set priorities; it determines the majority of our daily actions. Research suggests it is responsible for as much as 80% of the "success" in our lives."
- 23. "Emotional Intelligence is essential to interpersonal and intrapersonal relationships at school, at home, and at work." - McCown et al.
- 24. "Like all learning, the development of emotional intelligence comes from building new patterns in the brain. These new patterns develop when we have experiences that we can link to background knowledge. The learning is integrated by experiencing cause and effect, and through practice." - Freedman et al.
- 25. Thank you