English support stages of learning (kumi)
Download as pptx, pdf1 like520 views
This document provides guidance for teachers on supporting English language learners. It discusses common hurdles students may face in listening, speaking, reading and writing. It then outlines the teacher's role in building rapport, motivating students, and differentiating instruction. Finally, it summarizes the typical stages of second language acquisition: pre-production, early production, speech emergence, intermediate fluency, and advanced fluency. Teachers are advised to have realistic expectations and assess students' progress through the stages.
1 of 21
Download to read offline
















Ad
Recommended
Teaching Writing As An Integrated Skill Ekl
Teaching Writing As An Integrated Skill EklErin Lowry
╠²
This document discusses strategies for integrating writing into language lessons. It provides an overview of writing for learning, writing skills, and writing for different purposes or genres. Various techniques are proposed, such as reinforcement writing, adapting textbook activities, using graphic organizers, sequencing pictures, and having students write poems, comics, or blogs. Sample rubrics are also included.Day 3 New Tutor Training
Day 3 New Tutor Training Christine Loewe
╠²
The document outlines four essential components of reading: phonics, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension, detailing methods for teaching each component. It emphasizes the importance of phonics for pronunciation and understanding sounds, as well as strategies for improving reading fluency and comprehension through various techniques. Additionally, it provides practical activities and strategies to help students become competent, independent readers.What is vocabulary
What is vocabularyUzma Tahir
╠²
1) A person's vocabulary consists of words they are familiar with in a language and develops with age, serving as a fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge.
2) There are many strategies for improving and expanding one's vocabulary, including extensive reading, repetition, learning words in context, using vocabulary trees, word walls, root words, prefixes and suffixes, synonyms and antonyms, word formation charts, word lists, and word games.
3) Mastering vocabulary is important for effective communication, understanding, thinking, and being understood by others. Regular practice over time is needed to significantly improve one's vocabulary.Differentiating the writing process for ell writers
Differentiating the writing process for ell writersliserhull1976
╠²
The document provides tips and strategies for teaching writing. It discusses using mentor texts to expose students to good writing examples, annotating texts to increase comprehension, and stretching out the writing process by taking smaller steps and slowing down. The document also addresses including language instruction, guiding students through drafting, teaching the difference between right and wrong, and giving specific feedback on writing.Vocabulary building 12
Vocabulary building 12nalini jennett
╠²
This document discusses vocabulary building. It defines vocabulary as knowledge of words and their meanings. Building vocabulary is important for communication, learning, and academic success. Some effective strategies for building vocabulary include learning prefixes, suffixes, roots, and origins of words. The document provides examples of prefixes and suffixes and their meanings. Direct instruction of vocabulary in context along with repetition and review are recommended for teaching vocabulary.July 2016 AEI - English as a Second Language Assessment
July 2016 AEI - English as a Second Language Assessmentnbteacher
╠²
This presentation discusses the English Second Language Assessment (ESLA) used in New Brunswick. The ESLA evaluates students' English proficiency through four components: listening, reading, writing, and oral proficiency interviews. It assesses what students can do with English in real-life situations. The presentation reviews the standards and test specifications for each component, providing examples of question types for reading and details about scoring rubrics for writing and oral interviews. Scores on the four components are weighted equally and combined to calculate an overall ESLA result.Answering skills
Answering skillsKimo11
╠²
1. Note taking is an important practice for capturing information from textbooks and lectures. It improves listening skills, focus, organization of information, understanding, and retention.
2. There are different note taking methods like the Cornell Method and Mapping Method. Effective notes are written legibly using key words and cue words to make them concise.
3. The "5 R's of Note Taking" are: Record, Reduce, Recite, Reflect, and Review. This helps to actively engage with the material by writing, reciting without notes, reflecting on ideas, and reviewing main points.Speaking listening class-online
Speaking listening class-onlineJo Byrne
╠²
This document outlines the content and activities for a session on speaking, listening, and communicating. It includes learning outcomes related to expressing oneself clearly, using linguistic techniques for cohesion, listening critically, and recognizing non-verbal communication. Participants are asked to self-assess their confidence in these areas and identify what could help improve. The session covers topics like back-referencing, discourse markers, intonation, and non-verbal communication. Activities include demonstrating communication techniques, a dictagloss exercise to reconstruct a text, and planning and sharing a speech. Homework includes reviewing session content and selecting a topic for a summative assessment presentation.Using the Developmental Writing Scale
Using the Developmental Writing ScaleJane Farrall
╠²
The document discusses the Developmental Writing Scale, a 14-point scale used to assess writing development from emergent to conventional levels. It provides descriptions and examples for each level, along with accommodation considerations. The Grove Education Centre in Australia uses this scale to measure progress toward its goal of increasing student achievement in writing. Staff collect student writing samples throughout the year to rate on the scale during moderation sessions, aiming to improve the percentage of students moving up one level each year.Chapter 9, Productive skills: speaking and writing
Chapter 9, Productive skills: speaking and writingAlejandro Stipic
╠²
This document discusses approaches to teaching speaking and writing skills in the classroom. It emphasizes creating a safe environment where students are motivated and encouraged to practice speaking. Communicative activities should involve meaningful exchanges to practice language. Role plays and real-life scenarios can offer practice for specific grammar and functions. When focusing on fluency, teachers should avoid interrupting to correct accuracy. Different speaking contexts require different genres. When teaching writing, copying exercises may help learners but not make them better writers. Teachers should encourage students to follow a preparation process for writing assignments and provide feedback that is helpful, not discouraging.Literacy Through Curriculum: Using the Australian Curriculum as a springboard...
