English grammar in use
- 1. English grammar in use Yigit Ozkaya
- 2. Content ’ü« English Tenses Exercise ’ü« Prepositions in English Exercise ’ü« Articles in English Exercise ’ü« Conditionals Exercise ’ü« Reported speech Exercise ’ü« Complex Object Exercise
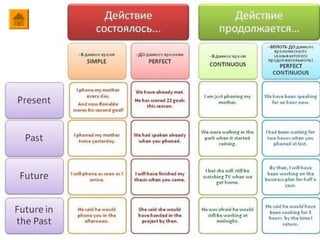
- 3. English Tenses ’ü« ąŚą░čćą░čüčéčāčÄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░ ą▓ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ą╗čÅčÄčé čéčĆčāą┤ąĮąŠčüčéąĖ ą┤ą╗čÅ ąĖąĘčāčćą░čÄčēąĖčģ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąĖą╣. ą×ą▒čŖčÅčüąĮčÅąĄčéčüčÅ čŹč鹊 č鹥ą╝, čćč鹊 čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ą░ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ą▓ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ ąĮąĄą┐ąŠčģąŠąČą░ ąĮą░ čéčā, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆą░čÅ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ ą▓ čĆčāčüčüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ, čģąŠčéčÅ ąĮąĄą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┐ą░čĆą░ą╗ą╗ąĄą╗ąĖ ą┐čĆąŠą▓ąĄčüčéąĖ ą▓čüąĄ ąČąĄ ą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠ. ą×ą┤ąĮą░ą║ąŠ čā čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝čŗ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąĖčģ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ąĄčüčéčī ąĮąĄąŠčüą┐ąŠčĆąĖą╝ąŠąĄ ą┤ąŠčüč鹊ąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąŠ ŌĆō ąŠąĮą░ ąŠą▒ą╗ą░ą┤ą░ąĄčé čüčéčĆąŠą│ąŠą╣ čāą┐ąŠčĆčÅą┤ąŠč湥ąĮąĮąŠčüčéčīčÄ, ą╗ąŠą│ąĖčćąĮąŠčüčéčīčÄ, ąĖ ą┐ąŠą┤čćąĖąĮčÅąĄčéčüčÅ ąĘą░ą║ąŠąĮą░ą╝ ą│čĆą░ą╝ą╝ą░čéąĖą║ąĖ. ąÉąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąĖąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░. ąÜčĆą░čéą║ą░čÅ čģą░čĆą░ą║č鹥čĆąĖčüčéąĖą║ą░ ’ü« ąÆčüąĄą│ąŠ ą▓ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓čāąĄčé 12 ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┤ąĄą╗čÅčéčüčÅ ąĮą░ č湥čéčŗčĆąĄ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐čŗ: ’ü« - simple ąĖą╗ąĖ indefinite (ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ ą┐čĆąŠčüčéčŗčģ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ); ’ü« - continuous ąĖą╗ąĖ progressive (ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ ą┤ą╗ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ąĖą╗ąĖ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ąŠą╗ąČąĄąĮąĮčŗčģ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ);
- 4. ’ü« - perfect (ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ čüąŠą▓ąĄčĆčłąĄąĮąĮčŗčģ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ); ’ü« - perfect continuous ąĖą╗ąĖ perfect progressive (ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ čüąŠą▓ąĄčĆčłąĄąĮąĮčŗčģ ą┤ą╗ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ). ’ü« ąÆ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ čéą░ą║ ąČąĄ, ą║ą░ą║ ąĖ ą▓ čĆčāčüčüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ, ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖąĄ, ą▓čŗčĆą░ąČąĄąĮąĮąŠąĄ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ąŠą╝, ą╝ąŠąČąĄčé ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤ąĖčéčī ą▓ ą┐čĆąŠčłąĄą┤čłąĄą╝, ąĮą░čüč鹊čÅčēąĄą╝, ąĖą╗ąĖ ą▒čāą┤čāčēąĄą╝. ąĪąŠąŠčéą▓ąĄčéčüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠ, ą║ą░ąČą┤ą░čÅ ąĖąĘ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĮčŗčģ ą▓čŗčłąĄ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ą╝ąŠąČąĄčé ą▒čŗčéčī ą▓čŗčĆą░ąČąĄąĮą░ ą▓ ą┐čĆąŠčłąĄą┤čłąĄą╝ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ (past tense), ąĮą░čüč鹊čÅčēąĄą╝ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ (present tense), ąĖą╗ąĖ ą▒čāą┤čāčēąĄą╝ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ (future tense). ’ü« ąÜą░ąČą┤ą░čÅ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ą▓ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąŠą╝ čÅąĘčŗą║ąĄ ą▓čŗčĆą░ąČą░ąĄčé čĆą░ąĘąĮčŗąĄ čüąĖčéčāą░čåąĖąĖ.
