English Reviewer
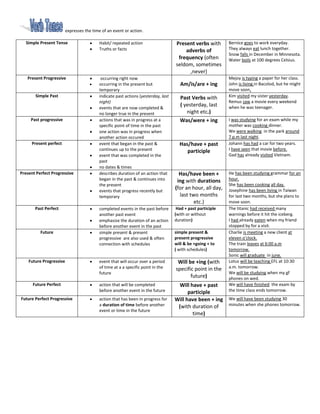
- 1. expresses the time of an event or action. Simple Present Tense Habit/ repeated action Present verbs with Bernice goes to work everyday. Truths or facts adverbs of They always eat lunch together. Snow falls in December in Minnesota. frequency (often Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius. seldom, sometimes ,never) Present Progressive occurring right now Mejoy is typing a paper for her class. occurring in the present but Am/is/are + ing John is living in Bacolod, but he might temporary move soon. Simple Past indicate past actions (yesterday, last Past Verbs with Kim visited my sister yesterday. night) Remus saw a movie every weekend events that are now completed & ( yesterday, last when he was teenager. no longer true in the present night etc.) Past progressive actions that was in progress at a Was/were + ing I was studying for an exam while my specific point of time in the past mother was cooking dinner. one action was in progress when We were walking in the park around another action occured 7 p.m last night. Present perfect event that began in the past & Has/have + past Johann has had a car for two years. continues up to the present participle I have seen that movie before. event that was completed in the Gad has already visited Vietnam. past no dates & times Present Perfect Progressive describes duration of an action that Has/have been + He has been studying grammar for an began in the past & continues into ing with durations hour. the present She has been cooking all day. events that progress recently but (for an hour, all day, Josephine has been living in Taiwan temporary last two months for last two months, but she plans to etc.) move soon. Past Perfect completed events in the past before Had + past participle The titanic had received many another past event (with or without warnings before it hit the iceberg. emphasize the duration of an action duration) I had already eaten when my friend before another event in the past stopped by for a visit. Future simple present & present simple present & Charlie is meeting a new client at progressive are also used & often present progressive eleven o’clock. connection with schedules will & be +going + to The train leaves at 6:00 a.m ( with schedules) tomorrow. Sonic will graduate in june. Future Progressive event that will occur over a period Will be +ing (with Lotus will be teaching EFL at 10:30 of time at a a specific point in the specific point in the a.m. tomorrow. future We will be studying when my gf future) phones on wed. Future Perfect action that will be completed Will have + past We will have finished the exam by before another event in the future participle the time class ends tomorrow. Future Perfect Progressive action that has been in progress for Will have been + ing We will have been studying 30 a duration of time before another (with duration of minutes when she phones tomorrow. event or time in the future time)
- 2. Structure of a sentence The Simple sentence – one INDEPENDENT CLAUSE Compound sentence- two or more independent clauses Compound complex- 2 or more independent clauses & 1 or more dependent clause Complex- 1 independent clause & 1 or more dependent clause Types of Sentence Functions Declarative- state an idea Exclamatory- strong emotions Interrogative- ask a question Imperative- give orders or directions Sentence Topic introducer- introduces the topic Topic sentence- defines the topic in the paragraph Supporting / developer/ subordinating sentences- makes up the body of paragraph Clincher/ concluding- concludes the paragraph Irrelevant- not relevant to the paragraph Main Idea: controlling thought or central message Explicit main idea- expressed or stated Implicit main idea- (inferred or implied) not clearly stated Sentence Fragment: is a part or piece, of a sentence placed by itself as if it were a complete sentence. Fragment made from an appositive- rename Prepositional phrase- introduced by preposition (in, on, at) Participial phrase- with –ing form Infinitive phrase- to + simple verb Relative pronoun clause- (that, which, who, whom, whose, whichever, whoever, whomever)