Employee Performance and Motivation.pptx
- 1. By: Dr. Ghulam Dastgeer +92-333-5111-469 hellodastgeer@gmail.com Employee Performance and Motivation
- 4. Our Responsibilities ’éŚ My responsibilities ’éŚ I am here to give you values ’éŚ For your money ’éŚ For your time ’éŚ Your responsibilities ’éŚ Be a studentŌĆ” ’éŚ DonŌĆÖt be an evaluator ’éŚ All things are working perfectly out there, just disconnect yourself from all those things.
- 5. The EmployeeŌĆ”. ’éŚ Organizations are the people/employee in them; that employee make the placeŌĆ” ’éŚ Performance of the organizations depends on the quality, dedication, enthusiasm, expertise and skills of the employees working in them at all levels.
- 6. ŌĆó Every individual employee in an organization needs proper: ŌĆō Recruitment ŌĆō Selection ŌĆō Orientation ŌĆō Socialization ŌĆō Job design ŌĆō Pay and Rewards ŌĆō Training ŌĆō Performance management ŌĆō Feedback ŌĆō Couching ŌĆō Mentoring ŌĆō Counseling ŌĆō Conflict resolution/management ŌĆō Leadership ŌĆō Motivation ŌĆō Career development ŌĆō Safety and Health ŌĆō Employee wellbeing ŌĆō Employee-Employer Relationships ŌĆō Stress management ŌĆō Work life and family life balance ŌĆō Retirement and old age benefits...etcŌĆ”
- 7. ŌĆó Every individual in an organization is different: ŌĆō Behavior ŌĆō Attitude ŌĆō Personality ŌĆō Emotions ŌĆō Moods ŌĆō Values ŌĆō Perception ŌĆō Decision Making ŌĆō Motivation ŌĆō Leadership skills
- 8. ’éŚ Q: why do certain individuals perform better than others? or What factors cause an employee to perform at a certain level?
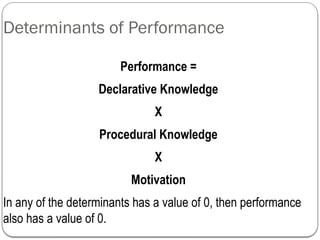
- 9. Determinants of Performance Performance = Declarative Knowledge X Procedural Knowledge X Motivation In any of the determinants has a value of 0, then performance also has a value of 0.
- 10. A. Declarative Knowledge ’éŚ Declarative knowledge is information about facts an things, including information regarding a given taskŌĆÖs requirements, labels, principles, and goals.
- 11. B. Procedural Knowledge ŌĆó Procedural knowledge is combination of knowing what to do and how to do it and include cognitive and physical skills
- 12. C. Motivation ’éŚ Motivation involves three types of Choices ’éŚ Expenditure of effort (I will go to work today) ’éŚ Level of effort (I will put in my best efforts at work) ’éŚ Persistence of effort (I will persist no matter what)
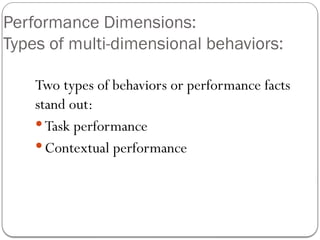
- 13. Performance Dimensions: Types of multi-dimensional behaviors: Two types of behaviors or performance facts stand out: ’éŚ Task performance ’éŚ Contextual performance
- 14. Task performance T.P is defined as activities that ’éŚ From the perspective of managers: performance on the job often consist of outcomes. ’éŚ Goals/actions, not the activities, that are important. ’éŚ Transform raw materials into the goods and services. ’éŚ How many sales were made? ’éŚ How much was waste reduces? ’éŚ How many were made?