- 5. ’ü« ą¤čĆąŠčüčéčŗąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░ ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░čÄčé čäą░ą║čé ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠąČą┤ąĄąĮąĖčÅ ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖčÅ, ą▒ąĄąĘąŠčéąĮąŠčüąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠ ą┐čĆąŠčéčÅąČąĄąĮąĮąŠčüčéąĖ čŹč鹊ą│ąŠ ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖčÅ. ąóą░ą║ąČąĄ ąŠąĮąĖ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÄčéčüčÅ ą┤ą╗čÅ ąŠą┐ąĖčüą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖą╣, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤čÅčé čü ąĮąĄą║ąŠč鹊čĆąŠą╣ čĆąĄą│čāą╗čÅčĆąĮąŠčüčéčīčÄ. ’ü« ąöą╗ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░, ą║ą░ą║ čüą╗ąĄą┤čāąĄčé ąĖąĘ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅ, ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░čÄčé č鹊, čćč鹊 ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤ąĖčé ą▓ č鹥č湥ąĮąĖąĄ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą│ąŠ-ą╗ąĖą▒ąŠ ą┐čĆąŠą╝ąĄąČčāčéą║ą░ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ, ą║ą░ą║ ą┐čĆą░ą▓ąĖą╗ąŠ, ąĘą░ą┤ą░ąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ č鹥ą╝ ą╝ąŠą╝ąĄąĮč鹊ą╝, ąŠ ą║ąŠč鹊čĆąŠą╝ ąĖą┤ąĄčé čĆąĄčćčī. ąóą░ą║ąČąĄ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗čŗ ą┤ą░ąĮąĮąŠą╣ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐čŗ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ą▓čüąĄą│ą┤ą░ čüčéčĆąŠčÅčéčüčÅ čü ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖąĄą╝ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ą░ be, ąĖ ą║ ąĮąĖą╝ ą▓čüąĄą│ą┤ą░ ą┤ąŠą▒ą░ą▓ą╗čÅąĄčéčüčÅ ąŠą║ąŠąĮčćą░ąĮąĖąĄ "-ing". ’ü« ąĪąŠą▓ąĄčĆčłąĄąĮąĮčŗąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░ ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░čÄčé ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖčÅ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ čāąČąĄ ąĘą░ą▓ąĄčĆčłąĖą╗ąĖčüčī ą║ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą╝čā-ą╗ąĖą▒ąŠ ą╝ąŠą╝ąĄąĮčéčā ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ. ąōą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗čŗ ą▓ ą┤ą░ąĮąĮąŠą╣ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ ą▓čüąĄą│ą┤ą░ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÄčéčüčÅ čü ą▓čüą┐ąŠą╝ąŠą│ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ąŠą╝ have, ąĖ ąŠąĮąĖ ą▓čüąĄą│ą┤ą░ čüč鹊čÅčé ą▓ č乊čĆą╝ąĄ ą┐čĆąĖčćą░čüčéąĖčÅ ą┐čĆąŠčłąĄą┤čłąĄą│ąŠ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ. ’ü« ąĪąŠą▓ąĄčĆčłąĄąĮąĮčŗąĄ ą┤ą╗ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮą░, ą║ą░ą║ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĮąŠ ąĖąĘ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅ, ąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗čÅčÄčé ą▓ čüąĄą▒ąĄ ą┐čĆąĖąĘąĮą░ą║ąĖ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ čüąŠą▓ąĄčĆčłąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ ąĖ ą┤ą╗ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐čŗ, ąŠąĮąĖ ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░čÄčé ą┤ąĄą╣čüčéą▓ąĖčÅ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ąŠą╗ąČą░ą╗ąĖčüčī ąĮą░ ą┐čĆąŠčéčÅąČąĄąĮąĖąĖ ąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤ą░ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ. ąōą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗čŗ ą┤ą░ąĮąĮąŠą╣ ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐čŗ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÄčé ą┤ą▓ą░ ą▓čüą┐ąŠą╝ąŠą│ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ą░ ŌĆō have ąĖ been, ąĖ ąĖą╝ąĄčÄčé ąŠą║ąŠąĮčćą░ąĮąĖąĄ "-ing".
