Endocrine Signaling.ppt
- 1. 1 Endocrine Signaling / Signal Transduction
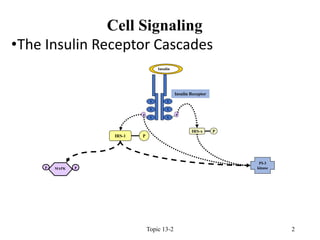
- 2. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades Topic 13-2 2 Cell Signaling Insulin Receptor IRS-1 P Y Y Y Y Y Y PI-3 kinase Insulin IRS-x P P P MAPK P P
- 3. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó Ras ŌĆó ras gene - originally discovered as a viral oncogene ŌĆóAlso part of the normal genome ŌĆóMany tumor cells contain a mutant ras ŌĆóProtein product Ras ŌĆó Small G-protein ŌĆó At inner surface of plasma membrane ŌĆó Lipid group embedded in inner leaflet ŌĆóForms an important link to nucleus via mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK) Topic 13-2 3 Cell Signaling
- 4. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó MAPK ŌĆóBest characterized group ŌĆō extracellular signal- regulated kinase (ERK) family ŌĆóAct via either of two pathways: ŌĆó RTKs such as the insulin cascade ŌĆó Also via G-protein coupled receptors ŌĆóERK activation via coupling to ŌĆó Ras and ŌĆó Raf a protein serine/threonine kinase Topic 13-2 4 Cell Signaling
- 5. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó Ras Raf and MAPK Topic 13-2 5 Cell Signaling Insulin
- 6. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó Ras Raf and MAPK Topic 13-2 6 Grb-2 Cell Signaling IRS-1 P Insulin Receptor Y Y Y Y Y Y Insulin P P SH2 domain GTP test SOS (is a GEF) GDP
- 7. ŌĆó The Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó Raf recruitment ŌĆó Raf then phosphorylates MAPK/ERK kinase known as MEK ŌĆó MEK has dual specificity ŌĆō phosphorylates ŌĆó Threonine ŌĆó Tyrosine ŌĆó These are separated by one aa residue ŌĆó Example ERK2 ŌĆō Thr 183 and Tyr 185 ŌĆó Downstream effects of ERK - transcription Topic 13-2 7 Cell Signaling
- 8. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóMechanism of Ras activation ŌĆóMediated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) ŌĆó Stimulate release of bound GDP ŌĆó Exchange for GTP ŌĆóActivation of Ras-GTP terminated by GTP hydrolysis ŌĆó GTPase-activating proteins interact and accelerate GTP hydrolysis Topic 13-2 8 Cell Signaling
- 9. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóMechanism of Ras activation Topic 13-2 9 Cell Signaling
- 10. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóRas activation ŌĆóA well characterized GEF is Sos ŌĆóSos is bound to Grb2 ŌĆó Found in the cytosol ŌĆóGrb2 is an adaptor protein ŌĆó Has no other intrinsic activity ŌĆó Has SH2 domain ŌĆō high affinity for phospho-tyrosine (eg on IRS) ŌĆóSos-Grb2 localized to the membrane via Ras Topic 13-2 10 Cell Signaling
- 11. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóRas activation ŌĆóSos-Grb2 localized to the membrane via Ras ŌĆóSos stimulates GTP exchange activating Ras Topic 13-2 11 Cell Signaling
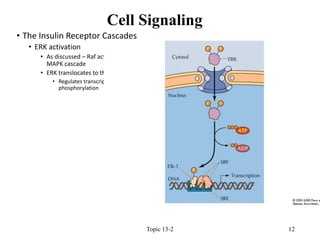
- 12. ŌĆó The Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆó ERK activation ŌĆó As discussed ŌĆō Raf activates the MAPK cascade ŌĆó ERK translocates to the nucleus ŌĆó Regulates transcription factors by phosphorylation Topic 13-2 12 Cell Signaling
- 13. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóERK activation ŌĆóMany growth factors invoke rapid transcriptional induction of immediate-early genes ŌĆó Mediated via serum response element ŌĆó Recognized by several factors including ŌĆó SRF ŌĆó Elk1 Topic 13-2 13 Cell Signaling
- 14. ŌĆóThe Leptin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóCytokine superfamily receptors ŌĆóNo catalytic domain ŌĆóInteract with nonreceptor protein- tyrosine kinases ŌĆó Src family ŌĆó JAK family Topic 13-2 14 Cell Signaling
- 15. ŌĆóThe Leptin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóJAK/STAT Pathway ŌĆóMore immediate connection to transcription ŌĆóDirectly affects transcription factor localization and function ŌĆó Key elements ŌĆō signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) ŌĆóAlso other interactions via MAPK and PI3K Topic 13-2 15 Cell Signaling
- 16. ŌĆóThe Leptin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóJAK/STAT Pathway ŌĆóSTATs contain SH2 domains ŌĆóInactive in unstimulated cells ŌĆóLocalized to cytoplasm ŌĆóLeptin binding to its receptor causes recruitment of STATs which bind to phosphotyrosine via SH2 ŌĆóSTATs are then phosphorylated by Janus Kinase (JAK) ŌĆóSTATs then dimerise and are translocated to the nucleus ŌĆō stimulation of transcription Topic 13-2 16 Cell Signaling
