Endocrine online
Download as ppt, pdf3 likes684 views
The document discusses the endocrine system and hormone function. It covers topics such as: - The main endocrine glands that release hormones and their functions in controlling cell activity and metabolism. - The two main mechanisms by which hormones act - through membrane receptors or by directly interacting with DNA. - How hormones bind to target cells and cause changes through second messengers or gene transcription. - Negative feedback loops help control hormone release by inhibiting upstream glands from producing more hormones.
1 of 16
Download to read offline









Ad
Recommended
Endocrine system
Endocrine systemtazuddin
Ìı
The endocrine system regulates metabolic processes through hormones secreted into the bloodstream. The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, thymus, pancreas, and gonads. Hormones influence target cells through second messenger systems or direct gene activation. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland regulate other endocrine glands through feedback loops to maintain homeostasis.Hormones and their functions.
Hormones and their functions.Pabna University Of Science and Technology
Ìı
This document is an assignment on hormones within the pharmacology course, covering various aspects such as definitions, classifications, and functions of hormones produced by endocrine glands. It details steroid and non-steroid hormones, their modes of action, and the effects of adrenocorticosteroids, including relevant diseases and hormone therapies. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of hormones in life and the necessity of understanding their functions and related disorders.Effect of Exercise on Endocrine System
Effect of Exercise on Endocrine SystemShalu Thariwal
Ìı
The document discusses the impact of exercise on the endocrine system, highlighting the roles of various hormones and glands involved in physiological responses to physical activity. It explains how hormone levels change with exercise, the effects of both acute and chronic exercise on hormone secretion, and the regulatory feedback mechanisms in the endocrine system. Additionally, it reviews studies on hormonal responses to resistance training and aerobic exercise, focusing on growth hormone, testosterone, and cortisol among others.Hormone new 1 (2)
Hormone new 1 (2)Sania Tahir
Ìı
This document discusses molecular endocrinology and hormones. It defines endocrinology, describes the major endocrine glands and hormones, and explains hormone structure, synthesis, mechanisms of action, transport, and regulation. Key points include that hormones act as chemical messengers to modify distant organ functions, are produced in one part of the body and carried via circulation to target tissues, and include proteins, peptides, amino acid derivatives, and steroids. Human physiology part 6
Human physiology part 6john paul Oliveros
Ìı
The document summarizes principles of hormonal control systems, including:
1) There are three main classes of hormones - amines, peptides/proteins, and steroids. Thyroid hormones are amine derivatives, while peptide hormones make up the majority. Steroids are produced in the adrenal cortex and gonads.
2) Hormones are transported through the blood and interact with target cells via membrane or intracellular receptors to exert their effects on processes like metabolism and growth.
3) The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a key control system, with the hypothalamus secreting releasing hormones to stimulate the anterior pituitary's release of trophic hormones that target endocrine glands.Hormone
HormoneFarhan Ali
Ìı
Hormones act through specific receptors on target cells. Hormone receptors are large proteins that determine the specificity of hormone action. Hormones can act by changing membrane permeability, binding to intracellular receptors to affect gene expression, or activating second messengers through G-protein coupling which then mediate the hormone's physiological response. Hormone action can also occur via tyrosine kinase activation either through receptors with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity or receptors that activate tyrosine kinases.Hormones 1гоÑовÑй new
Hormones 1гоÑовÑй newKamara Saidu Paul
Ìı
Hormones act as biological regulators through three main levels - the nervous system, hormonal regulation, and intracellular enzymes. There are two main types of hormones - those produced by endocrine glands which enter the bloodstream, and local hormones which regulate tissues locally. Hormones regulate key processes like metabolism, digestion, and ion concentration in the body. They act through receptors on the surface of cells or inside cells, and trigger second messengers that lead to biological responses like protein synthesis. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland work together to regulate other endocrine glands and control numerous bodily functions through hormone release and feedback loops.Presentation 19 - Chemical Signals In Animals
Presentation 19 - Chemical Signals In AnimalsMa'am Dawn
Ìı
Hormones are chemical signals produced by glands that are transported to target organs to induce responses. They bind to receptors in cell membranes or nuclei to exert effects. Hormone levels and receptor function are controlled by feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. The endocrine system regulates processes like growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the action of hormones, while the nervous system provides more rapid responses. Diseases can occur if hormone levels become abnormal or receptors are damaged.Action of hormones
Action of hormonesRohit Paswan
Ìı
Hormones bind to specific receptors that initiate cellular responses. Water-soluble hormones bind to membrane receptors, while lipid-soluble hormones bind to intracellular receptors. Receptor activation leads to second messenger systems or direct gene activation, amplifying the hormone's effects and eliciting responses like muscle contraction, secretion, transport changes, or metabolic effects.Mechanism & action hormone
Mechanism & action hormoneInternational Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
1) Hormones are organic substances that regulate growth, metabolism and other functions by acting as biochemical messengers. They can be classified based on their chemical composition and target organs.
2) Hormone action involves processes like synergism, permissiveness, antagonism and feedback loops. Lipid-soluble hormones like steroids directly enter cells and activate genes, while water-soluble hormones trigger intracellular signaling cascades.