- 7. English Tenses. Exercises ’ü« 1. This time tomorrow you ___ sitting in a deck chair on the beach. 1)Are 2)Were 3)Will 4)will be
- 8. ’ü« 2. Before you telephoned, I ___ watching television. 1)Was 2)will be 3)Am 4) have ’ü« 3. After the storm ___ finished, many people were found lying in the street. 1)Has 2)Had 3)Were 4)did
- 9. ’ü« 4. Tomorrow we ___ taking the day off. 1)Will 2)Have 3)Were 4)are ’ü« 5. How many times ___ you been there? 1)Has 2)Will 3)Have 4)did
- 10. ’ü« 6. It's time we ___. 1)Go 2)Went 3)are going 4)going ’ü« 7. He asked me what I ___ doing there. 1)Am 2)Did 3)will be 4)was
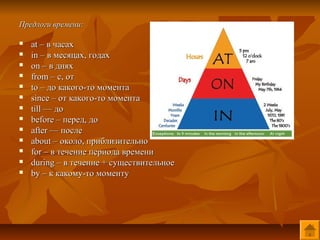
- 11. Prepositions in English ą¤čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠą│ąĖ ąĮą░ą┐čĆą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖčÅ: ’ü« towards ŌĆō ą┐ąŠ ąĮą░ą┐čĆą░ą▓ą╗ąĄąĮąĖčÄ ’ü« to the left ŌĆö ąĮą░ą╗ąĄą▓ąŠ ą║ ’ü« to the right ŌĆö ąĮą░ą┐čĆą░ą▓ąŠ ’ü« away, from ŌĆö ąŠčé ’ü« up ŌĆö ą▓ą▓ąĄčĆčģ ’ü« through ŌĆō č湥čĆąĄąĘ, čüą║ą▓ąŠąĘčī ’ü« down ŌĆō ą▓ąĮąĖąĘ ’ü« out of ŌĆö ąĖąĘ ’ü« off ŌĆö čü ’ü« into ŌĆö ą▓ ’ü« onto ŌĆö ąĮą░ ’ü« along ŌĆö ą▓ą┤ąŠą╗čī ’ü« past ŌĆö ą╝ąĖą╝ąŠ ’ü« across ŌĆō č湥čĆąĄąĘ
- 12. ą¤čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠą│ąĖ ą╝ąĄčüč鹊ą┐ąŠą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ: ’ü« above ŌĆö ąĮą░ą┤ ’ü« over ŌĆö ąĮą░ą┤ ’ü« between ŌĆō ą╝ąĄąČą┤čā ’ü« near, at, by, beside ŌĆō ąŠą║ąŠą╗ąŠ, ą▓ąŠąĘą╗ąĄ, čā ’ü« behind ŌĆō ąĘą░, čüąĘą░ą┤ąĖ ’ü« under ŌĆö ą┐ąŠą┤ ’ü« below ŌĆō ą┐ąŠą┤ ’ü« outside ŌĆö ąĖąĘ ’ü« in front of ŌĆö ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą┤
- 13. ą¤čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠą│ąĖ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ: ’ü« at ŌĆō ą▓ čćą░čüą░čģ ’ü« in ŌĆō ą▓ ą╝ąĄčüčÅčåą░čģ, ą│ąŠą┤ą░čģ ’ü« on ŌĆō ą▓ ą┤ąĮčÅčģ ’ü« from ŌĆō c, ąŠčé ’ü« to ŌĆō ą┤ąŠ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą│ąŠ-č鹊 ą╝ąŠą╝ąĄąĮčéą░ ’ü« since ŌĆō ąŠčé ą║ą░ą║ąŠą│ąŠ-č鹊 ą╝ąŠą╝ąĄąĮčéą░ ’ü« till ŌĆö ą┤ąŠ ’ü« before ŌĆō ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą┤, ą┤ąŠ ’ü« after ŌĆö ą┐ąŠčüą╗ąĄ ’ü« about ŌĆō ąŠą║ąŠą╗ąŠ, ą┐čĆąĖą▒ą╗ąĖąĘąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠ ’ü« for ŌĆō ą▓ č鹥č湥ąĮąĖąĄ ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤ą░ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ ’ü« during ŌĆō ą▓ č鹥č湥ąĮąĖąĄ + čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮąŠąĄ ’ü« by ŌĆō ą║ ą║ą░ą║ąŠą╝čā-č鹊 ą╝ąŠą╝ąĄąĮčéčā