Literacy Through Curriculum: Using the Australian Curriculum as a springboard...Jane Farrall
╠²
This document provides an overview of how the Australian curriculum can be used as a framework to develop literacy at the Adelaide West Special Education Centre. It discusses key concepts in literacy development including balanced literacy, communication, mastery versus emergent views of literacy. Time recommendations and achievement standards are presented for various learning areas from the Australian curriculum adapted for students with disabilities. The use of individual goal setting and reporting on the general capabilities is also described as part of a balanced literacy approach at the school.Strategies and skills during shared reading for esl
Strategies and skills during shared reading for eslmreiss50
╠²
The document outlines strategies and skills for shared reading aimed at ESL students, emphasizing the importance of engagement and understanding of text. It describes techniques such as filling in sentences, discussing text directionality, identifying words, and using visuals to enhance comprehension. Shared reading is portrayed as a collaborative approach where teachers model reading strategies and students gradually participate, making it effective for learners at various language and reading levels.Teaching writing and vocabulary
Teaching writing and vocabularyF├Ītima Molina Rodr├Łguez
╠²
This document discusses strategies for teaching writing and vocabulary to young English language learners ages 4-7. It outlines techniques for teaching writing such as modeling the writing process, using group writing activities, and encouraging experimentation. It also provides principles for vocabulary instruction, emphasizing direct and indirect teaching methods, pre-teaching vocabulary, and giving multiple exposures through engaging activities like "Word of the Day" and scavenger hunts. Classroom activities are suggested to develop both writing and vocabulary skills in a fun, supportive way for young learners.Vocabulary
VocabularyKim Hutton-Brown
╠²
Vocabulary is the most important feature of written English. There are two main techniques for improving vocabulary - passive learning through daily activities like reading, and active learning through conscious effort. Some tips for building vocabulary include using new words immediately, learning word roots, using a thesaurus, keeping a vocabulary journal, doing word puzzles, and learning one new word every day. Regular practice in divergent ways and asking for feedback can help commit new words to long-term memory.Spm paper 1
Spm paper 1Sophia Kamal
╠²
The document provides time management and writing tips for the SPM English Language Paper 1 exam. It recommends allocating 1 hour and 45 minutes total for the paper, with 1 hour and 15 minutes for Section A and 30 minutes for writing and 10 minutes for editing in Section B. For Section A, it advises 15 minutes for preparation, 15 minutes for writing, and 10 minutes for editing. Section A is worth 35 marks and evaluates format, content, and language. Section B is worth 50 marks and involves continuous writing in various compositions. It stresses the importance of reading to improve writing skills.Spm answering techniques
Spm answering techniquesMohamad Razif Bin Disa
╠²
The document outlines guidelines for students preparing for the 1119 English exam, covering time management and the structure of both papers. It details the types of directed writing tasks, strategies for reading and writing effectively, and the marking schemes for various sections. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of practice in enhancing writing skills and understanding English through reading.Vocabulary instruction for academic success
Vocabulary instruction for academic successGRAi9
╠²
This document is a summary of a book on vocabulary instruction for academic success. It provides an overview of the book's contents, including its focus on the importance of vocabulary knowledge, strategies for developing oral language skills and promoting wide reading, creating a word-conscious classroom environment, teaching individual words, and teaching word-learning strategies. The foreword discusses how the book addresses key issues around vocabulary development and offers practical teaching suggestions and examples.Developing speaking skill
Developing speaking skillIrina K
╠²
This document discusses developing speaking skills in teaching English as a foreign language. It outlines some key characteristics of effective speaking, including using gestures, emphasis, and interacting with the audience. It also lists activities that can promote speaking practice, such as discussions, role-plays, storytelling, picture narration, and reporting. The document provides suggestions for teachers, such as reducing their own speaking time, providing feedback, and diagnosing issues to give targeted practice.Listening and Reading comprehensions
Listening and Reading comprehensionsIna Qzero
╠²
This document discusses testing reading and listening comprehension. It outlines three main levels of reading comprehension strands: literature comprehension, interpretive comprehension, and critical reading. It also discusses how listening comprehension is assessed through having students retell texts, answer questions, and take notes after a teacher reads aloud. The document provides strategies for improving listening comprehension such as reading aloud texts and having students take notes, take bulleted notes, or discuss ideas to support note-taking.Teaching productive skills
Teaching productive skillsTheo Navarro
╠²