3) The document discusses the mechanisms and characteristics of hormone action, including the different classes of receptors, signal amplification pathways, and how lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones elicit their effects on target cells and tissues. Negative and positive feedback loops help regulate hormone secretion.Biochemistry of hormones
Biochemistry of hormonesSeenam Iftikhar
Ìı
Hormones are chemical substances produced in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and cause changes to structures and functions in distant target organs. There are two main types of hormone receptors - cell surface receptors for water-soluble hormones that generate intracellular messengers, and intracellular receptors for lipid-soluble hormones that alter gene expression. Hormones regulate important bodily functions like growth, metabolism, mood, immune response, reproduction, and preparing the body for events like puberty or stress. The effects of hormones are controlled by their rates of secretion, transport, receptor levels in target tissues, and degradation.Molecular endocrine2
Molecular endocrine2International Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
This document summarizes the biosynthesis of the main categories of hormones: peptides and proteins, steroids, amino acid derivatives, and fatty acid derivatives. It discusses the processes of gene transcription and translation that produce peptide hormones. It explains how steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol in the mitochondria, and their lipid solubility allows diffusion into target cells. Amino acid derivatives include thyroid hormones and catecholamines from tyrosine. Fatty acid derivatives include eicosanoids like prostaglandins. The document also summarizes the mechanisms of action for hydrophilic and lipophilic hormones, including cell surface receptors and nuclear receptors, and signal transduction pathways.Sistem endokrin bs2
Sistem endokrin bs2Risky Indra Kurniawan
Ìı
This document discusses the mechanism of hormone action in the human body. It describes the different types of chemical messenger systems including endocrine hormones, which are released into the bloodstream and influence distant target cells. The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to regulate various bodily functions through negative and positive feedback loops. Hormones can act as paracrines, autocrines, or cytokines. The complexity of the endocrine system is also summarized.Molecular and Cell Biology of the Endocrine System
Molecular and Cell Biology of the Endocrine SystemImhotep Virtual Medical School
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system and hormone-receptor interactions. It describes the endocrine system's role in maintaining homeostasis through feedback loops and its effects on various physiological processes. Hormones can be classified into different categories based on their chemical structure and include peptides, proteins, steroids, and vitamin derivatives. Hormones act by binding to specific receptors located on cells and tissues, and receptor activation initiates intracellular signaling cascades that allow hormones to exert their effects. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland play central roles in regulating other endocrine glands.Signalling mechanism of hormones and neuroendocrine
Signalling mechanism of hormones and neuroendocrineBurhan Umer
Ìı
This document summarizes various aspects of hormone signalling mechanisms, including their classification, synthesis, receptors, and measurement. It discusses how hormones can act through second messenger systems or by activating genes after binding with nuclear receptors. Feedback control of hormone secretion can be negative or positive.hormones: mechanism amd action 2
hormones: mechanism amd action 2International Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
Hormones act through specific receptors and pathways to regulate target tissues. Water-soluble hormones bind to cell membrane receptors and use second messengers like cAMP to trigger intracellular effects. Lipid-soluble hormones like steroids diffuse into cells, bind intracellular receptors, and form complexes that regulate gene expression. Hormone levels are maintained through feedback loops, with negative feedback inhibiting further hormone release and positive feedback amplifying it. Hormones are cleared by metabolic degradation, binding to tissues, and excretion by the liver and kidneys.Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modified
Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modifiedTeal Agency by Joe Bolu Company
Ìı
Hormones are classified based on their mechanism of action and solubility. Lipophilic hormones diffuse into cells and bind intracellular receptors, while hydrophilic hormones trigger second messenger systems. Hormone levels are measured using sensitive radioimmunoassay or ELISA techniques. Radioimmunoassay relies on competition between natural and tagged hormones for antibody binding sites. ELISA uses multiple antibodies to capture hormones and an enzyme reaction to detect hormone amounts proportional to concentrations. These assays allow detection of hormones present in extremely low quantities in the blood. lect 2 introduction to hormones 2021
lect 2 introduction to hormones 2021Dr Shamshad Begum loni
Ìı
This lecture introduces hormones, including their classification, synthesis, secretion, transport, and measurement. Hormones are chemical substances secreted into the bloodstream that influence target cells. They are classified by chemical structure as proteins/polypeptides, steroids, or derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. Hormones act through receptor binding and intracellular signaling to regulate processes like homeostasis, growth, development, and reproduction. Their effects are modulated by feedback loops and vary over daily/seasonal cycles. Measurement techniques include bioassays, radioimmunoassays, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.Endocrine system parta
Endocrine system partaAHarris07
Ìı
The endocrine system regulates activities in the body through hormone signals. Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted in small amounts and travel through the bloodstream to target tissues. Their effects are generally slower but longer lasting than the nervous system. Hormones can communicate between cells as autocrine, paracrine, or pheromone signals. They have various chemical structures including proteins, lipids, and steroids. Hormone secretion is controlled through feedback loops between glands. Hormones are transported through the bloodstream and target tissues, where they interact with specific receptors to regulate functions up or down.Hormones
Hormoneswww.caafimaadka.net
Ìı
This document provides an overview of hormones, including:
1. Hormones are chemicals secreted by endocrine glands that travel through the blood and influence other glands and organs. There are two major classes: protein hormones and steroid hormones.
2. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control hormone release through negative feedback loops. The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland.
3. Hormone disorders can occur if glands do not produce the proper hormones. Examples include congenital adrenal hyperplasia and androgen insensitivity syndrome.Hormone action
Hormone actionDr. Aamir Ali Khan
Ìı
The document discusses the mechanisms and actions of hormones, defining them as biochemical messengers produced by glands that regulate various bodily functions. It classifies hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic categories based on their water solubility, detailing their interaction with cell receptors and how they influence gene activation and cellular responses. The document outlines the processes of action for both water-soluble and lipid-soluble hormones, emphasizing their unique pathways and roles in physiological effects.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE SYSTEMISF COLLEGE OF PHARMACY MOGA
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, detailing how endocrine hormones function as chemical signals that regulate various bodily processes. It explains the differences between peptide and steroid hormones, their mechanisms of action, and lists key hormones produced by the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs. Additionally, it highlights the role of other organs in hormone production and regulation of physiological functions.Lecture1
Lecture1Ahmed Hassan
Ìı
The document discusses several key topics in endocrine physiology:
1. It describes early endocrine experiments in the 1800s by Berthold and Bernard that helped establish the concepts of hormone targets and homeostasis.
2. It summarizes the major classes of hormones - peptides/proteins, amines, steroids, and eicosanoids - and how they are synthesized and regulated.