- 15. Contextual performance ’éŚ From the perspective of Employees: it is what workers do day in and day out on the job (activities on various tasks). ’éŚ From this perspective performance consists of behaviors, and how well those behaviors are executed. ’éŚ Behaviors that contribute to organizationŌĆÖs effectiveness and provide a good environment in which task performance can occur
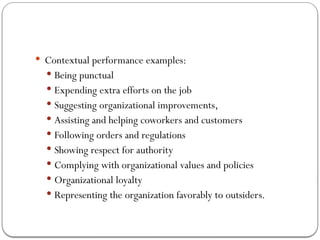
- 16. ’éŚ Contextual performance examples: ’éŚ Being punctual ’éŚ Expending extra efforts on the job ’éŚ Suggesting organizational improvements, ’éŚ Assisting and helping coworkers and customers ’éŚ Following orders and regulations ’éŚ Showing respect for authority ’éŚ Complying with organizational values and policies ’éŚ Organizational loyalty ’éŚ Representing the organization favorably to outsiders.
- 17. ’éŚ Q; why both task and contextual performance are important dimensions to take into account in performance management systems???
- 18. Personal Development, Motivation and PERFORMANCE
- 19. ŌĆó No matter how Successful you may be there is ALWAYS a room for IMPROVEMENT. Strive to the maximum of your potential. DonŌĆÖt take the ordinary road of mediocrity.
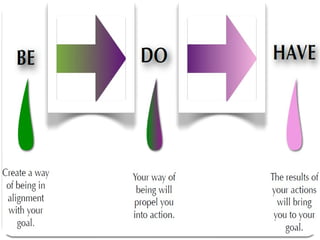
- 20. You can have more than you have got because you can become more than you are (Jim Rohn). Traditional (wrong formula) HAVE: have enough (money, resources, things) DO: so what you want BE: be happy, successful, educated, talented, Life is not designed to give us what we need, but the life is designed to give us what we deserve.
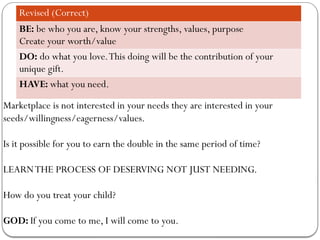
- 21. Revised (Correct) BE: be who you are, know your strengths, values, purpose Create your worth/value DO: do what you love.This doing will be the contribution of your unique gift. HAVE: what you need. Marketplace is not interested in your needs they are interested in your seeds/willingness/eagerness/values. Is it possible for you to earn the double in the same period of time? LEARNTHE PROCESS OF DESERVING NOT JUST NEEDING. How do you treat your child? GOD: If you come to me, I will come to you.
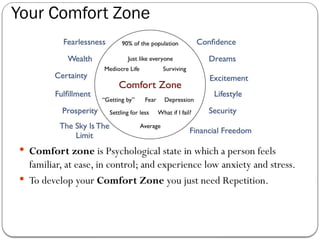
- 24. Your Comfort Zone ’éŚ Comfort zone is Psychological state in which a person feels familiar, at ease, in control; and experience low anxiety and stress. ’éŚ To develop your Comfort Zone you just need Repetition.
- 25. Expending Your Comfort Zone ’éŚ Objective in expending your Comfort Zone is to raise our optimal performance level and become confortable with that new level. ’éŚ Your brain is your server, Give it chance to learn and repeat it. ’éŚ Real limitationsVs Perceived Limitations
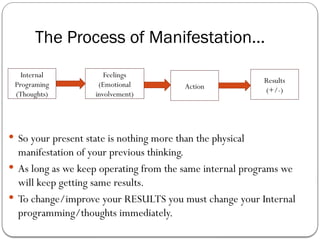
- 26. The Process of ManifestationŌĆ” ’éŚ So your present state is nothing more than the physical manifestation of your previous thinking. ’éŚ As long as we keep operating from the same internal programs we will keep getting same results. ’éŚ To change/improve your RESULTS you must change your Internal programming/thoughts immediately. Internal Programing (Thoughts) Feelings (Emotional involvement) Action Results (+/-)
- 27. What is motivation? ’éŚ Motivation is the ability to take control on your mind and to turn problems and difficulties into solutions and energy to successfully achieve your goals.
