Endoscopes - Biomedical Engineering
- 1. Endoscopes Flexible and Capsule Endoscopes Prepared by: Pritesh B.Gohil (1005) Guided By: Jagrut Gadit The M.S. University of Baroda Faculty of Technology and Engineering
- 2. ï±History Rigid Semi- Flexible Fibre Optic Video Bozzini 1805 1853 1868 1932 1957 1975 2000
- 3. âą The first real endoscope that was developed was made by Phillip Bozzini in 1805 to examine the urethra, the bladder and vagina. âą Adolf Kussmaul in 1868 used a straight rigid metal tube over a flexible obturator to perform the first gastroscopy. âą Building on the work of others, Rudolph Schindler constructed the first practical gastroscope in 1932. âą In 1957 Basil Hirschowitz developed his fiberscope. âą In 1975, D.W. Brewer developed âVideo-fibre- laryngoscopyâ âą 2000: G. Iddan and P. Swain âWireless capsule endoscopyâ
- 4. ï±Introduction What is endoscope? ïŒAn instrument which can be introduced into the body to give a view of its internal parts. ïŒThis is used to examine the interior of the hollow organ or cavity of the body which is called endoscopy. ïŒPhysicians use endoscopy to diagnose, monitor, and surgically treat various medical problems.
- 5. When is endoscopy used? ïŒ Endoscopes were first developed to look at parts of the body that couldnât be seen any other way. 1. To prevent and screen for cancer 2. To find cancer early 3. Looking for causes of symptoms 4. Looking at problems found on imaging tests 5. Destroying or removing cancer cell
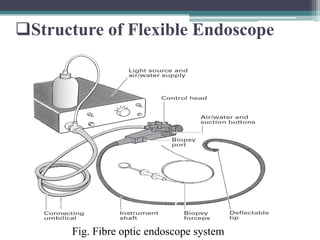
- 6. ï±Structure of Flexible Endoscope Fig. Fibre optic endoscope system
- 7. a) Illumination ïŒ external high-intensity source ïŒ one or more light-carrying bundles ïŒ light bundles run uninterruptedly ïŒ xenon arc (300 W) or halogen-filled tungsten filament lamps (150 W) ïŒ Light is focused by a parabolic mirror
- 8. b) Instrument tip Fig. Basic designâcontrol head and bending section.
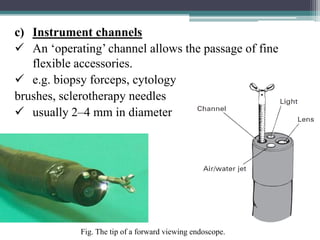
- 9. c) Instrument channels ïŒ An âoperatingâ channel allows the passage of fine flexible accessories. ïŒ e.g. biopsy forceps, cytology brushes, sclerotherapy needles ïŒ usually 2â4 mm in diameter Fig. The tip of a forward viewing endoscope.
- 10. d) Tissue-sampling device Fig. Biopsy cups open. Fig. Control handle for forceps. Fig. Cytology brush with outer sleeve.
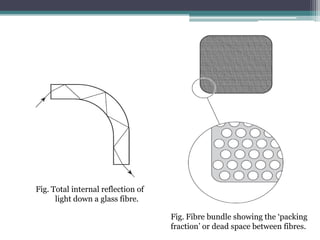
- 11. ï±Fibre Optic Endoscope ïŒBased optical viewing bundles. ïŒViewing bundle diameter 2-3 mm ïŒBundle consist of 20 000â40 000 fine glass fibres with 10 ”m in diameter. ïŒLight focused onto the face of each fibre is transmitted by repeated internal reflection. ïŒtransmission of an image depends upon spatial orientation of each fibre. ïŒIn most modern instruments the distal lens which focuses the image onto the bundle is fixed.
- 12. Fig. Total internal reflection of light down a glass fibre. Fig. Fibre bundle showing the âpacking fractionâ or dead space between fibres.
- 13. ï±Video Endoscopes ïŒmechanically similar to fibre-endoscopes. ïŒcharged couple device (CCD) âchipâ and supporting electronics mounted at the tip. ïŒCCD chip is an array of 33 000â100 000 individual photo cells. ïŒRespond to the reflected photons.
- 14. Fig. Static red, green and blue filters in the âcolourâ chip.