3. Feedback control mechanisms, especially negative feedback loops, are a major way the endocrine system regulates hormone production and maintains homeostasis.Endo 2 kevin
Endo 2 kevinKevin Balda
Ìı
Hormones act on target cells through receptor proteins and second messenger systems. Lipid-soluble hormones enter cells and activate nuclear receptors to regulate gene transcription. Water-soluble hormones bind membrane receptors and use second messengers like cAMP or Ca2+ to trigger intracellular responses. Insulin and growth factors activate tyrosine kinase receptors to phosphorylate proteins and regulate metabolism.Chapter+45
Chapter+45AlbanyHighSchool
Ìı
Both the nervous system and endocrine system regulate physiological processes, though they differ in their communication methods and response times. The endocrine system uses hormones like epinephrine, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters. Key endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries/testes, and thymus gland. Hormone signaling occurs via models like the protein/steroid models and involves signal transduction pathways.Hormones and their feedback system
Hormones and their feedback systemFiza Khan
Ìı
This document discusses chemical messengers and hormones, including:
1. Chemical messengers can be categorized as local messengers, neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, hormones, and pheromones. Hormones differ in that they are secreted by endocrine glands and circulate through the bloodstream to target distant cells.
2. Hormones control biochemical reactions in target cells by increasing substance transport, stimulating enzyme/protein synthesis, or activating/suppressing enzymes. The major classes of hormones are proteins, amines, steroids, and eicosanoids.
3. Hormone secretion is regulated by feedback control systems, which can be either positive or negative. Negative feedback systems help maintainthe regulation of hormone secretion
the regulation of hormone secretionDe Toute Beauté KäVëëñ
Ìı
The document discusses various releasing hormones including corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), and growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). These releasing hormones are produced by the hypothalamus and stimulate the secretion of other hormones from the anterior pituitary gland, including adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), and growth hormone (GH). The releasing hormones play an important role in stress response, metabolism, reproduction, and postnatal growth.Mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling molecules
Mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling moleculesKoppukonda Shanthi
Ìı
The document discusses the mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling molecules. It describes how hormones can act through cell surface receptors or intracellular receptors. The cyclic AMP pathway is explained in detail, where a hormone binds to a G protein-coupled receptor, activating G proteins and adenylate cyclase to produce the second messenger cyclic AMP. Cyclic AMP then activates protein kinase A and a phosphorylation cascade, regulating processes like glycogen breakdown. Calcium signaling is also summarized, involving calcium release from intracellular stores and activation of calcium binding proteins.Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmones
Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmonesraj kumar
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of endocrine glands and hormones. It describes how hormones are secreted into the blood and carried to target cells containing receptor proteins. Hormones affect metabolism in target organs and help regulate body processes. The major types of hormones include amines, polypeptides, proteins, lipids, and glycoproteins. Hormones can act through nuclear receptors, second messengers, or tyrosine kinase pathways to produce effects in target cells. The pituitary gland contains anterior and posterior lobes that secrete trophic and other hormones important for regulation.Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmones
Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmonesraj kumar
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of endocrine glands and hormones. It describes how endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to target distant cells. Hormones can be classified based on their chemical structure as amines, polypeptides, lipids, glycoproteins, or prohormones/prehormones. Hormones act through nuclear receptors, second messengers, or tyrosine kinase pathways to regulate metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pancreatic glands are described in terms of their hormone secretions and functions.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Action of hormones
Action of hormonesRohit Paswan
Ìı
Hormones bind to specific receptors that initiate cellular responses. Water-soluble hormones bind to membrane receptors, while lipid-soluble hormones bind to intracellular receptors. Receptor activation leads to second messenger systems or direct gene activation, amplifying the hormone's effects and eliciting responses like muscle contraction, secretion, transport changes, or metabolic effects.Mechanism & action hormone
Mechanism & action hormoneInternational Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
1) Hormones are organic substances that regulate growth, metabolism and other functions by acting as biochemical messengers. They can be classified based on their chemical composition and target organs.
2) Hormone action involves processes like synergism, permissiveness, antagonism and feedback loops. Lipid-soluble hormones like steroids directly enter cells and activate genes, while water-soluble hormones trigger intracellular signaling cascades.