- 14. ’ü« ą¤čĆąĖčćąĖąĮąĮčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠą│ąĖ: because of ŌĆō ą┐ąŠč鹊ą╝čā čćč鹊 in accordance with ŌĆō čüąŠą│ą╗ą░čüąĮąŠ, ą▓ čüąŠąŠčéą▓ąĄčéčüčéą▓ąĖąĖ čü on account of ŌĆō ą▓čüą╗ąĄą┤čüčéą▓ąĖąĄ, ąĖąĘ-ąĘą░ thanks to ŌĆō ą▒ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą┤ą░čĆčÅ
- 15. Prepositions Exercises ’ü« ąŻą┐čĆą░ąČąĮąĄąĮąĖąĄ 1. ąÆčüčéą░ą▓čīč鹥 ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠą│ąĖ on, in ąĖą╗ąĖ into. 1. Where is the book? - - It is ... the table. 2. Where is the tea? ŌĆö It is ... the cup. 3. Put the plates ... the table. 4. Put the book ... the bag. 5. There is a beautiful picture ... the wall. 6. He went ... the room. 7. I like to sit ... the sofa ... my room. 8. Mother is cooking dinner ... the kitchen. 9. She went ... the room and sat down ... the sofa. 10. There are many people ... the park today. 11. There is a girl standing ... the bridge. Why is she crying? - She has dropped her doll ... the water. 12. There is no tea ... my cup. 13. Pour some tea ... my cup. 14. Put these flowers ... the window-sill. 15. I saw many people ... the plat-form waiting for the train. 16. We went ... the garden and sat down ... a bench.
- 16. ’ü« ąŻą┐čĆą░ąČąĮąĄąĮąĖąĄ 2. ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą▓ąĄą┤ąĖč鹥 ąĮą░ ą░ąĮą│ą╗ąĖą╣čüą║ąĖą╣ čÅąĘčŗą║ čüą╗ąĄą┤čāčÄčēąĖąĄ čüą╗ąŠą▓ąŠčüąŠč湥čéą░ąĮąĖčÅ. ’ü« ąÆ č湥čéčŗčĆąĄ čćą░čüą░, ą▓ ą┐ąŠą╗ąŠą▓ąĖąĮąĄ čłąĄčüč鹊ą│ąŠ, ą▒ąĄąĘ č湥čé-ą▓ąĄčĆčéąĖ čéčĆąĖ, ąĮą░ ąĘą░ą║ą░č鹥, ą▓ č湥čéą▓ąĄčĆčéčī ą┐čÅč鹊ą│ąŠ, ą▓ ą┐ąŠą╗ąĮąŠčćčī, ą▓ ą┐čÅčéčī ą╝ąĖąĮčāčé čłąĄčüč鹊ą│ąŠ, ą▒ąĄąĘ ą┤ąĄčüčÅčéąĖ ą┤ą▓ą░, ą┐ąŠą╗ą┤ąĄąĮčī, ąĮą░ ą▓ąŠčüčģąŠą┤ąĄ čüąŠą╗ąĮčåą░, ą▓ ą┤ą▓ą░ą┤čåą░čéčī ą┐čÅčéčī čéčĆąĄčéčīąĄą│ąŠ. ’ü«
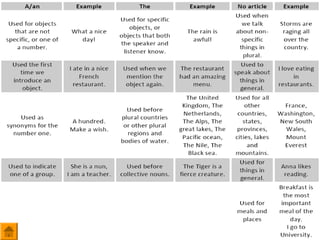