- 15. Fig. Sequential colour illumination.
- 16. ï±Advantage and Disadvantage ï§ Fibre optic Endoscopes ï§ Advantages ïŒSimplicity ïŒNo video processing ïŒSmall diameter capillary ïŒPortable instrument ï§ Disadvantage ïŒ Only endoscopist alone can see
- 17. ï§ Video Endoscopes ï§ Advantages ïŒBrighter view ïŒFacilitates communication with patients & assistants. ïŒMovement of shaft and tip easy ï§ Disadvantages ïŒVideo processing required ïŒIt is not portable ïŒAvailable in limited size
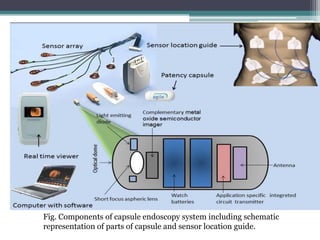
- 18. ï±Capsule Endoscope ïŒCapsule endoscopy is a combination of the device that physicist G. Iddan had developed and that devised by Paul Swain. ïŒCapsule endoscopy is indicated in various small bowel diseases such as obscure gastrointestinal bleeding, celiac disease and other types of malabsorption syndrome, polyposis, Crohn disease etc.
- 19. Fig. Components of capsule endoscopy system including schematic representation of parts of capsule and sensor location guide.
- 20. ï±Features ïŒLength: 26 mm ïŒWeight: 3.4 gram ïŒBattery type: Silver Oxide Cell ïŒBattery life: 8 hours ïŒOperation temperature: 20-40ÌC ïŒLight: 6 white LED ïŒFrame rate per second: 2 ïŒCamera type: CCD or CMOS ïŒAntennas: 8
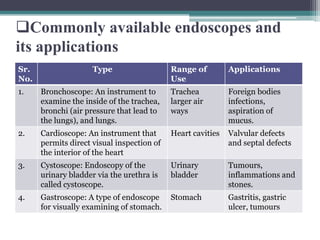
- 21. ï±Commonly available endoscopes and its applications Sr. No. Type Range of Use Applications 1. Bronchoscope: An instrument to examine the inside of the trachea, bronchi (air pressure that lead to the lungs), and lungs. Trachea larger air ways Foreign bodies infections, aspiration of mucus. 2. Cardioscope: An instrument that permits direct visual inspection of the interior of the heart Heart cavities Valvular defects and septal defects 3. Cystoscope: Endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra is called cystoscope. Urinary bladder Tumours, inflammations and stones. 4. Gastroscope: A type of endoscope for visually examining of stomach. Stomach Gastritis, gastric ulcer, tumours
- 22. Sr. No. Type Range of Use Applications 5. Laparoscopes: An instrument called a laparoscope is inserted through a small incision (cut) which is made in the abdominal wall to permit structures within the abdomen and pelvis to be seen. Abdominal cavity Tumours, family planning operations livers, gallbladder surgery 6. to see the vessels Intravascular To know state of vessels 7. Otoscope: An instrument consisting of a magnifying lens and light; used for examining the external ear Tympanic membrane Infections, perforation of ear drum, pressure condition in the middle ear 8. Proctoscope: An endoscope for examining the rectum Rectum Haemorrhoids (piles) 9. Sigmoidoscope: An endoscope for examining the sigmoid colon Rectum and distal part of colon Bowel lesions side pockets of the bowel
- 23. ï±Refferences [1]. www.blackwellpublishing.com Basic endoscopic equipment [2]. www.șĘșĘߣshare.com Capsule Endoscopy by Ashish Kumar [3]. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/52732 Capsule Endoscopy by Uday C Ghoshal [4]. Biomedical Instrumentation and Measurements - R. Anandanatarajan
- 24. THANK YOU

















![ï±Refferences
[1]. www.blackwellpublishing.com
Basic endoscopic equipment
[2]. www.șĘșĘߣshare.com
Capsule Endoscopy by Ashish Kumar
[3]. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/52732
Capsule Endoscopy by Uday C Ghoshal
[4]. Biomedical Instrumentation and Measurements -
R. Anandanatarajan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endoscopespptpdf-181118111658/85/Endoscopes-Biomedical-Engineering-23-320.jpg)