3) The document discusses the mechanisms and characteristics of hormone action, including the different classes of receptors, signal amplification pathways, and how lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones elicit their effects on target cells and tissues. Negative and positive feedback loops help regulate hormone secretion.Biochemistry of hormones
Biochemistry of hormonesSeenam Iftikhar
Ìı
Hormones are chemical substances produced in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and cause changes to structures and functions in distant target organs. There are two main types of hormone receptors - cell surface receptors for water-soluble hormones that generate intracellular messengers, and intracellular receptors for lipid-soluble hormones that alter gene expression. Hormones regulate important bodily functions like growth, metabolism, mood, immune response, reproduction, and preparing the body for events like puberty or stress. The effects of hormones are controlled by their rates of secretion, transport, receptor levels in target tissues, and degradation.Molecular endocrine2
Molecular endocrine2International Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
This document summarizes the biosynthesis of the main categories of hormones: peptides and proteins, steroids, amino acid derivatives, and fatty acid derivatives. It discusses the processes of gene transcription and translation that produce peptide hormones. It explains how steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol in the mitochondria, and their lipid solubility allows diffusion into target cells. Amino acid derivatives include thyroid hormones and catecholamines from tyrosine. Fatty acid derivatives include eicosanoids like prostaglandins. The document also summarizes the mechanisms of action for hydrophilic and lipophilic hormones, including cell surface receptors and nuclear receptors, and signal transduction pathways.Sistem endokrin bs2
Sistem endokrin bs2Risky Indra Kurniawan
Ìı
This document discusses the mechanism of hormone action in the human body. It describes the different types of chemical messenger systems including endocrine hormones, which are released into the bloodstream and influence distant target cells. The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to regulate various bodily functions through negative and positive feedback loops. Hormones can act as paracrines, autocrines, or cytokines. The complexity of the endocrine system is also summarized.Molecular and Cell Biology of the Endocrine System
Molecular and Cell Biology of the Endocrine SystemImhotep Virtual Medical School
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system and hormone-receptor interactions. It describes the endocrine system's role in maintaining homeostasis through feedback loops and its effects on various physiological processes. Hormones can be classified into different categories based on their chemical structure and include peptides, proteins, steroids, and vitamin derivatives. Hormones act by binding to specific receptors located on cells and tissues, and receptor activation initiates intracellular signaling cascades that allow hormones to exert their effects. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland play central roles in regulating other endocrine glands.Signalling mechanism of hormones and neuroendocrine
Signalling mechanism of hormones and neuroendocrineBurhan Umer
Ìı
This document summarizes various aspects of hormone signalling mechanisms, including their classification, synthesis, receptors, and measurement. It discusses how hormones can act through second messenger systems or by activating genes after binding with nuclear receptors. Feedback control of hormone secretion can be negative or positive.hormones: mechanism amd action 2
hormones: mechanism amd action 2International Medicine School - Management and Science University
Ìı
Hormones act through specific receptors and pathways to regulate target tissues. Water-soluble hormones bind to cell membrane receptors and use second messengers like cAMP to trigger intracellular effects. Lipid-soluble hormones like steroids diffuse into cells, bind intracellular receptors, and form complexes that regulate gene expression. Hormone levels are maintained through feedback loops, with negative feedback inhibiting further hormone release and positive feedback amplifying it. Hormones are cleared by metabolic degradation, binding to tissues, and excretion by the liver and kidneys.Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modified
Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modifiedTeal Agency by Joe Bolu Company
Ìı
Hormones are classified based on their mechanism of action and solubility. Lipophilic hormones diffuse into cells and bind intracellular receptors, while hydrophilic hormones trigger second messenger systems. Hormone levels are measured using sensitive radioimmunoassay or ELISA techniques. Radioimmunoassay relies on competition between natural and tagged hormones for antibody binding sites. ELISA uses multiple antibodies to capture hormones and an enzyme reaction to detect hormone amounts proportional to concentrations. These assays allow detection of hormones present in extremely low quantities in the blood. lect 2 introduction to hormones 2021
lect 2 introduction to hormones 2021Dr Shamshad Begum loni
Ìı
This lecture introduces hormones, including their classification, synthesis, secretion, transport, and measurement. Hormones are chemical substances secreted into the bloodstream that influence target cells. They are classified by chemical structure as proteins/polypeptides, steroids, or derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. Hormones act through receptor binding and intracellular signaling to regulate processes like homeostasis, growth, development, and reproduction. Their effects are modulated by feedback loops and vary over daily/seasonal cycles. Measurement techniques include bioassays, radioimmunoassays, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.Endocrine system parta
Endocrine system partaAHarris07
Ìı
The endocrine system regulates activities in the body through hormone signals. Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted in small amounts and travel through the bloodstream to target tissues. Their effects are generally slower but longer lasting than the nervous system. Hormones can communicate between cells as autocrine, paracrine, or pheromone signals. They have various chemical structures including proteins, lipids, and steroids. Hormone secretion is controlled through feedback loops between glands. Hormones are transported through the bloodstream and target tissues, where they interact with specific receptors to regulate functions up or down.Hormones
Hormoneswww.caafimaadka.net
Ìı
This document provides an overview of hormones, including:
1. Hormones are chemicals secreted by endocrine glands that travel through the blood and influence other glands and organs. There are two major classes: protein hormones and steroid hormones.
2. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control hormone release through negative feedback loops. The hypothalamus secretes hormones that stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland.
3. Hormone disorders can occur if glands do not produce the proper hormones. Examples include congenital adrenal hyperplasia and androgen insensitivity syndrome.Hormone action
Hormone actionDr. Aamir Ali Khan
Ìı
The document discusses the mechanisms and actions of hormones, defining them as biochemical messengers produced by glands that regulate various bodily functions. It classifies hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic categories based on their water solubility, detailing their interaction with cell receptors and how they influence gene activation and cellular responses. The document outlines the processes of action for both water-soluble and lipid-soluble hormones, emphasizing their unique pathways and roles in physiological effects.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE SYSTEMISF COLLEGE OF PHARMACY MOGA
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, detailing how endocrine hormones function as chemical signals that regulate various bodily processes. It explains the differences between peptide and steroid hormones, their mechanisms of action, and lists key hormones produced by the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs. Additionally, it highlights the role of other organs in hormone production and regulation of physiological functions.Lecture1
Lecture1Ahmed Hassan
Ìı
The document discusses several key topics in endocrine physiology:
1. It describes early endocrine experiments in the 1800s by Berthold and Bernard that helped establish the concepts of hormone targets and homeostasis.
2. It summarizes the major classes of hormones - peptides/proteins, amines, steroids, and eicosanoids - and how they are synthesized and regulated.
3. Feedback control mechanisms, especially negative feedback loops, are a major way the endocrine system regulates hormone production and maintains homeostasis.Endo 2 kevin
Endo 2 kevinKevin Balda
Ìı
Hormones act on target cells through receptor proteins and second messenger systems. Lipid-soluble hormones enter cells and activate nuclear receptors to regulate gene transcription. Water-soluble hormones bind membrane receptors and use second messengers like cAMP or Ca2+ to trigger intracellular responses. Insulin and growth factors activate tyrosine kinase receptors to phosphorylate proteins and regulate metabolism.Chapter+45
Chapter+45AlbanyHighSchool
Ìı
Both the nervous system and endocrine system regulate physiological processes, though they differ in their communication methods and response times. The endocrine system uses hormones like epinephrine, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters. Key endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries/testes, and thymus gland. Hormone signaling occurs via models like the protein/steroid models and involves signal transduction pathways.Hormones and their feedback system
Hormones and their feedback systemFiza Khan
Ìı
This document discusses chemical messengers and hormones, including:
1. Chemical messengers can be categorized as local messengers, neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, hormones, and pheromones. Hormones differ in that they are secreted by endocrine glands and circulate through the bloodstream to target distant cells.