- 28. Importance of Motivation Cost of: Cost of : ’éŚ failing to fully engage: ’éŚ Passion ’éŚ Talent ’éŚ intelligence ’éŚ Taxes ’éŚ Interest Charges ’éŚ Labor cost
- 29. The Rise and Fall of Motivation ’éŚ Motivation 1.0 ŌĆō presumed that humans were biological creatures, struggling to obtain our basic needs for food, security. (Extrinsic) ’éŚ Motivation 2.0 ŌĆō presumed that humans also responded to rewards and punishments.That worked fine for routine tasks but incompatible with how we organize. (Extrinsic) ’éŚ Motivation 3.0 ŌĆō the upgrade we now need, presumes that humans also have a drive to learn, to create, and to better the world. (Intrinsic) Book: ŌĆ£DriveŌĆØ by D.Pink
- 30. The Thing Mind-set of The Industrial Age ’éŚ The main assists and primary drives of economics prosperity in the IndustrialAge were ’éŚ MACHINES and CAPITAL. ’éŚ People were treated: ’éŚ as THINGS ’éŚ as Expense ’éŚ All you want is a ŌĆ£personŌĆÖs bodyŌĆØ ’éŚ Replaceable
- 31. ’éŚ You have to control and Manage PeopleŌĆ” ’éŚ Carrot-and-stick motivational philosophy ’éŚ Carrot: Reward ’éŚ Stick: fear and punishment Treating people like things results in: ’éŚ 1. insult them ’éŚ 2. alienates them ’éŚ 3. depersonalizes work ’éŚ 4. low trust ’éŚ 5. unionized ’éŚ 6. litigious culture People disempower themselves by believing that others must change before their own circumstances can improve.
- 32. Carrots and Sticks: The Seven Deadly Flaws This motivation will only work if donkey is hungry enough, the carrot is sweet enough and the load is light enough. If the combination is missing???
- 33. The Whole Person Paradigm ’éŚ Human beings are not THINGS needing to be managed and controlled; they are four dimensional Body, Mind , Heart , and Soul.. Book:ŌĆ£8th HabitŌĆØ by S.R. Covy
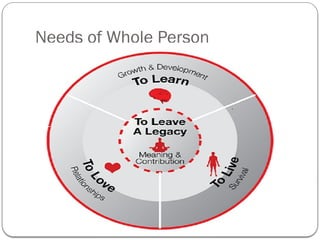
- 34. Needs of Whole Person
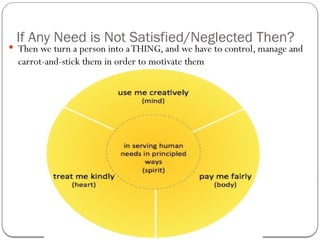
- 35. If Any Need is Not Satisfied/Neglected Then? ’éŚ Then we turn a person into aTHING, and we have to control, manage and carrot-and-stick them in order to motivate them
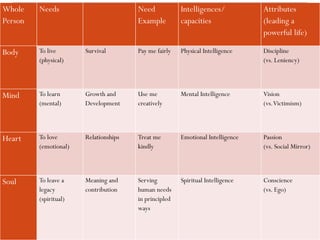
- 36. Whole Person Needs Need Example Intelligences/ capacities Attributes (leading a powerful life) Body To live (physical) Survival Pay me fairly Physical Intelligence Discipline (vs. Leniency) Mind To learn (mental) Growth and Development Use me creatively Mental Intelligence Vision (vs.Victimism) Heart To love (emotional) Relationships Treat me kindly Emotional Intelligence Passion (vs. Social Mirror) Soul To leave a legacy (spiritual) Meaning and contribution Serving human needs in principled ways Spiritual Intelligence Conscience (vs. Ego)
- 37. Highest manifestations of these four intelligences ’éŚ Vision: to seeing with the mindŌĆÖs eye what is possible in people, in projects, in causes and in enterprises, mindŌĆÖs capacity to create. ’éŚ Discipline: deal with hard, pragmatic, brutal facts of reality and doing what it takes to make things happen. ’éŚ Passion: is the fire, the desire, the strength of conviction and the drive that sustain the discipline to achieve the vision. ’éŚ Conscience: is the inward moral sense of what is right and what is wrong, the drive towards meaning and contribution. The guiding force to vision, discipline and passion.
