Eng 102 final assignment
- 1. Name:Muhammed Surname:UYGUR Number:20111835 Section:BÃTE Course:Eng-102 Subjet:Introduction to computers and information technology 1
- 2. 2
- 3. Introduction to computers and information technology Regardless of the fact that we now have an general idea of the basic components and the functions of a computer system, this overview is not enough to provide us with thorough understanding of each component. We then seek a comprehensive understanding of each component of the computer system by determining how important each element is. 3
- 4. Introduction to computers and information technology We consider any data or instructions that enter the computerâs memory space as input. Due to the variety of fields of studies that exist today, there has been respective input devices for the entering of data for processing. Popular input devices include: keyboard, mouse, stylus, digital camera, microphone, and scanner. 4
- 5. Introduction to computers and information technology 5
- 6. Introduction to computers and information technology We consider data that has been processed into a useable form as output. Computer systems can generate several types of output, depending on the hardware and software being used âit may be printed, seen, or heard. Popular output devices include: printer, speaker, and monitor. 6
- 7. Introduction to computers and information technology 7
- 8. Introduction to computers and information technology The system unit is a case that contains electronic components of the computer, which are used to process data. The processor (CPU) impacts on the computer overall computing power and manages most computing operations. Processors contain a control unit and an arithmetic logic unit, that together performs processing. 8
- 9. Introduction to computers and information technology 9
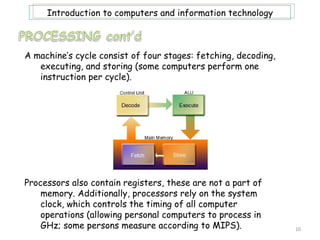
- 10. Introduction to computers and information technology A machineâs cycle consist of four stages: fetching, decoding, executing, and storing (some computers perform one instruction per cycle). Processors also contain registers, these are not a part of memory. Additionally, processors rely on the system clock, which controls the timing of all computer operations (allowing personal computers to process in GHz; some persons measure according to MIPS). 10
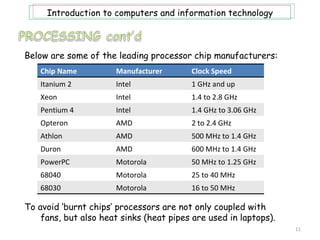
- 11. Introduction to computers and information technology Below are some of the leading processor chip manufacturers: Chip Name Manufacturer Clock Speed Itanium 2 Intel 1 GHz and up Xeon Intel 1.4 to 2.8 GHz Pentium 4 Intel 1.4 GHz to 3.06 GHz Opteron AMD 2 to 2.4 GHz Athlon AMD 500 MHz to 1.4 GHz Duron AMD 600 MHz to 1.4 GHz PowerPC Motorola 50 MHz to 1.25 GHz 68040 Motorola 25 to 40 MHz 68030 Motorola 16 to 50 MHz To avoid âburnt chipsâ processors are not only coupled with fans, but also heat sinks (heat pipes are used in laptops). 11
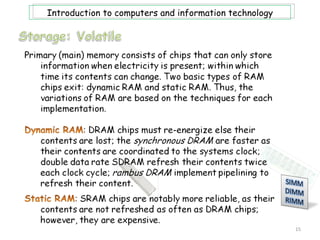
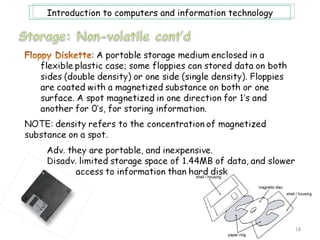
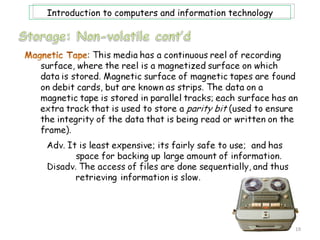
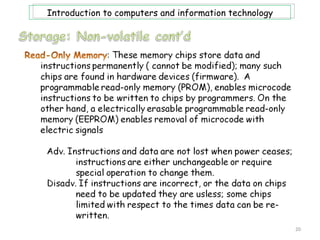
- 12. Introduction to computers and information technology Storage, or memory, consists of electrical components that store instructions and data waiting to be executed by the processor, as well as their results. The computer system stores three categories of items: OS and software; application programs; and data being processed. Computer memory consist of two types of memory: volatile and non-volatile. An example of volatile memory is RAM, while ROM is and example of non-volatile memory. It is also important to note at this point, that when information in memory is being accessed it can be retrieved sequentially or directly. Also the terms storage medium is singular, while storage media is plural; and storage devices are technology to get/store data. 12
- 13. Introduction to computers and information technology 13
- 14. Introduction to computers and information technology 14
- 15. Introduction to computers and information technology 15
- 16. Introduction to computers and information technology 16
- 17. Introduction to computers and information technology 17
- 18. Introduction to computers and information technology 18
- 19. Introduction to computers and information technology 19
- 20. Introduction to computers and information technology 20
- 21. Introduction to computers and information technology 21
- 22. Introduction to computers and information technology 22