2. Hormones control biochemical reactions in target cells by increasing substance transport, stimulating enzyme/protein synthesis, or activating/suppressing enzymes. The major classes of hormones are proteins, amines, steroids, and eicosanoids.
3. Hormone secretion is regulated by feedback control systems, which can be either positive or negative. Negative feedback systems help maintainthe regulation of hormone secretion
the regulation of hormone secretionDe Toute Beauté KäVëëñ
Ìı
The document discusses various releasing hormones including corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), and growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). These releasing hormones are produced by the hypothalamus and stimulate the secretion of other hormones from the anterior pituitary gland, including adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), and growth hormone (GH). The releasing hormones play an important role in stress response, metabolism, reproduction, and postnatal growth.Mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling molecules
Mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling moleculesKoppukonda Shanthi
Ìı
The document discusses the mechanisms of action of hormones and signaling molecules. It describes how hormones can act through cell surface receptors or intracellular receptors. The cyclic AMP pathway is explained in detail, where a hormone binds to a G protein-coupled receptor, activating G proteins and adenylate cyclase to produce the second messenger cyclic AMP. Cyclic AMP then activates protein kinase A and a phosphorylation cascade, regulating processes like glycogen breakdown. Calcium signaling is also summarized, involving calcium release from intracellular stores and activation of calcium binding proteins.Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modified
Mechanism of action of hormones (babajimi joseph b.i. et al)modifiedTeal Agency by Joe Bolu Company
Ìı
Similar to Endocrine online (20)
Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmones
Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmonesraj kumar
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of endocrine glands and hormones. It describes how hormones are secreted into the blood and carried to target cells containing receptor proteins. Hormones affect metabolism in target organs and help regulate body processes. The major types of hormones include amines, polypeptides, proteins, lipids, and glycoproteins. Hormones can act through nuclear receptors, second messengers, or tyrosine kinase pathways to produce effects in target cells. The pituitary gland contains anterior and posterior lobes that secrete trophic and other hormones important for regulation.Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmones
Endocrine Glands; Secretion&Action Of Harmonesraj kumar
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of endocrine glands and hormones. It describes how endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to target distant cells. Hormones can be classified based on their chemical structure as amines, polypeptides, lipids, glycoproteins, or prohormones/prehormones. Hormones act through nuclear receptors, second messengers, or tyrosine kinase pathways to regulate metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pancreatic glands are described in terms of their hormone secretions and functions.Endocrine glands
Endocrine glandsChy Yong
Ìı
The document discusses endocrine glands and hormones. It explains that endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, lacking ducts, and hormones are carried to target cells containing receptors. Hormones affect metabolism and regulate body processes like growth and reproduction. The mechanisms of hormone action depend on their chemical structure, with some binding to nuclear receptors to alter gene expression and others using second messengers to enact cellular responses. The pituitary gland is described as having anterior and posterior lobes that secrete trophic and regulatory hormones under control of the hypothalamus.1. Hormones and their examples, characteristics
1. Hormones and their examples, characteristicsRichmondOheneAddo
Ìı
The document provides a comprehensive overview of hormones, including their definitions, classifications, mechanisms of action, and clinical correlations. It covers various types of hormones such as hormonal amines, steroids, and peptides, detailing their chemical properties, signaling pathways, and effects on cellular functions. The text also discusses the regulation of hormone levels and includes clinical examples related to hormone signaling and its impact on health.Hormones and related diseases.......pptx
Hormones and related diseases.......pptxAlyaaKaram1
Ìı
This document discusses hormones, their mechanisms of action, and related diseases. It begins with an introduction to hormones and their roles in the body. Hormones act through receptors on cells and can elicit cellular responses through second messengers like cAMP or calcium. The document then discusses hormone synthesis, storage, release, transport, and the feedback loops that regulate hormone levels. Specific sections cover steroid hormone action, protein hormone signaling, receptors, and examples like insulin. Abnormalities in hormone signaling can cause diseases related to hormone excess or deficiency.Intoduction to endocrine
Intoduction to endocrineluxaeterna556
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, its physiology, and how hormones function. It describes various types of hormones, their mechanisms of action, and the regulation of hormonal secretion through feedback systems. Additionally, it discusses hormone transport, disposal, and measurement methods, along with the location of major endocrine glands.Endocrine System
Endocrine Systemthana123
Ìı
The document discusses the endocrine system and hormones. It defines hormones as regulatory substances released by cells to regulate other cells. Hormones can travel through different systems like endocrine, neuroendocrine, and paracrine systems. The key glands of the endocrine system include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads. Hormones maintain homeostasis, growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction. The document discusses the different types of hormones like proteins/peptides, steroids, and amines as well as their synthesis and mechanisms of action.Endocrine new.ppt
Endocrine new.pptAnnaKhurshid
Ìı
The document discusses the endocrine system, which regulates homeostasis through the secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream. It describes the major endocrine glands and hormones, including the hypothalamus and pituitary gland which regulate other glands. The hormones act on target cells through various mechanisms, such as binding to intracellular receptors to activate genes or binding to cell surface receptors and triggering secondary messengers like cAMP. The endocrine system works in tandem with the nervous system to coordinate bodily functions.Introduction to hormones
Introduction to hormones Dr Shamshad Begum loni
Ìı
This document provides an introduction to hormones, including their classification, synthesis, secretion, transport, and measurement. The key points are:
1. Hormones are chemical substances secreted into the blood that influence target cells elsewhere in the body. They are classified by their chemical structure as proteins/polypeptides, steroids, or derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine.
2. Hormones are synthesized and secreted via different mechanisms depending on their chemical properties. They are transported through the blood, often bound to plasma proteins, and cleared from the blood through various metabolic and excretory pathways.