- 39. ’éŚ Competition in biology, ecology, and sociology, is a contest between organisms, animals, individuals, groups, etc., for territory, a niche, or a location of resources, for resources and goods, mates, for prestige, recognition, awards, or group or social status, for leadership. ’éŚ Competition is the opposite of cooperation. It arises whenever at least two parties strive for a goal which cannot be shared or which is desired individually but not in sharing and cooperation
- 40. ’éŚ Q: what are the outputs/results of COMPETITION?
- 41. Means: ’éŚ Goal/Aimlessness ’éŚ Stress ’éŚ Tension ’éŚ Jealousy ’éŚ Selfishness ’éŚ Separation ’éŚ Conflict ’éŚ Grouping ŌĆó Proud ŌĆó Greed ŌĆó Envy ŌĆó Ego ŌĆó We vs. they ŌĆó Ingratitude ŌĆó Divorce ŌĆó Forget yourself ŌĆó Low self-esteem ŌĆó Even you go for more and more and more BuyingŌĆ”..
- 44. ’éŚ Regardless of my environment, education and experience, who is responsible for my attitude, motivation, mood, results etcŌĆ”.? ’éŚ Who has to accept responsibility? ’éŚ ME ’éŚ Can I change my attitude/mood/motivation regardless of my environment, education and experience???
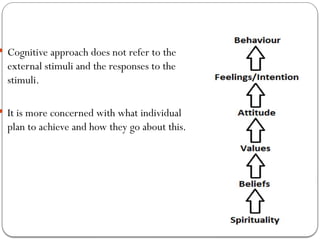
- 46. ’éŚ Cognitive approach does not refer to the external stimuli and the responses to the stimuli. ’éŚ It is more concerned with what individual plan to achieve and how they go about this.
- 47. Goal-Setting Theory ’éŚ Goal-setting theory contends that performance goals play a key role in motivation. ’éŚ The theory proposes that goals can mobilize employee efforts, direct attention, increase persistence, and affect the strategies employees use to accomplish tasks. ’éŚ Specific, difficult, and employee-accepted goals will lead to higher levels of performance than easy, vague (such as do your best) or nonexistent one.
- 48. ’éŚ Purpose answers the existential question ŌĆ£WHYŌĆØ: why are you here, on this planet, at this time? ’éŚ The answer will hold up in every part of your life; it will apply to your family life, work life, social life and community life. ’éŚ Mission: what you do (reason of your existence) ’éŚ Vision: a picture of a future you would like to create. ’éŚ Failure in goals motivates you more and more and will cause you to dream and learn more. ’éŚ Leaving a legacy (have made a contribution in the world) is another way of saying that you have lived a life of purpose ’éŚ Remember: Living on purpose is one way to live a meaningful life.
- 49. ’éŚ A man with purpose can not be molded, stressed, or cursed or demotivated. ’éŚ Always keep the end/goal in mind. ’éŚ Until you have objectives you remain young and alive. ’éŚ What happens with people after their retirement? ’éŚ Why do female look too old even at the age of 40? ’éŚ Wise people always know about themselves. Spend some time for youŌĆ”
- 50. Competition Vs. Goal-orientation ’éŚ Our school systems are preparing our children for competitionŌĆ” ’éŚ If Baby ŌĆ£AŌĆØ focus on competition strategy and baby ŌĆ£BŌĆØ focus on Goal-orientation strategy, after 20 years who will be successful? ŌĆó Who are successful in this world Goal oriented or competition oriented? ŌĆó Do you know any person who got success with competition oriented strategy?