- 17. ŌĆóThe Leptin Receptor Cascades ŌĆóJAK/STAT Pathway Topic 13-2 17 Cell Signaling
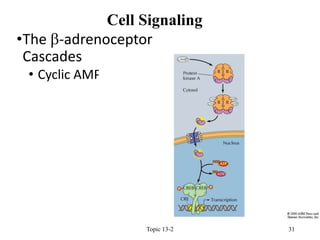
- 18. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆóBinding of a small messenger molecule ŌĆóEpinephrine/norepinephrine ŌĆóInteraction with the receptor causes a conformational change ŌĆóActivates G-protein binding sites in C-terminal domain ŌĆóG-protein interacts with another integral membrane protein (enzyme) ŌĆō adenylyl cyclase ŌĆóDownstream effects via cyclic-AMP Topic 13-2 18 Cell Signaling
- 19. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades Topic 13-2 19 Cell Signaling - S- S- Extracellular domain Intracellular domain Transmembrane domain
- 20. ŌĆó The b-adrenoceptor Cascades Topic 13-2 20 Cell Signaling
- 21. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Mechanism of G-protein signaling ŌĆóCyclic AMP an important messenger for a number of hormone axes ŌĆóGTP essential for activation of the enzyme which generates cyclic AMP ŌĆō adenylyl cyclase Topic 13-2 21 Cell Signaling
- 22. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Mechanism of G-protein signaling Topic 13-2 22 Cell Signaling
- 23. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó G-protein structure ŌĆóThree subunits ŌĆō a, b, g ŌĆó Heterotrimeric G-proteins ŌĆóa subunit binds guanine nucleotides ŌĆō regulatory ŌĆóWhen inactivated a is bound to GDP and the b and g subunits ŌĆóa and g subunits also attached to membrane via lipid moieties Topic 13-2 23 Cell Signaling
- 24. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó G-protein function ŌĆóHormone binding induces a conformational change in the receptor ŌĆóC-terminal domain of receptor interacts with G- protein ŌĆó Release of bound GDP ŌĆó Exchange for GTP ŌĆóActivated a subunit dissociates ŌĆóa subunit activates adenylyl cyclase Topic 13-2 24 Cell Signaling
- 25. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó G-protein function Topic 13-2 25 Cell Signaling
- 26. G-protein diversity ŌĆó20 different a subunits ŌĆó6 b subunits ŌĆó12 g subunits ŌĆóDifferent G-proteins associate with different receptors (c-terminal domain specificity) ŌĆóSpecific intracellular targets ŌĆób-adrenoceptor-linked G-protein ŌĆō Gs ŌĆóStimulates adenylyl cyclase ŌĆóOther G-proteins inhibit adenylyl cyclase - Gi Topic 13-2 26 Cell Signaling
- 27. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway ŌĆóFormed from ATP via adenylyl cyclase action ŌĆóDegraded to AMP by phosphodiesterase Topic 13-2 27 Cell Signaling
- 28. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway ŌĆóMost effects of cAMP mediated via protein kinase A (PKA) ŌĆó cAMP binds to regulatory subunits of PKA ŌĆó Regulatory and catalytic subunits dissociate ŌĆó Catalytic subunits activated ŌĆó Phosphorylate serine residues on target proteins ŌĆóGood example of signal amplification Topic 13-2 28 Cell Signaling
- 29. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway ŌĆóActivation of protein kinase A Topic 13-2 29 Cell Signaling
- 30. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway ŌĆóMany cases ŌĆō activation of transcription of target genes containing cAMP response element (CRE) ŌĆóSignal carried by catalytic subunit of PKA ŌĆó Phosphorylates transcription factor ŌĆō CRE-binding protein (CREB) - dimerises ŌĆóActivation of cAMP-inducible genes Topic 13-2 30 Cell Signaling
- 31. ŌĆóThe b-adrenoceptor Cascades ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway Topic 13-2 31 Cell Signaling
- 32. ŌĆó Cyclic AMP pathway ŌĆóImportant in proliferation, differentiation of many cell types ŌĆóProtein kinases ŌĆóProtein kinase A ŌĆóNot independent action ŌĆóProtein phosphorylation reversed by phosphatases ŌĆó Terminate responses following receptor activation of protein kinases Topic 13-2 32 Cell Signaling
- 33. ŌĆóProtein kinases ŌĆóProtein kinase A ŌĆóLevel of phosphorylation of substrates finely controlled by balance of actions of the kinase and phosphatases Topic 13-2 33 Cell Signaling
- 34. ŌĆóThe Insulin Receptor Cascades ŌĆō Interaction with the Leptin Pathway Topic 13-2 34 Cell Signaling OB-RlL OB-Rs Leptin MAPK P Y Y Leptin P P Insulin Receptor S T A T S T A T Shc JAK IRS-1 P Y Y Y Y Y Y PI-3 kinase Atypical PKC GLUCOSE FFA Insulin INTERSTITIAL SPACE IRS-x P Nucleus PPAR Mitochondrion Fatty Acid Ox-n. CD36 ACC P GLUT4 Akt P P P AMPK P