3. Hormone levels in the blood are measured using techniques like radioimmunoassay (RIA)Endocrine biochemistryyyyyyy in endocrinology.ppt
Endocrine biochemistryyyyyyy in endocrinology.pptAnnaKhurshid
Ìı
The endocrine system, alongside the nervous system, regulates fundamental bodily functions through hormones, which are chemical messengers transported via the bloodstream to target cells. It maintains internal balance, coordinates growth and development, and controls sexual reproduction through mechanisms including positive and negative feedback. Hormones vary in structure, including proteins, amino acids, and steroids, and their actions significantly impact physiological responses such as metabolism, behavior, and homeostasis.BCH 2103 Part 1.pdf
BCH 2103 Part 1.pdfFRANCISLOLEM
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of endocrine system mechanisms including:
1. Hormones are chemical signals released from endocrine glands that target and regulate distant cells and tissues. They are transported via the bloodstream and elicit slow, long-lasting responses.
2. The endocrine and nervous systems are both communication systems but differ in target specificity, signal type, speed of signal/effect, duration of effect, and type of control and action.
3. Major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, pineal gland, and parathyroid glands. Many other organs have secondary endocrine functions.HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMMeegsEstabillo2
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of the endocrine system and pituitary gland:
- The endocrine system regulates reproduction, growth, metabolism, and other processes via hormones transported by the bloodstream. The pituitary gland and hypothalamus play central roles by controlling hormone release.
- The hypothalamus regulates the posterior pituitary via neural connections and the anterior pituitary via hypothalamic-releasing hormones transported through a portal system.
- The posterior pituitary stores and releases oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) under neural control. ADH deficiency or excess can cause diabetes insipidus or water retention disorders.10-INTRODUCTION-TO-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM.pptx
10-INTRODUCTION-TO-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM.pptxAminaAkhtar7
Ìı
The endocrine system is a network of glands producing hormones that regulate bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood. Hormones are classified into autocrine, paracrine, neurotransmitter, and endocrine messengers, with different mechanisms of action and stability based on their structure. Feedback control mechanisms, including negative and positive feedback, regulate hormone secretion, ensuring homeostasis and proper functioning of the endocrine system.Endocrine Physiology introduction.pptx
Endocrine Physiology introduction.pptxdina merzeban
Ìı
The endocrine system coordinates body functions through chemical messenger systems including hormones. Hormones can act locally as neurotransmitters or at distant sites as endocrine hormones. They are classified based on their site of secretion and target cells. The pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands and has anterior and posterior lobes that secrete hormones like growth hormone, ACTH, TSH, and oxytocin. Hormones act through cell surface receptors and intracellular signaling to regulate processes like growth, metabolism, and reproduction.Endocrine system Physiology introduction.pptx
Endocrine system Physiology introduction.pptxdina merzeban
Ìı
"This comprehensive PowerPoint presentation provides a detailed overview of the physiology of the endocrine system. Explore the intricate network of glands, hormones, and their target tissues that regulate essential bodily functions. Learn about the mechanisms of hormone action, including receptor binding and signal transduction. Discover the roles of major endocrine glands like the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and pancreas in maintaining homeostasis. This presentation is ideal for students, educators, and healthcare professionals seeking a clear and concise understanding of endocrine physiology. Key topics covered include:
* Hormone classification and synthesis
* Feedback mechanisms and regulation
* Specific gland functions and associated hormones
* Common endocrine disorders and their physiological basis
* Clinical correlations and applications
Whether you're preparing for an exam, teaching a class, or simply interested in the fascinating world of endocrinology, this PowerPoint offers a valuable resource for mastering the core principles of endocrine physiology."
hormone final.pptx
hormone final.pptxYadav Raj
Ìı
Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by endocrine glands and circulate in the bloodstream. They control metabolic processes and trigger physiological responses in target cells. There are two main classes of hormones - lipophilic hormones like steroids that pass through cell membranes to bind intracellular receptors, and hydrophilic peptides/amines that bind surface receptors and trigger intracellular signaling cascades using second messengers like cAMP or calcium. The endocrine system coordinates key body functions through the action of hormones, maintaining homeostasis.Ad
More from kmilaniBCC (13)
Endocrine ii online
Endocrine ii onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes the major endocrine glands and hormones of the human body. It describes the pituitary gland and its anterior and posterior lobes which secrete hormones that regulate other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pineal gland, pancreas and gonads are also outlined along with their key hormones and functions in maintaining homeostasis. Imbalances in certain hormones are discussed as they relate to diseases.Urinary anat online
Urinary anat onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of urine formation and the urinary system. It describes how the kidneys filter blood to form urine via glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and secretion. It then discusses the roles of the nephron, loop of Henle and hormones. Finally, it briefly outlines the functions of other urinary organs like the ureters, urinary bladder and urethra, and the process of urination.Kidney anat online
Kidney anat onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
This document provides an overview of the structure and function of the urinary system. It discusses the key organs - kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. It then focuses on kidney anatomy, including internal structures like the cortex, medulla and nephrons. Nephrons are described as the functional units that form urine, consisting of a glomerulus for filtration and renal tubules for processing. The mechanisms of blood filtration and urine production by nephrons are also summarized.Nutrients online
Nutrients onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document discusses nutrients and digestion. It defines the major nutrients - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. It describes their sources and functions. The document also discusses absorption of nutrients in the digestive system, regulation of food intake, obesity, and common digestive disorders like celiac disease, diarrhea, jaundice, and cancer.Digest anat online
Digest anat onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The digestive system consists of two main parts: the alimentary canal and accessory organs. The alimentary canal includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines and digests and absorbs food through mechanical and chemical processes. Accessory organs like the liver, pancreas and salivary glands produce enzymes that aid digestion. Food is ingested, propelled through the system, digested, absorbed in the small intestine, and waste is eliminated as feces in the large intestine and rectum.Digest ii online
Digest ii onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes the key accessory digestive glands - the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The pancreas secretes enzymes to break down nutrients and hormones to regulate blood sugar. The liver produces bile to emulsify fats and performs many metabolic functions. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver and releases it in response to food in the duodenum.Respiratory phys online
Respiratory phys onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
1) Breathing involves inspiration where gases flow into the lungs and expiration where gases exit. Changes in lung volume cause changes in pressure, driving gas flow.