Teaching speaking and writing to adults and young adults is challenging due to a lack of motivation and the need for creative, engaging activities. Teachers should adapt lessons to student interests and conduct needs analyses to understand their English requirements. Focus on practical, real-life applications and utilize personal experiences to enhance engagement in both speaking and writing activities.Working with ELL Writers
Working with ELL WritersMegan McIntyre
╠²
This document provides information and strategies for working with English language learner (ELL) writers at the University of South Florida. It begins by providing statistics on the international student population, noting that the majority are graduate students from China and India studying engineering, business, health, or STEM fields. The document explains that ELL writers may be unfamiliar with academic conventions and have a difference between their speaking and writing skills. It recommends focusing consultations on higher-order concerns like thesis, organization, and assignment expectations before addressing lower-order grammar and syntax issues. Examples are provided of strategies for assessing needs, reviewing papers, and closing sessions.Controlled writing
Controlled writingBeberly Fabayos
╠²
The document discusses controlled writing as an educational approach to reinforce grammar, syntax, and mechanics for language learners, contrasting it with free writing. It highlights the role of controlled writing in preventing errors from first language interference, providing frameworks for practice at various levels of student ability, and introducing new language structures. Additionally, it emphasizes the effectiveness of controlled writing tasks in promoting structured writing and enhancing students' grammatical knowledge.Graphic organizer
Graphic organizer Ashnielkookie
╠²
Graphic organizers are visual displays that help learners organize information. They connect content in a meaningful way to improve understanding. There are four main types: sequential, conceptual, cyclical, and hierarchical organizers. Graphic organizers benefit students by organizing information, requiring higher-order thinking, building analytical skills, providing scaffolding, and engaging students with graphics. They also help teachers structure lessons and assess student understanding. Common uses of graphic organizers include sequencing events, analyzing concepts, note-taking, comparing ideas, and relating information to main topics. Effective implementation involves familiarizing students with organizers, using examples, and reviewing student work.Using Games in Teaching Vocabulary
Using Games in Teaching VocabularyEvi Sofiawati
╠²
This document discusses using games to teach vocabulary. It explains that games can help lower students' affective filters, promote active participation and problem solving, and cater to different learning styles. It then provides an example lesson plan that uses several vocabulary games, including ambiguous pictures, association, matching, and crossword, to teach occupation-related vocabulary to 5th and 6th grade students. The games are designed to engage students physically and intellectually while reinforcing the new vocabulary terms based on theories of multiple intelligences, learning styles, constructivism, and total physical response.Writing Skills: WWTM GAME
Writing Skills: WWTM GAMEBreenLi
╠²
Controlled activities focus on practicing language skills like spelling and handwriting. They are done to practice the language itself. Free activities allow for self-expression and creativity, with content being most important. The process approach emphasizes starting writing early and using pre-writing activities like brainstorming, while the product approach focuses on the final writing and correcting errors.Decoding Skills
Decoding SkillsMiami-Dade County Public Schools
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to decoding skills and assessing students' mastery of various phonics concepts and reading skills. It addresses how to identify issues with blends, digraphs, and diphthongs; the importance of reinforcement activities; assessing structural analysis abilities; strategies for teaching English language learners; and methods for evaluating students' understanding of context clues and contractions. A variety of activities are proposed to teach and reinforce these critical early reading skills.AAC & Literacy: In Partnership to Develop Language
AAC & Literacy: In Partnership to Develop LanguageJane Farrall
╠²
This document provides information on strategies for combining augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) with emergent literacy instruction. It discusses why AAC and literacy should be partnered to develop language, noting the need for meaningful communication and engagement. Shared reading is recommended, using techniques like Comment, Ask, Respond (CAR) and its extension, Putting the CROWD in the CAR, which involves completion, recall, open-ended questions, WH- questions, and distancing. Predictable chart writing is also outlined as an interactive writing activity where students compose text with an adult using a repeated sentence structure.Module 2 study guide
Module 2 study guideHDMcWhorter
╠²
The document discusses teaching English as a second language. It explains that as communities become more multicultural, teaching English must become a more important part of the curriculum. It also discusses different methodologies for teaching listening, speaking, reading and writing skills to English language learners from elementary through high school levels. These include developing basic interpersonal communication skills as well as cognitive academic language proficiency. Understanding theories of second language acquisition, such as Krashen's theory, is important for instructors to effectively teach English skills.Teaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary s...
Teaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary s...JennyPalo1
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of teaching literacy skills. It covers topics like defining literacy, the changing nature of literacy in the 21st century, developing fundamental reading skills like phonological awareness early on, the four language skills, the importance of oral language, and instructional strategies to develop vocabulary, fluency, and reading comprehension. Effective literacy instruction requires matching students with texts at their appropriate reading level to ensure success.Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...porfazhiie
╠²
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. MorrisonMore Related Content
What's hot (19)
Using the Developmental Writing Scale
Using the Developmental Writing ScaleJane Farrall
╠²
The document discusses the Developmental Writing Scale, a 14-point scale used to assess writing development from emergent to conventional levels. It provides descriptions and examples for each level, along with accommodation considerations. The Grove Education Centre in Australia uses this scale to measure progress toward its goal of increasing student achievement in writing. Staff collect student writing samples throughout the year to rate on the scale during moderation sessions, aiming to improve the percentage of students moving up one level each year.Chapter 9, Productive skills: speaking and writing
Chapter 9, Productive skills: speaking and writingAlejandro Stipic
╠²
This document discusses approaches to teaching speaking and writing skills in the classroom. It emphasizes creating a safe environment where students are motivated and encouraged to practice speaking. Communicative activities should involve meaningful exchanges to practice language. Role plays and real-life scenarios can offer practice for specific grammar and functions. When focusing on fluency, teachers should avoid interrupting to correct accuracy. Different speaking contexts require different genres. When teaching writing, copying exercises may help learners but not make them better writers. Teachers should encourage students to follow a preparation process for writing assignments and provide feedback that is helpful, not discouraging.Literacy Through Curriculum: Using the Australian Curriculum as a springboard...
Literacy Through Curriculum: Using the Australian Curriculum as a springboard...Jane Farrall
╠²
This document provides an overview of how the Australian curriculum can be used as a framework to develop literacy at the Adelaide West Special Education Centre. It discusses key concepts in literacy development including balanced literacy, communication, mastery versus emergent views of literacy. Time recommendations and achievement standards are presented for various learning areas from the Australian curriculum adapted for students with disabilities. The use of individual goal setting and reporting on the general capabilities is also described as part of a balanced literacy approach at the school.Strategies and skills during shared reading for esl
Strategies and skills during shared reading for eslmreiss50
╠²
The document outlines strategies and skills for shared reading aimed at ESL students, emphasizing the importance of engagement and understanding of text. It describes techniques such as filling in sentences, discussing text directionality, identifying words, and using visuals to enhance comprehension. Shared reading is portrayed as a collaborative approach where teachers model reading strategies and students gradually participate, making it effective for learners at various language and reading levels.Teaching writing and vocabulary
Teaching writing and vocabularyF├Ītima Molina Rodr├Łguez
╠²
This document discusses strategies for teaching writing and vocabulary to young English language learners ages 4-7. It outlines techniques for teaching writing such as modeling the writing process, using group writing activities, and encouraging experimentation. It also provides principles for vocabulary instruction, emphasizing direct and indirect teaching methods, pre-teaching vocabulary, and giving multiple exposures through engaging activities like "Word of the Day" and scavenger hunts. Classroom activities are suggested to develop both writing and vocabulary skills in a fun, supportive way for young learners.Vocabulary
VocabularyKim Hutton-Brown
╠²
Vocabulary is the most important feature of written English. There are two main techniques for improving vocabulary - passive learning through daily activities like reading, and active learning through conscious effort. Some tips for building vocabulary include using new words immediately, learning word roots, using a thesaurus, keeping a vocabulary journal, doing word puzzles, and learning one new word every day. Regular practice in divergent ways and asking for feedback can help commit new words to long-term memory.Spm paper 1
Spm paper 1Sophia Kamal
╠²
The document provides time management and writing tips for the SPM English Language Paper 1 exam. It recommends allocating 1 hour and 45 minutes total for the paper, with 1 hour and 15 minutes for Section A and 30 minutes for writing and 10 minutes for editing in Section B. For Section A, it advises 15 minutes for preparation, 15 minutes for writing, and 10 minutes for editing. Section A is worth 35 marks and evaluates format, content, and language. Section B is worth 50 marks and involves continuous writing in various compositions. It stresses the importance of reading to improve writing skills.Spm answering techniques
Spm answering techniquesMohamad Razif Bin Disa
╠²
The document outlines guidelines for students preparing for the 1119 English exam, covering time management and the structure of both papers. It details the types of directed writing tasks, strategies for reading and writing effectively, and the marking schemes for various sections. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of practice in enhancing writing skills and understanding English through reading.Vocabulary instruction for academic success
Vocabulary instruction for academic successGRAi9
╠²
This document is a summary of a book on vocabulary instruction for academic success. It provides an overview of the book's contents, including its focus on the importance of vocabulary knowledge, strategies for developing oral language skills and promoting wide reading, creating a word-conscious classroom environment, teaching individual words, and teaching word-learning strategies. The foreword discusses how the book addresses key issues around vocabulary development and offers practical teaching suggestions and examples.Developing speaking skill
Developing speaking skillIrina K
╠²