- 18. ąØąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī ’ü« ąÜąŠą│ą┤ą░ ąĮčāąČąĮąŠ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘąŠą▓ą░čéčī ąĮąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī a/an: ’ü« ąóąŠą╗čīą║ąŠ čü ąĖčüčćąĖčüą╗čÅąĄą╝čŗą╝ąĖ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ ą▓ ąĄą┤ąĖąĮčüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╝ čćąĖčüą╗ąĄ, ą║ąŠą│ą┤ą░ ą╝čŗ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖą╝ ąŠ ąĮąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ ą▓ąĄčēąĖ: I canŌĆÖt find a taxi ŌĆö čÅ ąĮąĄ ą╝ąŠą│čā ąĮą░ą╣čéąĖ čéą░ą║čüąĖ. ąÜą░ą║ąŠąĄ čéą░ą║čüąĖ? ąöą░ ą╗čÄą▒ąŠąĄ, ąĮąĄ ą▓ą░ąČąĮąŠ. ąÆ č鹊ą╝ čüą╗čāčćą░ąĄ, ąĄčüą╗ąĖ ą╝čŗ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖą╝ ąŠ ąĮąĄąĖčüčćąĖčüą╗čÅąĄą╝čŗčģ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ, ą╗ąĖą▒ąŠ ąŠ ą╝ąĮąŠąČąĄčüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╝ čćąĖčüą╗ąĄ ąĖčüčćąĖčüą╗čÅąĄą╝čŗčģ, č鹊 ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ some: Give me some water, please. There are some taxis at the taxi rank. ’ü« ąÆ č鹊ą╝ čüą╗čāčćą░ąĄ, ą║ąŠą│ą┤ą░ ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄčé ąĮą░ą╝ ąĘą░čĆą░ąĮąĄąĄ ąĮąĄ ąĖąĘą▓ąĄčüč鹥ąĮ, ą┐čĆąĖ ą┐ąĄčĆą▓ąŠą╝ čāą┐ąŠą╝ąĖąĮą░ąĮąĖąĖ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ ąĮąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī, ąĮąŠ ą┐čĆąĖ ą┐ąŠčüą╗ąĄą┤čāčÄčēąĄą╝ čāą┐ąŠą╝ąĖąĮą░ąĮąĖąĖ čāąČąĄ ąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣: I have got a car. The car is red. ’ü« ąØąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī čćą░čüč鹊 ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ ą┐ąŠčüą╗ąĄ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ąŠą▓ have ąĖ be: I have got a pen. She is a teacher. ’ü« ąØąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī ą▓čŗčüčéčāą┐ą░ąĄčé ą▓ ą║ą░č湥čüčéą▓ąĄ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░ ┬½per┬╗: He works five days a week ŌĆö ąŠąĮ čĆą░ą▒ąŠčéą░ąĄčé 5 ą┤ąĮąĄą╣ ą▓ ąĮąĄą┤ąĄą╗čÄ ’ü« ąØąĄąŠą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ ą║ąŠą│ą┤ą░ ą╝čŗ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖą╝ ąŠ ą┐čĆąĄą┤čüčéą░ą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗ąĄ ą║ą╗ą░čüčüą░ ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╝ąĄč鹊ą▓: An African elephant has larger ears than an Indian elephant.