2) Several factors influence breathing pressures, including atmospheric pressure, the elastic recoil of the lungs, and alveolar surface tension maintained by pulmonary surfactant.
3) The main muscles of breathing are the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles. Inspiration is an active process where muscles contract to increase lung volume, while expiration is usually passive as muscles relax.Respiratory anat online
Respiratory anat onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document provides an overview of the respiratory system, including both the superior and inferior respiratory organs and tissues. It describes the main functions of respiration which involves gas exchange in the lungs and transport of gases in the blood between the respiratory and circulatory systems. Key organs of the respiratory system are described such as the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and alveoli. The anatomy and tissues of these organs are summarized.Heart 2 online
Heart 2 onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document discusses the anatomy and physiology of the human heart. It describes the structure of cardiac muscle cells and how they contract. It explains that the heart contracts rhythmically through an electrical conduction system, generating action potentials that cause contractions. It details the roles of the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and Purkinje fibers in conducting electrical signals and coordinating atrial and ventricular contractions. It also discusses electrocardiography, the cardiac cycle, factors regulating heart rate, common heart diseases, and congestive heart failure.Heart 1 online
Heart 1 onlinekmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes the anatomy and function of the heart. It describes the layers of the heart tissue, including the epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. It outlines the four chambers of the heart - the right and left atria which receive blood, and the right and left ventricles which pump blood out. It details the heart valves that ensure one-way blood flow, including the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary and aortic valves. It explains the pathway of blood through the heart in both the pulmonary and systemic circuits.Blood online 1
Blood online 1kmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes key aspects of blood composition and function. It notes that blood consists of plasma and formed elements, including erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and transport oxygen throughout the body. The functions of blood include distribution of materials, regulation of processes like pH and temperature, and protection from infection and blood loss through clot formation. Red blood cells are produced through erythropoiesis in the bone marrow and their production is stimulated by the hormone erythropoietin. Common blood disorders like anemia result in a low oxygen-carrying capacity and can be caused by factors like blood loss, marrow destruction, and genetic mutationsBlood online 3
Blood online 3kmilaniBCC
Ìı
This document discusses human blood groups and types. It explains that blood types are determined by the presence or absence of antigens on red blood cells, specifically the A, B, and Rh antigens. People have one of four main blood types - A, B, AB, or O - depending on which antigens are present. It also describes how blood typing works by testing a blood sample against various antibodies to detect agglutination. The Rh factor further divides blood types into positive or negative based on the presence of the Rh antigen. Understanding blood groups is important for blood transfusions and preventing diseases like erythroblastosis fetalis.Blood online 2
Blood online 2kmilaniBCC
Ìı
The document summarizes the types and functions of white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets. There are two main types of leukocytes - granulocytes which have granules and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, and agranulocytes which lack granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes. Platelets are fragments of megakaryocytes that initiate clot formation through a process involving vascular constriction, platelet plug formation, and coagulation of fibrin to form a blood clot and stop bleeding. Disorders can involve excessive clotting leading to thromboembolism or inadequate clotting causing bleeding.Ad
Endocrine online
- 1. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 15 Part I Overview ïHormone types ïHormone activity
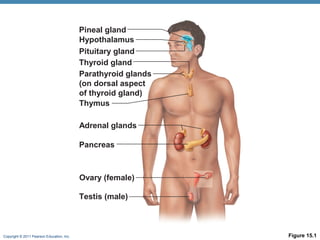
- 2. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Endocrine System Function ⢠Control cell activity ⢠metabolism ⢠Release hormones ⢠Slower control than CNS/PNS ⢠Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands
- 3. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Endocrine System: Overview ⢠Some organs have endocrine and exocrine function ⢠pancreas and gonads ⢠adipose cells, thymus, small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart ⢠Hypothalamus has neural and endocrine functions
- 4. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.1 Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Parathyroid glands (on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland) Thymus Thyroid gland Adrenal glands Pancreas Ovary (female) Testis (male)
- 5. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chemical Messengers ⢠Hormones: Long ranging chemical signals, travel through blood or lymph ⢠Autocrine: chemicals affect the cells that secretes them ⢠âself stimulatingâ ⢠Paracrine: locally acting chemicals that affect other cells
- 6. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Hormone Action ⢠How hormones cause change: 1. Open or close ion channels 2. Stimulate synthesis of proteins 3. Activate or deactivate enzymes 4. Induce secretion 5. Stimulate mitosis
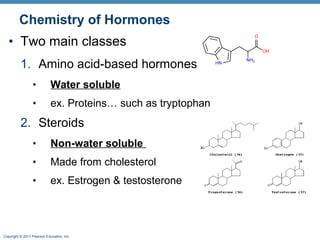