This document discusses developing speaking skills in teaching English as a foreign language. It outlines some key characteristics of effective speaking, including using gestures, emphasis, and interacting with the audience. It also lists activities that can promote speaking practice, such as discussions, role-plays, storytelling, picture narration, and reporting. The document provides suggestions for teachers, such as reducing their own speaking time, providing feedback, and diagnosing issues to give targeted practice.Listening and Reading comprehensions
Listening and Reading comprehensionsIna Qzero
╠²
This document discusses testing reading and listening comprehension. It outlines three main levels of reading comprehension strands: literature comprehension, interpretive comprehension, and critical reading. It also discusses how listening comprehension is assessed through having students retell texts, answer questions, and take notes after a teacher reads aloud. The document provides strategies for improving listening comprehension such as reading aloud texts and having students take notes, take bulleted notes, or discuss ideas to support note-taking.Teaching productive skills
Teaching productive skillsTheo Navarro
╠²
Teaching speaking and writing to adults and young adults is challenging due to a lack of motivation and the need for creative, engaging activities. Teachers should adapt lessons to student interests and conduct needs analyses to understand their English requirements. Focus on practical, real-life applications and utilize personal experiences to enhance engagement in both speaking and writing activities.Working with ELL Writers
Working with ELL WritersMegan McIntyre
╠²
This document provides information and strategies for working with English language learner (ELL) writers at the University of South Florida. It begins by providing statistics on the international student population, noting that the majority are graduate students from China and India studying engineering, business, health, or STEM fields. The document explains that ELL writers may be unfamiliar with academic conventions and have a difference between their speaking and writing skills. It recommends focusing consultations on higher-order concerns like thesis, organization, and assignment expectations before addressing lower-order grammar and syntax issues. Examples are provided of strategies for assessing needs, reviewing papers, and closing sessions.Controlled writing
Controlled writingBeberly Fabayos
╠²
The document discusses controlled writing as an educational approach to reinforce grammar, syntax, and mechanics for language learners, contrasting it with free writing. It highlights the role of controlled writing in preventing errors from first language interference, providing frameworks for practice at various levels of student ability, and introducing new language structures. Additionally, it emphasizes the effectiveness of controlled writing tasks in promoting structured writing and enhancing students' grammatical knowledge.Graphic organizer
Graphic organizer Ashnielkookie
╠²
Graphic organizers are visual displays that help learners organize information. They connect content in a meaningful way to improve understanding. There are four main types: sequential, conceptual, cyclical, and hierarchical organizers. Graphic organizers benefit students by organizing information, requiring higher-order thinking, building analytical skills, providing scaffolding, and engaging students with graphics. They also help teachers structure lessons and assess student understanding. Common uses of graphic organizers include sequencing events, analyzing concepts, note-taking, comparing ideas, and relating information to main topics. Effective implementation involves familiarizing students with organizers, using examples, and reviewing student work.Using Games in Teaching Vocabulary
Using Games in Teaching VocabularyEvi Sofiawati
╠²
This document discusses using games to teach vocabulary. It explains that games can help lower students' affective filters, promote active participation and problem solving, and cater to different learning styles. It then provides an example lesson plan that uses several vocabulary games, including ambiguous pictures, association, matching, and crossword, to teach occupation-related vocabulary to 5th and 6th grade students. The games are designed to engage students physically and intellectually while reinforcing the new vocabulary terms based on theories of multiple intelligences, learning styles, constructivism, and total physical response.Writing Skills: WWTM GAME
Writing Skills: WWTM GAMEBreenLi
╠²
Controlled activities focus on practicing language skills like spelling and handwriting. They are done to practice the language itself. Free activities allow for self-expression and creativity, with content being most important. The process approach emphasizes starting writing early and using pre-writing activities like brainstorming, while the product approach focuses on the final writing and correcting errors.Decoding Skills
Decoding SkillsMiami-Dade County Public Schools
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to decoding skills and assessing students' mastery of various phonics concepts and reading skills. It addresses how to identify issues with blends, digraphs, and diphthongs; the importance of reinforcement activities; assessing structural analysis abilities; strategies for teaching English language learners; and methods for evaluating students' understanding of context clues and contractions. A variety of activities are proposed to teach and reinforce these critical early reading skills.AAC & Literacy: In Partnership to Develop Language
AAC & Literacy: In Partnership to Develop LanguageJane Farrall
╠²
This document provides information on strategies for combining augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) with emergent literacy instruction. It discusses why AAC and literacy should be partnered to develop language, noting the need for meaningful communication and engagement. Shared reading is recommended, using techniques like Comment, Ask, Respond (CAR) and its extension, Putting the CROWD in the CAR, which involves completion, recall, open-ended questions, WH- questions, and distancing. Predictable chart writing is also outlined as an interactive writing activity where students compose text with an adult using a repeated sentence structure.Similar to English support stages of learning (kumi) (20)
Module 2 study guide
Module 2 study guideHDMcWhorter
╠²
The document discusses teaching English as a second language. It explains that as communities become more multicultural, teaching English must become a more important part of the curriculum. It also discusses different methodologies for teaching listening, speaking, reading and writing skills to English language learners from elementary through high school levels. These include developing basic interpersonal communication skills as well as cognitive academic language proficiency. Understanding theories of second language acquisition, such as Krashen's theory, is important for instructors to effectively teach English skills.Teaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary s...
Teaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary skills.pptxTeaching literary s...JennyPalo1
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of teaching literacy skills. It covers topics like defining literacy, the changing nature of literacy in the 21st century, developing fundamental reading skills like phonological awareness early on, the four language skills, the importance of oral language, and instructional strategies to develop vocabulary, fluency, and reading comprehension. Effective literacy instruction requires matching students with texts at their appropriate reading level to ensure success.Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...porfazhiie
╠²
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. MorrisonDeveloping Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Mo...piousrassiwv
╠²
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. Morrison
Developing Literacy Reading and Writing To With and by Children Timothy G. MorrisonEarly Literacy Development.pptx
Early Literacy Development.pptxTaraPoole5
╠²
Tara Poole presents on components of a holistic early literacy program. She acknowledges the traditional territories of local First Nations and emphasizes building relationships through trauma-informed practice. Literacy is defined as understanding, analyzing, and communicating through diverse texts for various purposes. A comprehensive literacy program includes building background knowledge, language development, phonological awareness, phonics, reading time, fluency, comprehension, and assessment. Phonological awareness involves hearing sounds in words while phonemic awareness involves hearing individual sounds. Explicit instruction is needed in concepts of print, phonological awareness, phonemic awareness, phonics, word work, vocabulary, comprehension strategies, fluency, and ensuring access to decodable books. Assessment, goal setting, andChart of SLA Principles OverviewFINAL.pdf
Chart of SLA Principles OverviewFINAL.pdfKatherineMadrid6
╠²
The document summarizes several key principles and theories of second language acquisition (SLA) introduced between the 1960s-1990s. It outlines the main proponents, time periods, features, and implications for the classroom of each principle/theory, including: behaviorist views of SLA, Krashen's comprehensible input hypothesis, stages of language development, interlanguage development, output hypothesis, interaction hypothesis, differences between basic interpersonal communication skills and cognitive academic language proficiency, the link between SLA and acculturation, and the impact of individual learner characteristics on SLA. The document serves as a useful overview of the major developments in SLA theory and principles during this time period.Theoretical Presentation
Theoretical PresentationLuis Holguin
╠²
Here are some strategies you can implement to help students improve their oral communication skills in English:
- Provide structured opportunities for students to practice speaking in small groups or with a partner on a daily basis. Give them topics or prompts to discuss.
- Model conversational skills by thinking out loud. Repeat what students say and rephrase it correctly as needed.
- Encourage risk-taking by praising students for attempting communication even if mistakes are made. Correct errors gently.
- Incorporate role plays, simulations, debates and oral presentations to give students authentic reasons to speak.
- Allow wait time after asking questions so students can process the language before responding.
- Use visual aids, gestures, drawings to support oralVideo ppt example 12 mb vid
Video ppt example 12 mb vidKatie Omenitsch
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts and strategies for teaching reading to English language learners. It defines important terms and acronyms, discusses linguistic theories of language acquisition, and outlines stages of language learning and common errors. The document also explores strategies for engaging beginning and intermediate English learners, including using leveled texts, running reading records, analyzing errors, and graphic organizers.Reading vocabulary Wiseman
Reading vocabulary WisemanCynthia Wiseman
╠²
This document discusses strategies for developing reading skills in adult students. It recommends activating students' background knowledge before reading, using prereading activities like shadow reading. Goals for reading speed and comprehension should be set. Specific reading exercises and materials at different difficulty levels can be used to help students see their progress. Praise and rewards can motivate students as they work to improve their reading proficiency.Literacy 2.0
Literacy 2.0nmangum
╠²
This document provides an overview of a professional development workshop on Literacy 2.0. The summary is:
The workshop will help participants 1) develop an understanding of Web 2.0 tools and Literacy 2.0, and 2) increase understanding of effective literacy instruction components in order to 3) plan ways to incorporate Web 2.0 tools in their classrooms to boost literacy learning.Oral Language
Oral LanguageHonor Moorman
╠²
The document discusses the importance of oral language development and its connection to literacy. It covers stages of language development from infancy through elementary school age and conditions that support language learning. Additionally, it addresses components of reading development including phonemic awareness, phonics, sight words, fluency, and comprehension.Ch. 4 oracy & literacy for english language learners
Ch. 4 oracy & literacy for english language learnerssadhonau1
╠²
This document discusses standards and goals for teaching English to ELL students. It addresses the four key language skills - listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
It notes that developing oral language proficiency takes time, starting with one-two word responses and progressing to complex sentences. For reading, background knowledge is more important than grammar. A variety of strategies are recommended for literacy development, including visuals, prereading activities, and integrating content with literacy. Error correction should focus on the message, not just form. Technology can provide meaningful practice and authentic texts.Reading skills