- 19. ą×ą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĄą╗ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī ’ü« ąĪ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ąĮą░ą╝ ąĖąĘą▓ąĄčüčéąĮčŗ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ą▓čŗą┤ąĄą╗čÅčÄčéčüčÅ ąĖąĘ čĆčÅą┤ą░ ą▓ąĄčēąĄą╣. ąÜąŠą│ą┤ą░ ą╝čŗ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖą╝ ąŠ č湥ą╝-č鹊 ą║ąŠąĮą║čĆąĄčéąĮąŠą╝. ąóą░ą║ąŠąĄ čćą░čüč鹊 ą┐čĆąŠąĖčüčģąŠą┤ąĖčé ą┐čĆąĖ ą┐ąŠą▓č鹊čĆąĮąŠą╝ čāą┐ąŠą╝ąĖąĮą░ąĮąĖąĖ: Bob has got a car and a bike. The car is green and the bike is blue. ’ü« ąĪ čāąĮąĖą║ą░ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ: the sun, the Earth ’ü« ąĪ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮą░ą╝ąĖ ą│ą░ąĘąĄčé (the Guardian), ą║ąĖąĮąŠč鹥ą░čéčĆąŠą▓ (the Odeon), č鹥ą░čéčĆąŠą▓ (the Empire), ą╝čāąĘąĄąĄą▓ (the Louvre), ą║ąŠčĆą░ą▒ą╗ąĄą╣ (the Marie Celeste), ąŠčĆą│ą░ąĮąĖąĘą░čåąĖčÅą╝ąĖ (the United Nations) ’ü« ąĪ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝ąĖ čĆąĄą║ (the Thames); čü ą│čĆčāą┐ą┐ą░ą╝ąĖ ąŠčüčéčĆąŠą▓ąŠą▓ (the Seychelles); čü ą╝ą░čüčüąĖą▓ą░ą╝ąĖ ą│ąŠčĆ (the Alps); čü ą┐čāčüčéčŗąĮčÅą╝ąĖ (the Sahara); čü ąŠą║ąĄą░ąĮą░ą╝ąĖ (the Atlantic); čü ą║ą░ąĮą░ą╗ą░ą╝ąĖ (the Panama canal); čüčéčĆą░ąĮą░ą╝ąĖ, ąĄčüą╗ąĖ ąŠąĮąĖ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé ą▓ čüąĄą▒čÅ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░ čéąĖą┐ą░ States, Kingdom, Republic (the UK); čü čćą░čüčéčÅą╝ąĖ čüą▓ąĄčéą░ (the North/East/South/West) ’ü« ąĪ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮą░ą╝ąĖ ą╝čāąĘčŗą║ą░ą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ąĖąĮčüčéčĆčāą╝ąĄąĮč鹊ą▓ ąĖ čéą░ąĮčåąĄą▓: the guitar, the salsa ’ü« ąĪ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝ąĖ čüąĄą╝ąĄą╣ (ąĮą░ą┐čĆ. the Browns) ąĖ ąĮą░čåąĖąŠąĮą░ą╗čīąĮąŠčüčéčÅą╝ąĖ, ąŠą║ą░ąĮčćąĖą▓ą░čÄčēąĖą╝ąĖčüčÅ ąĮą░ -sh, -ch, ąĖą╗ąĖ -ese (the French). ąÆ ąĖąĮąŠą╝ čüą╗čāčćą░ąĄ ą╝ąŠąČąĮąŠ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖčéčī ąĖ čü the ąĖ ą▒ąĄąĘ (the Egyptians/Egyptians) ’ü« ąĪąŠ ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝ąĖ: the Queen, the President. ąØą×: Queen Victoria (čé.ąĄ. ąĄčüą╗ąĖ čāą║ą░ąĘą░ąĮąŠ ąĖą╝čÅ ŌĆö ąĮąĄ čüčéą░ą▓ąĖą╝) ’ü« ąĪąŠ čüčĆą░ą▓ąĮąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ čüč鹥ą┐ąĄąĮčÅą╝ąĖ: the best. ąØą×: Most people enjoy going to the cinema ’ü« ąĪąŠ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░ą╝ąĖ day, morning, afternoon ąĖ evening: It was early in the morning when they left. ąØą×: at night, at noon, at midnight, by day/night ’ü« ąĪ ąĖčüč鹊čĆąĖč湥čüą║ąĖą╝ąĖ ą┐ąĄčĆąĖąŠą┤ą░ą╝ąĖ: the last Ice Age, the Vietnam war. ąØą×: World War I ’ü« ąĪąŠ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░ą╝ąĖ only, last ąĖ first (ąĄčüą╗ąĖ ąŠąĮąĖ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÄčéčüčÅ ą║ą░ą║ ą┐čĆąĖą╗ą░ą│ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗąĄ): She was the only one who didnŌĆÖt come