- 7. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chemistry of Hormones ⢠Two main classes 1. Amino acid-based hormones ⢠Water soluble ⢠ex. Proteins⦠such as tryptophan 2. Steroids ⢠Non-water soluble ⢠Made from cholesterol ⢠ex. Estrogen & testosterone
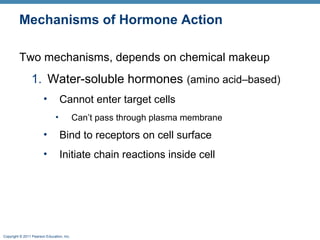
- 8. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Mechanisms of Hormone Action Two mechanisms, depends on chemical makeup 1. Water-soluble hormones (amino acidâbased) ⢠Cannot enter target cells ⢠Canât pass through plasma membrane ⢠Bind to receptors on cell surface ⢠Initiate chain reactions inside cell
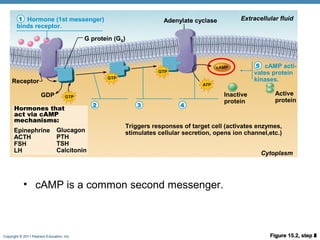
- 9. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Membrane Receptors and Second-Messengers ⢠Hormone signaling mechanism 1. Hormone (primary messenger) binds to surface receptor 2. Receptor activates internal signals(secondary messengers) 3. Triggers change in the cell ⢠Increased mitosis ⢠Protein production
- 10. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.2, step 1 Hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor. Receptor Hormones that act via cAMP mechanisms: Epinephrine ACTH FSH LH Extracellular fluid Cytoplasm Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin 1 Figure 15.2, step 2 Hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor. Receptor activates G protein (GS). Receptor G protein (GS) Hormones that act via cAMP mechanisms: Epinephrine ACTH FSH LH Extracellular fluid Cytoplasm GDP Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin 1 2 Figure 15.2, step 3 Hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor. Receptor activates G protein (GS). G protein activates adenylate cyclase. Receptor G protein (GS) Adenylate cyclase Hormones that act via cAMP mechanisms: Epinephrine ACTH FSH LH Extracellular fluid Cytoplasm GDP Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin 1 2 3 Figure 15.2, step 4 Hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor. Receptor G protein (GS) Adenylate cyclase Hormones that act via cAMP mechanisms: Epinephrine ACTH FSH LH Extracellular fluid Cytoplasm GDP Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin 1 2 3 4 Figure 15.2, step 5 Hormone (1st messenger) binds receptor. cAMP acti- vates protein kinases.Receptor G protein (GS) Adenylate cyclase Triggers responses of target cell (activates enzymes, stimulates cellular secretion, opens ion channel,etc.) Hormones that act via cAMP mechanisms: Epinephrine ACTH FSH LH Inactive protein Extracellular fluid Cytoplasm Active protein GDP Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin 1 4 5 ⢠cAMP is a common second messenger.
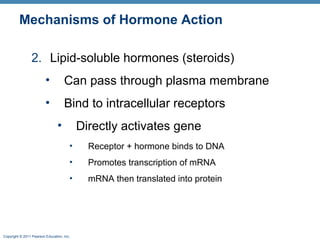
- 11. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Mechanisms of Hormone Action 2. Lipid-soluble hormones (steroids) ⢠Can pass through plasma membrane ⢠Bind to intracellular receptors ⢠Directly activates gene ⢠Receptor + hormone binds to DNA ⢠Promotes transcription of mRNA ⢠mRNA then translated into protein
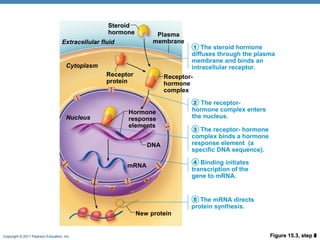
- 12. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.3, step 1 Receptor- hormone complex Receptor protein Cytoplasm Nucleus Extracellular fluid Steroid hormone The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptor. Plasma membrane 1 Figure 15.3, step 2 Receptor- hormone complex Receptor protein Cytoplasm Nucleus Extracellular fluid Steroid hormone The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptor. The receptor- hormone complex enters the nucleus. Plasma membrane 1 2 Figure 15.3, step 3 DNA Hormone response elements Receptor- hormone complex Receptor protein Cytoplasm Nucleus Extracellular fluid Steroid hormone The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptor. The receptor- hormone complex enters the nucleus. The receptor- hormone complex binds a hormone response element (a specific DNA sequence). Plasma membrane 1 2 3 Figure 15.3, step 4 mRNA DNA Hormone response elements Receptor- hormone complex Receptor protein Cytoplasm Nucleus Extracellular fluid Steroid hormone The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptor. The receptor- hormone complex enters the nucleus. The receptor- hormone complex binds a hormone response element (a specific DNA sequence). Binding initiates transcription of the gene to mRNA. Plasma membrane 1 2 3 4 Figure 15.3, step 5 mRNA New protein DNA Hormone response elements Receptor- hormone complex Receptor protein Cytoplasm Nucleus Extracellular fluid Steroid hormone The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds an intracellular receptor. The receptor- hormone complex enters the nucleus. The receptor- hormone complex binds a hormone response element (a specific DNA sequence). Binding initiates transcription of the gene to mRNA. The mRNA directs protein synthesis. Plasma membrane 1 2 3 4 5
- 13. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Target Cell Activation ⢠Target cell activation depends on: 1. Presence of receptor ⢠Target cells must have specific hormone receptors ⢠Receptors are often limited to specific tissues 1. Hormone concentration 2. Number of receptors on cell 3. binding of receptor and hormone
- 14. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Target Cell Activation ⢠Hormones can influence receptor numbers ⢠Up-regulation âmore receptors ⢠Down-regulation â lose receptors
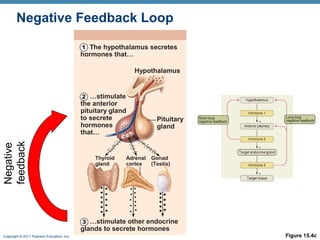
- 15. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Control of Hormone Release ⢠Negative feedback loops ⢠Help control hormone release ⢠Hormones produced inhibit upstream glands ⢠ex. To make hormone 3 you need hormones 1 and 2. ⢠Negative feedback loop is hormone 3 inhibits production of hormones 1 and 2. ⢠Prevents overproduction of hormones
- 16. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 15.4c Hypothalamus Thyroid gland Adrenal cortex Gonad (Testis) Pituitary gland 1 The hypothalamus secretes hormones that⦠2 â¦stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete hormones that⦠3 â¦stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones Negative feedbackNegative Feedback Loop