- 52. The Law of Pain and Gain
- 53. The Law of Pain and Gain ’éŚ There are two forces that motivate people to do what they do: ’éŚ the desire to avoid pain or ’éŚ the desire to gain pleasure. ’éŚ The decisions you make, the actions you take, and the habits you indulge in, are all based upon this principle.
- 54. ’éŚ What drive our behavior is instinctive reaction to pain and pleasure, not intellectual calculation. (many times our emotions/the sensations that we link to our thoughts rather our intellect that really drives us) ’éŚ Remember:We all do more to avoid pain than we will to gain pleasure. ’éŚ WHEN DO PEOPLE CHANGE?When cost of no change is greater than cost of change, people change.
- 55. Use of Pain and Gain ’éŚ What we can learn from this? ’éŚ We can learn to condition our minds, bodies, and emotions to link massive pain or pleasure to whatever we choose. By changing what we link pain and pleasure to, we will instantly change our behavior. ’éŚ i.e Advertisers clearly understand that what drives us is not so much our intellect as the sensations that we link to their products. ’éŚ When our emotions are at their peak, sensations are their most intense, they flash an image of their product continuously until we link it to these desired feeling.
- 57. Miss use of this law ’éŚ Most people focus on how to avoid pain and gain pleasure in the short tem, and thereby create ling-term pain fro themselves.
- 58. ’éŚ 1. Pain-associating questions: ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What will this cost you?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What has it cost you in the past?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What is it costing the people you love?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What is it costing you in (vehicleŌĆöwork, family, etc.)?ŌĆØ ’éŚ 2. Pleasure-associating questions: ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£If you change this now, how will your life be?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What will you gain?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What will it mean for the people you love?ŌĆØ ’éŚ ŌĆó ŌĆ£What will it give you?ŌĆØ
- 59. Non-Cognitive approaches ’éŚ The reinforcement strategy ’éŚ 1. Positive reinforcement ’éŚ 2. Negative reinforcement ’éŚ 3. Punishment ’éŚ 4. Extinction ’éŚ 4. Extinction
- 60. Reinforcement theory can be applied using a set of techniques known as behavior modification. ’éŚ 1. Positive reinforcement ’éŚ Refers to increasing the frequency of a behavior by following the behavior with a pleasurable consequences ’éŚ 2. Negative reinforcement ’éŚ Increase the frequency of a behavior by removing something displeasureable after the behavior is performed. ’éŚ 3. Punishment ’éŚ Seeks to decrease the frequency of a behavior by introducing an adverse consequence immediately after the behavior. ’éŚ 4. Extinction ’éŚ Seeks to decrease the frequency of a behavior by removing the consequence that is reinforcing it.
- 61. Belief Systems: The Power to Create and The Power to Destroy Motivation ’éŚ The most powerful motivation comes from within our belief system. ’éŚ A belief is a ŌĆ£feeling of certainty about somethingŌĆØ. ’éŚ People will do a lot for money, more for a good leader, but most for a belief. ’éŚ It is not the events of our lives that shapes us, but our beliefs (the meaning we attach/how interpret to those events).
- 62. ’éŚ Beliefs are guiding forces to tell us what will lead to pain and what will lead to pleasure. ’éŚ Once accepted our beliefs become unquestioned commands to our nervous system and affect our immune systems and can either give us the resolve to take action, or weaken and destroy our motivation. ’éŚ Beliefs can impact on our emotions, actions and bodies, diseases. ’éŚ Our beliefs about the illness and its treatment play more significant role than the treatment itself (Psychoneuroimmunology; mind body relationship).