- 20. ąØčāą╗ąĄą▓ąŠą╣ ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī ’ü« ąĪ ąĮąĄąĖčüčćąĖčüą╗čÅąĄą╝čŗą╝ąĖ ąĖ ą╝ąĮąŠąČąĄčüčéą▓ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╝ąĖ čüčāčēąĄčüčéą▓ąĖč鹥ą╗čīąĮčŗą╝ąĖ, ą║ąŠą│ą┤ą░ ą╝čŗ ą│ąŠą▓ąŠčĆąĖą╝ ąŠ č湥ą╝-č鹊 ą▓ ąŠą▒čēąĄą╝ čüą╝čŗčüą╗ąĄ čŹč鹊ą│ąŠ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░. Planes are a safe means of transport. Tea is a very popular drink. ’ü« ąĪ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮą░ą╝ąĖ: Ann works as a librarian ’ü« ąĪ ąĮą░ąĘą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅą╝ąĖ ąĖą│čĆ, ą┤ąĮčÅą╝ąĖ, ą╝ąĄčüčÅčåą░ą╝ąĖ, ą┐čĆą░ąĘą┤ąĮąĖą║ą░ą╝ąĖ, čåą▓ąĄčéą░ą╝ąĖ, ąĮą░ą┐ąĖčéą║ą░ą╝ąĖ ąĖ ąĄą┤ąŠą╣. We had dinner with the Smiths on Friday. ’ü« ąĪ čÅąĘčŗą║ą░ą╝ąĖ. Bob speaks Polish, French and English fluently. ąØąŠ ąĄčüą╗ąĖ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāąĄčéčüčÅ čüą╗ąŠą▓ąŠ language č鹊 ą░čĆčéąĖą║ą╗čī čüčéą░ą▓ąĖčéčüčÅ: The French language is spoken in parts of Canada ’ü« ąĪ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮą░ą╝ąĖ čüčéčĆą░ąĮ, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ąĮąĄ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé ą▓ čüąĄą▒čÅ čüą╗ąŠą▓ą░ State, Kingdom ąĖą╗ąĖ Republic. Germany, India, Australia. ąśčüą║ą╗čÄč湥ąĮąĖčÅ: the Netherlands, the Gambia, the Vatican ’ü« ąĪ ąĖą╝ąĄąĮą░ą╝ąĖ čāą╗ąĖčå (Oxford street, Penny Lane), ą┐ą╗ąŠčēą░ą┤čÅą╝ąĖ (Trafalgar Square), ą╝ąŠčüčéą░ą╝ąĖ (London Bridge)
- 23. Articles Exercises ’ü« 1. Choose the correct variant. ’ü« I. ŌĆ”Smiths have a dog and a cat. a) ŌĆ” b) The c) A 2. He knows how to work on ŌĆ” computer. a) a b) an c) ŌĆ” 3. She was the first woman to swim across ŌĆ” English Channel. a) a b) ŌĆ” c) the 4. Go down ŌĆ” Kingston Street and turn left into Oxford Street. a) the b) a c) ŌĆ” 5. I donŌĆÖt like milk in ŌĆ” tea. a) ŌĆ” b) the čü) ą░ 6. At the end ofŌĆ” busy day, sleep is the best way to restore your energy. a) the b) a c) ŌĆ” 7. WeŌĆÖll go for a walk if ŌĆ” weather is fine. a) a b) ŌĆ” c) the 8. Could you give me ŌĆ” information I asked for in my letter? a) the b) ŌĆ” c) a 9. ŌĆ”war is a terrible thing. a) The b) ŌĆ” čü) ąÉ 10. I spent ŌĆ” very interesting holiday in England. a) the b) a c) ŌĆ”
- 24. Conditionals
- 25. Conditional Exercises ’ü« Open the brackets: ’ü« 1. If I hear the thief I (catch) him. 2. I (go) to the cinema if I had more time. 3. I will call her if I (find out) her number. 4. If they (be) rich they would stay in a more expensive hotel. 5. She (feel) ill if she eats so much. 6. If he skis too fast he (break) his leg. 7. You (get) wet if you donŌĆÖt take an umbrella. 8. He (cause) an accident if he drives too dangerously. 9. They would get drunk if they (drink) too much beer. 10. If you steal the purse they (arrest) you. 11. If she (explain) him the situation he will understand it. 12. If he offered me a job I (take) it.
