Engineers responsibility for safety
- 2. FOCUS ’āśSPACE SHUTTLE CHALLENGER ’āśTHREE MILE ISLAND ACCDENT ’āśBHOPAL GAS TRAGEDY ’āśUPHAAR CINEMA TRAGEDY
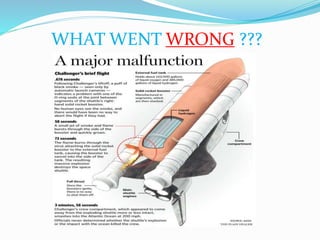
- 3. SPACE SHUTTLE CHALLENGER ’āśOn January 28, 1986, the NASA shuttle orbiter mission STS-51-L and the tenth flight of Space Shuttle Challenger (OV- 99) broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members, which consisted of five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists. ’āśThe spacecraft disintegrated over the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 11:39EST (16:39 UTC). Disintegration of the vehicle began after an O-ring seal in its right solid rocket booster failed at liftoff.
- 4. WHAT WENT WRONG ???
- 6. CAUSES FOR THE DESTRUCTION ’üČThe temperature was below freezing on the morning of January 28, 1986, when the Challenger prepared for its tenth launch. ’üČFailing of primary O-rings: The O- rings were never tested in extreme cold. On the morning of the launch, the cold rubber became stiff, failing to fully seal the joint.
- 7. ’üČDelays in launches The first delay of the Challenger mission was due to a weather front expected to move into the area, bringing rain and cold temperatures. The second launch delay was caused by a defective micro switch in the hatch locking mechanism and by problems in removing the hatch handle. ’üČPressure to launch NASA managers were anxious to launch the Challenger for several reasons, including economic considerations, political pressures, and scheduling backlogs.
- 8. How could this be saved ??? The Challenger disaster presents several issues that are relevant to engineers. ’ü▒One of the most important is engineers who are placed in management positions. It is important that these managers not ignore their own engineering experience, or the expertise of their subordinate engineers. They should keep this in mind when making any sort of decision that involves an understanding of technical matters. ’ü▒Another issue is the fact that managers encouraged launching due to the fact that there was insufficient low- temperature data.
- 9. ’ü▒As engineers test designs for ever-increasing speeds, loads, capacities and the like, they must always be aware of their obligation to society to protect the public welfare. After all, the public has provided engineers, through the tax base, with the means for obtaining an education and, through legislation, the means to license and regulate themselves. In return, engineers have a responsibility to protect the safety and well-being of the public in all of their professional efforts.
- 10. THREE MILE ISLAND ACCIDENT The Three Mile Island accident occurred on March 28, 1979, in reactor number 2 of Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station (TMI-2) in Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, United States, near Harrisburg. It was the most significant accident in U.S. commercial nuclear power plant history. The incident was rated a five on the seven-point International Nuclear Event Scale: Accident with wider consequences.
- 11. WHAT WENT WRONG ???
- 12. ’üČMinor malfunction caused the second reactor to shut down immediately. ’üČA relief valve was supposed to close, but it did not, contrary to what the instrumentation showed. ’üČOperators struggled to determined the problem and an appropriate solution. ’üČAfter almost 16 hours and the collaboration of 60 or more people, the situation was under control.
- 13. CAUSES FOR THE DESTRUCTION ’āśThe accident began with failures in the non-nuclear secondary system, followed by a stuck-open pilot-operated relief valve in the primary system, which allowed large amounts of nuclear reactor coolant to escape. ’āśThe mechanical failures were compounded by the initial failure of plant operators to recognize the situation as a loss- of-coolant accident due to inadequate training and human factors, such as human-computer interaction design oversights relating to ambiguous control room indicators in the power plant's user interface.