- 63. ’éŚ A false or limiting belief is also a belief. ’éŚ People so often develop limiting beliefs about who they are and what they are capable of because they havenŌĆÖt succeeded in the past. ’éŚ What is the difference between Optimistic and Pessimistic people? ’éŚ To change Beliefs: ’éŚ get your brain to associate massive pain to the old belief the associate tremendous pleasure to the idea of adopting a new empowering belief. ’éŚ Create doubts and start questioning your limiting beliefsŌĆ” then see the magic of MotivationŌĆ”. ’éŚ Remember: If you want to create long term and consistent changes in your behavior, you must change the BELIEFS that are holding you back.
- 64. Power of Imagination and Motivation ’éŚ You can succeed if you imagine something (i.e. your success) vividly enough just as easily as if you had the actual experiences. (used in self hypnosis) ’éŚ ThatŌĆÖs because our brains canŌĆÖt tell the difference between something we have vividly imagined and something we have actually experienced. ’éŚ With enough emotional intensity and repetition, our nervous systems experience something as real, even it hasnŌĆÖt occurred yet.
- 65. ’éŚ Intensify and increase number of outputs/results of behavior. ’éŚ For example:After completion of my PhD degree I will get; 1. A doctorate degree 2. Word DR. before my name 3. A good job 4. A status and respect in society 5. Handful earning 6. Proud for my parents 7. Making my dreams true 8. Having, home, car, bank balance 9. Opportunity to serve my society, country, religion 10. A happy married life
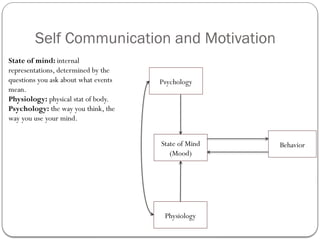
- 66. Self Communication and Motivation Behavior State of Mind (Mood) Psychology Physiology State of mind: internal representations, determined by the questions you ask about what events mean. Physiology: physical stat of body. Psychology: the way you think, the way you use your mind.
- 67. ’éŚ Problem Frame in Physiology and Psychology: ’éŚ WhatŌĆÖs wrong? ’éŚ When did it start? ’éŚ Whose fault is it? ’éŚ Why do these things happen to me only? ’éŚ How this problem limits me? ’éŚ How long have I had this problem? ’éŚ How does this problem cause me to fail? On average you use 48000-60000 words a day. Analyze the words you talk to yourself. Change the way you talk to yourself. Especially at the beginning of the day.
- 68. ’éŚ Solution Frame in Physiology and Psychology ’éŚ How can I make things better? ’éŚ What did I learn? ’éŚ How can I be better next time? ’éŚ When I get what I want, how will my life improve? ’éŚ What will I do to begin getting what I want? ’éŚ Why I am so fortune? ’éŚ Which part of my life is most blessed? ’éŚ What can I do to make a positive difference in my personal life? ’éŚ Where can I find the best learning opportunities today?
- 69. ’éŚ Exercise 01: ’éŚ Step one: ’éŚ Think about something bad/problem.And pretend you are depressed. Sit, talk, breath like you are depressed.And then feel the inner feelings and energy level. ’éŚ Step two: ’éŚ With same thinking, stand up, stretch your body, increase your voice, hit your chest And then feel the inner feelings and energy level.
- 70. Take full responsibility of RESULTS ’éŚ Take full responsibility: we have to inculcate in ourselves the belief that we are responsible for our actions/behavior. ’éŚ Making excuses/complaints cant give you full control on your Motivation/Actions ’éŚ Never think yourself a ŌĆ£VICTIMŌĆØ
- 71. Scare & Grief
- 72. Few more ideas to motivate ’éŚ 1. Live for others.Always focus that what is there in it for othersŌĆ” ’éŚ 2. DonŌĆÖt bother about those things that are not directly related to you or not under your control. ’éŚ 3.Take ALLAH (the creator) with you
- 73. Use your power of Choice ’éŚ You are free to choose. ’éŚ You are product of choice not chance (nature, environment, circumstances) ’éŚ Advice: Become selfish about yourselfŌĆ”..