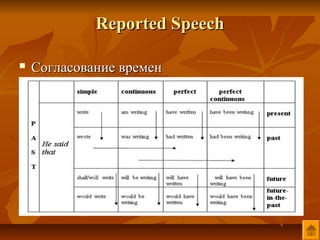
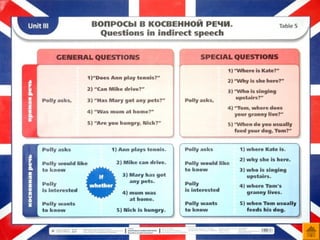
- 26. Reported Speech ’ü« ąĪąŠą│ą╗ą░čüąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮ
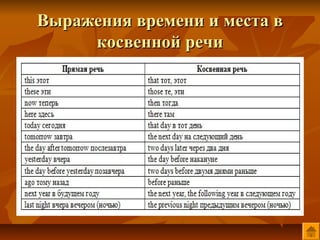
- 28. ąÆčŗčĆą░ąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĖ ąĖ ą╝ąĄčüčéą░ ą▓ ą║ąŠčüą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ čĆąĄčćąĖ
- 29. Reported speech Exercises ’ü« 1. ŌĆō ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąĖčłąĖč鹥 ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ą▓ ą║ąŠčüą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ čĆąĄčćąĖ, ąŠą▒čĆą░čéąĖč鹥 ą▓ąĮąĖą╝ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ąĮą░ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖąĄ ą╝ąĄčüč鹊ąĖą╝ąĄąĮąĖą╣ ąĖ ą▓ąĖą┤ąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮčŗčģ č乊čĆą╝ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ąŠą▓. ’ü« 1. They said, "This is our book." ’ü« They said __________. ’ü« 2. She said, "I went to the cinema yesterday." ’ü« She said __________. ’ü« 3. He said, "I am writing a test tomorrow." ’ü« He said __________. ’ü« 4. You said, "I will do this for him." ’ü« You said __________. ’ü« 5. She said, "I am not hungry now." ’ü« She said __________. ’ü« 6. They said, "We have never been here before." ’ü« They said __________.
- 30. ’ü« 2. ŌĆō ąÆąŠą┐čĆąŠčüčŗ ą▓ ą║ąŠčüą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ čĆąĄčćąĖ. ą¤ąĄčĆąĄą┐ąĖčłąĖč鹥 ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ ą▓ ą║ąŠčüą▓ąĄąĮąĮąŠą╣ čĆąĄčćąĖ, ąŠą▒čĆą░čéąĖč鹥 ą▓ąĮąĖą╝ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ąĮą░ ąĖąĘą╝ąĄąĮąĄąĮąĖąĄ ą╝ąĄčüč鹊ąĖą╝ąĄąĮąĖą╣ ąĖ ą▓ąĖą┤ąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮčŗčģ č乊čĆą╝ ą│ą╗ą░ą│ąŠą╗ąŠą▓. ’ü« 1. "Where is my umbrella?" she asked. ’ü« She asked __________. ’ü« 2. "How are you?" Martin asked us. ’ü« Martin asked us __________. ’ü« 3. He asked, "Do I have to do it?" ’ü« He asked __________. ’ü« 4. "Where have you been?" the mother asked her daughter. ’ü« The mother asked her daughter __________. ’ü« 5. "Which dress do you like best?" she asked her boyfriend. ’ü« She asked her boyfriend __________. ’ü« 6. "What are they doing?" she asked. ’ü« She wanted to know __________. ’ü« 7. "Are you going to the cinema?" he asked me. ’ü« He wanted to know __________.
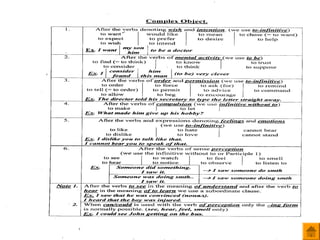
- 32. Complex object Exercises ’ü« ąŚą░ą║ąŠąĮčćąĖč鹥 ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ąŠąČąĄąĮąĖčÅ, ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÅ ąĖčüą┐ąŠą╗čīąĘčāčÅ čüą╗ąŠąČąĮąŠąĄ ą┤ąŠą┐ąŠą╗ąĮąĄąĮąĖąĄ (Complex Object). 1. She wants you ŌĆ” 2. We saw themŌĆ” 3. He considered herŌĆ” 4. Mary heard TimŌĆ” 5. Sarah watched her sister ŌĆ” 6. I noticed herŌĆ”ŌĆ” 7. We never expected them ŌĆ” 8. IŌĆÖd like my friend ŌĆ” 9. Mother wishes her daughter ŌĆ” 10. Father expected his son ŌĆ”
- 33. THE END