Reading skillsjivheshsali
╠²
Reading skills enable readers to understand written language through independence, comprehension, and fluency. They require abilities like phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and reading comprehension. Chall's Stages of Reading Development describes typical progression from prereading to advanced analysis and judgment. Top ways to improve reading skills include setting aside daily reading time, surrounding yourself with materials, family reading time, variety of activities, using the library, monitoring progress, and getting help for problems.Reading process
Reading processSukhmohinder Nagpal
╠²
This document discusses key components of a balanced reading program: phonological awareness and phonics skills, sight words and vocabulary development, reading fluency, and comprehension strategies. It emphasizes teaching reading as an interactive process involving prediction, inference making, and critical thinking. Explicit instruction in reading strategies is needed to help students actively integrate information from texts with their prior knowledge.Reading fundamentals final 7.17.10
Reading fundamentals final 7.17.10krobins9
╠²
The document summarizes a literacy workshop that covered the key components of reading instruction including phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. It discussed challenges some students face learning to read and strategies to help struggling readers, such as direct instruction in skills they have not acquired. It also covered the writing process and elements of an effective literacy block in the classroom.Supporting Low Level Readers in the Common Core Classroom
Supporting Low Level Readers in the Common Core ClassroomKristin Guest MS, CCC-SLP
╠²
This document provides strategies for speech language pathologists to support students with reading difficulties. It discusses the components of reading comprehension, including background knowledge, phonological awareness, decoding, fluency, and vocabulary. For each component, it identifies potential areas of difficulty for students and provides strategies SLPs can use to assess and support students. These include pre-teaching activities, modeling fluent reading, teaching spelling patterns, and incorporating vocabulary instruction across disciplines. References are also provided on effective practices for developing these reading skills in students.Richmond Feb 2020
Richmond Feb 2020Faye Brownlie
╠²
This document summarizes key points from a professional learning session on effective literacy practices for inclusive classrooms. It discusses strategies like building background knowledge, using visuals, focusing on meaning over isolated skills, and providing choice and relationships. Specific practices that support struggling readers are highlighted, like one-on-one support and conferencing. Questioning round-robin reading and skills in isolation, it advocates for high expectations, comprehensive instruction, and addressing students' individual needs.Quotations
QuotationsLfmoralesB
╠²
The document provides definitions, principles, and activities for four language skills: reading, writing, speaking, and listening. For reading, it defines reading as a complex skill involving various component operations. It emphasizes giving students time for extensive and sustained silent reading. For writing, it notes that writing involves putting letters together to form words, phrases, and sentences. It recommends sharing writing with other students to add authenticity. For speaking, it defines speaking as constructing and delivering understandable messages using correct pronunciation and intonation. It stresses including techniques to help students perceive and use language blocks. For listening, it defines listening as understanding not just words but also speaker's meanings, and as a reciprocal skill. It recommends using authentic tasks so students seeUpdated :Para professional pd reading presentation
Updated :Para professional pd reading presentationSusan Wegmann
╠²
The document provides an agenda and overview for a training on engaging reading practices for paraprofessionals. The agenda covers the fundamentals of reading over two morning sessions, including a lunch break, and an afternoon session applying the learning. The presentation discusses key areas of reading instruction including oral language, phonological awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. Examples and strategies are provided for developing skills in each area. Research supporting explicit instruction in these components is also summarized.Ad
English support stages of learning (kumi)
- 1. Enact a real life conversation between a homeroom tutor and an ES teacher? A heart- to -heart chat about the a student in your class who is on ES support
- 2. Hurdles ŌĆó When prior knowledge is being assessed ŌĆó While listening and speaking Struggling to express Struggling to be understood Struggling to understand ŌĆó While reading and writing Symbolism and imagery Density of words / spelling Speed Decoding words/ understanding sentences /ideas in paragraphs
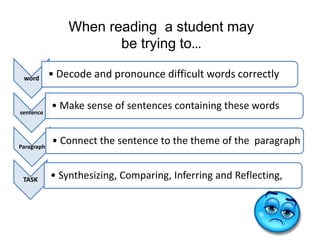
- 3. word ŌĆó Decode and pronounce difficult words correctly sentence ŌĆó Make sense of sentences containing these words Paragraph ŌĆó Connect the sentence to the theme of the paragraph TASK ŌĆó Synthesizing, Comparing, Inferring and Reflecting, When reading a student may be trying toŌĆ”
- 4. Q1. Why do you think PeteŌĆÖs uncle left the room in a hurry? Who was Pete? Oh! he had an uncle, Which room? Why did he leave? Was he in a hurry? Where can I find this answer? MaŌĆÖam. Can you help me? ItŌĆÖs in the beginning. Read it carefully. Here Hurry. Have you finished? No MaŌĆÖam
- 5. TeacherŌĆÖs Role Build a rapport Motivate Encourage Praise Have patience Be fair Differentiate Understand R E L AX
- 6. Pre ŌĆō Production (Silent Period). ŌĆó Early Production. ŌĆó Speech Emergence. ŌĆó Intermediate Fluency. Advanced Fluency.