- 14. How could this be saved ??? ’üČCritical human factors and user interface engineering problems were revealed in the investigation of the reactor control system's user interface. Despite the valve being stuck open, a light on the control panel ostensibly indicated that the valve was closed. As a result, the operators did not correctly diagnose the problem for several hours. ’üČThe operators had not been trained to understand the ambiguous nature of the pilot-operated relief valve indicator and to look for alternative confirmation that the main relief valve was closed. ’üČThe problem was not correctly diagnosed until a fresh shift came in who did not have the mindset of the first shift of operators. By this time major damage had occurred.
- 15. BHOPAL GAS TRAGEDY ’üČOver 500,000 people were exposed to methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas and other chemicals. The highly toxic substance made its way into and around the shanty towns located near the plant. ’üČBhopal gas tragedy, was a gas leak incident in India, considered the world's worst industrial disaster. It occurred on the night of 2ŌĆō3 December 1984 at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- 16. WHAT WENT WRONG ???
- 17. ’üČMost of the plant's MIC related safety systems were not functioning and many valves and lines were in poor condition. ’üČSeveral vent gas scrubbers had been out of service as well as the steam boiler, intended to clean the pipes. ’üČA connecting pipe was removed from the flare tower for maintenance purpose, which was used for burn off gases. ’üČFreon system used for cooling liquid MIC was shut down in June 1984 to save money.
- 18. CAUSES FOR THE DESTRUCTION ’āś The disaster was caused by a potent combination of under-maintained and decaying facilities, a weak attitude towards safety, and an undertrained workforce, culminating in worker actions that inadvertently enabled water to penetrate the MIC tanks in the absence of properly working safeguards. ’āśThe factory was not well equipped to handle the gas created by the sudden addition of water to the MIC tank. The MIC tank alarms had not been working for four years and there was only one manual back-up system, compared to a four-stage system used in the United States. ’āśUnderinvestment is cited as contributing to an environment. Attempts to reduce expenses affected the factory's employees and their conditions. Subsequent research highlights a gradual deterioration of safety practices in regard to the MIC, which had become less relevant to plant operations.
- 19. How could this be saved ??? The disaster could be prevented if these steps were not taken. ŌĆóThe use of hazardous chemicals (MIC) instead of less dangerous ones. ŌĆóStoring these chemicals in large tanks instead of over 200 steel drums. ŌĆóPossible corroding material in pipelines ŌĆóPoor maintenance after the plant ceased production in the early 1980s Failure of several safety systems. ŌĆóSafety systems shut down to save money - including the MIC tank refrigeration system which alone would have prevented the disaster.
- 20. UPHAAR CINEMA TRAGEDY The Uphaar Cinema fire, one of the worst fire tragedies in recent Indian history, occurred on Friday, 13 June 1997 at Uphaar Cinema, in Green Park, Delhi, during the 3-to-6 pm screening of the movie Border. Trapped inside, 59 people died, mostly due to suffocation, and 103 were seriously injured in the resulting stampede.
- 21. WHAT WENT WRONG ??? ’üČOn 13 June 1997 at about 6.55 a.m. the bigger of the two installed transformers, which were maintained by the digital video broadcaster on the ground floor of the cinema building, caught fire. ’üČThese transformers had developed issues repeatedly but the repairs had not been satisfactory. On the morning of the incident, another repair had caused loose connections which led to sparks that brought the whole hall down.
- 22. CAUSES FOR THE DESTRUCTION ’üČInstallation and maintenance of the DVA transformer in violation of Indian Electricity Rules (no periodic maintenance, no fire extinguishers, no isolation device, haphazard electrical cables). ’üČNo functional public announcement system (no announcement was made when the fire broke out). ’üČNo emergency lights, foot lights, exit lights (The cinema hall was in pitch darkness when the fire broke out). ’üČBlocked exits (many exit doors ŌĆō including the one leading to the terrace ŌĆō and gates were locked).
- 23. How could this be saved ??? This accident could be prevented if : ’ā╝DVA transformer were properly installed and maintained ’ā╝Proper announcements were made regarding the setting fire. ’ā╝Proper entry and emergency exit doors be provided.