- 7. Pre Production Stage or (Silent Stage) Stephen Krashen ŌĆóCan last for a year ŌĆóStudents should not be forced to speak ŌĆóStudents will respond very well to pictures and visuals ŌĆóTotal Physical Response method works well ŌĆóBenefit from buddies ŌĆóAlthough students do not produce language it does not mean they are not learning ŌĆóSimple Listening comprehension activities to build receptive vocabulary
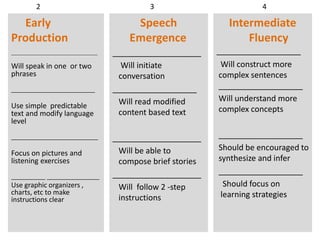
- 8. Early Production - 2 ŌĆó Can last up to for 6 months ŌĆó Active vocabulary of up to 1000 words ŌĆó Will speak in one or two phrases ŌĆó Will tend to memorize ŌĆó Accept one or two word responses ŌĆó Use pictures and visuals especially to build vocabulary ŌĆó Modify content information to language level ŌĆó Provide listening activities ŌĆó Use simple predictable text ŌĆó Support learning with graphic organizers, charts, graphs labeling and short sentence
- 9. Speech Emergence ŌĆō 3 ŌĆó Could have a vocabulary of about 3000 words ŌĆó Will ask short questions which may not be grammatically correct ŌĆó Will initiate conversation Beginning to develop Basic Interpersonal Social Communicative skills (BISC) ŌĆó Will be able to do some content work with teacher support ŌĆó Sound out stories phonetically ŌĆó Read modified text ŌĆó Match vocabulary words to definitions ŌĆó Understand and answer questions about graphs and charts ŌĆó Understand teacher explanations and two-step instructions ŌĆó Can compose brief stories based on personal experience
- 10. Intermediate Fluency - 4 ŌĆó Could have a vocabulary of about 6000 words ŌĆó Using more complex sentences in writing and speaking ŌĆó Are willing to express opinions and share thoughts ŌĆó Will ask questions to clarify thoughts ŌĆó They must be encouraged to synthesize and make Inferences ŌĆó A time for teachers to focus on learning strategies ŌĆó Will be able to understand more complex concepts
- 11. Advanced fluency ŌĆó It would take 4 to 10 years to reach C Cognitive Academic Learning Proficiency (CALP). ŌĆó Most students get exited from the program at this stage ŌĆó At the beginning of this stage students will need continuous support from classroom teachers especially in content area subjects.
- 12. Early Production _______________________________________ Will speak in one or two phrases ___________________________ Use simple predictable text and modify language level ____________________________ Focus on pictures and listening exercises ___________ _________________ Use graphic organizers , charts, etc to make instructions clear Speech Emergence ____________________ Will initiate conversation ___________________ Will read modified content based text ____________________ Will be able to compose brief stories ____________________ Will follow 2 -step instructions Intermediate Fluency ___________________ Will construct more complex sentences ___________________ Will understand more complex concepts ___________________ Should be encouraged to synthesize and infer ___________________ Should focus on learning strategies 2 3 4
- 13. Significance of BISC Jim Cummins Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills ŌĆó It is the language skills required in social surroundings ŌĆó In the playground / school bus/ dining hall sports field/ parties/talking on the phone ŌĆó This language is not demanding and it also does not mean that the student is proficient in the language
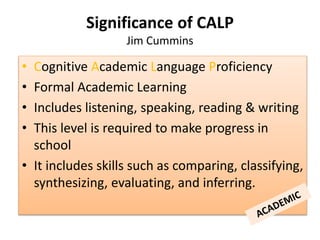
- 14. ŌĆó Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency ŌĆó Formal Academic Learning ŌĆó Includes listening, speaking, reading & writing ŌĆó This level is required to make progress in school ŌĆó It includes skills such as comparing, classifying, synthesizing, evaluating, and inferring. Significance of CALP Jim Cummins
- 15. ŌĆó With your expectations ŌĆó When setting your goals ŌĆó While making assessments . . . and watch your students move from one stage to the other!
- 16. Listening or Reading Comprehensions
- 17. Garbage What happens to our garbage when we throw it out? Most garbage is picked up outside our house in a truck and taken to the landfill. Some things like cardboard and glass can be recycled. Some people throw food garbage like banana peels into a pile in their yard called a compost pile. Worms and tiny bugs eat the food garbage and make good soil to make plants grow.
- 18. Basic Flow ŌĆó Read or Listen ŌĆó Understand ŌĆó Enrich Vocabulary ŌĆó Study Grammar ŌĆó Think Critically ŌĆó Find Out ŌĆó Write or Speak ŌĆó Present PYP Learner Profile
- 19. Comprehension skills ŌĆó Summarizing ŌĆó Sequencing ŌĆó Inferencing ŌĆó Comparing and contrasting ŌĆó Drawing conclusions ŌĆó Self-questioning ŌĆó Problem-solving ŌĆó Relating background knowledge ŌĆó Distinguishing between fact and opinion ŌĆó Finding the main idea, important facts, and supporting details
- 20. Test studentŌĆÖs comprehension with carefully crafted questions, taking care to use simple sentences and key vocabulary from the text they just read.. Literal level Why do the leaves turn red and yellow in the fall? Interpretive level Why do you think it needs water? Applied level How much water are you going to give it? Why?
- 21. Credits ŌĆó CALP and BISC Theorized by Jim Cummins ŌĆó Silent Period According to Stephen Krashen ŌĆó The five Stages As explained by Judie Hayne ŌĆó Comprehension Skills Color├Łn Colorado ŌĆō website ŌĆó Levels in questioning Colorin Colorado - website ŌĆó Images Clipart Hurdles TeacherŌĆÖs Role Basic Flow design