Enterprise Risk Management - GRC as a practice
- 1. Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance Mapping david.daniel@casewise.com David Daniel Leverage Architecture to Drive Consistent Enterprise GRC Management
- 2. 2 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential RISKSHAZARDSEvolution of an event from identification to retrospective Risk Lifecycle LIKELIHOOD OF OCCURANCE awareness controls contingencies recovery preparations OUTCOMES IMPACTSCONSEQUENCES TIME
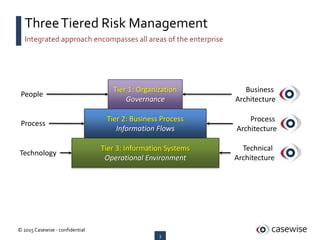
- 3. 3 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Integrated approach encompasses all areas of the enterprise ThreeTiered Risk Management Tier 1: Organization Governance Tier 2: Business Process Information Flows Tier 3: Information Systems Operational Environment People Process Technology Technical Architecture Process Architecture Business Architecture
- 4. 4 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Risk Awareness
- 5. 5 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential You canŌĆÖt manage what you donŌĆÖt know Risk Awareness ’é¦ Identify areas of concern ŌĆō Direct risks ŌĆō Indirect risks ’é¦ Outline risk objectives ŌĆō Supports construction of risk appetite model ŌĆō ŌĆ£Right sizesŌĆØ risk management practices ’é¦ Establish risk registry ŌĆō Maintain objective catalog ŌĆō Establish ownership ’é¦ Implement systematic identification processes ŌĆō Introduce risk awareness into strategic planning ŌĆō Benchmark against industry standards ŌĆō Inject risk mapping into SDLC TOOLING SERVICES workshops SERVICES workshops SERVICES practice building
- 6. 6 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Guiding Information and Information Systems Security Typical Information Security Objectives Confidentiality ŌĆ£Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary informationŌĆ”ŌĆØ A loss of confidentiality is the unauthorized disclosure of information. Integrity ŌĆ£Guarding against improper information modification or destruction, and includes ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticityŌĆ”ŌĆØ A loss of integrity is the unauthorized modification or destruction of information. Availability ŌĆ£Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of informationŌĆ”ŌĆØ A loss of availability is the disruption of access to or use of information or an information system.
- 7. 7 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Risk Controls
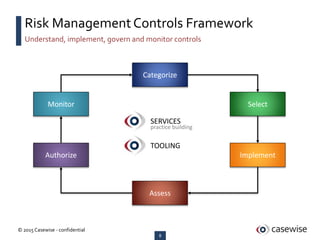
- 8. 8 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Understand, implement, govern and monitor controls Risk ManagementControls Framework Categorize Select Implement Assess Authorize Monitor SERVICES practice building TOOLING
- 9. 9 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential ŌĆó Market-centric orientation provides solid business guidance ŌĆó Fosters full-spectrum analysis of risk and compliance issues ŌĆó Aligns risk appetite with business goals and objectives ŌĆó Defines strong governance model to support compliance ŌĆó Translates risk into business terms that are easily consumable by stakeholders Control the activities that perform the business Controls ŌĆō Business Architecture P E S T LEGAL ENVIRONMENTAL political economic social technologic
- 10. 10 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Control the processes that operate the business Controls ŌĆō Process Architecture ŌĆó Objectively identifies key areas of concern for continuity planning ŌĆó Builds culture of compliance by overlaying strategic risk and compliance onto day-to-day activities ŌĆó Fosters innovation through risk awareness and response ŌĆó Institutionalizes GRC in the fabric of the enterprise
- 11. 11 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Control the systems that support the business Controls ŌĆōTechnicalArchitecture ŌĆó Risk management becomes core area of concern for solution development ŌĆó Supports objective recovery options in day-to-day operations ŌĆó Facilitates audit/compliance reporting ŌĆó Translates technical risk into business terms ŌĆó Defines both functional and non- functional requirements
- 12. 12 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Risk Mitigation and Response
- 13. 13 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential Event handling and residual risk must be addressed systematically Mitigation ’é¦ Prepare systematic recovery response to known risk ŌĆō Reduce ŌĆō Retain ŌĆō Avoid ŌĆō Transfer ’é¦ Map events to contingencies ŌĆō Develop systematic event response methodologies ŌĆō Understand how to respond to unforeseen events ’é¦ Understand Residual Risk ŌĆō Monitor and maintain residual risk register ŌĆō Provide feedback loop for continuous improvement SERVICES workshops SERVICES practice building SERVICES practice building
- 14. 14 ┬® 2015 Casewise - confidential ŌĆ£Tell me and I forget.Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.ŌĆØ - Benjamin Franklin Continuous Improvement ’é¦ Articulate responses objectively ŌĆō Construct root cause assessments to determine causes/responses to events ’é¦ Identify KRI (Key Risk Indicators) ŌĆō Update and Manage a catalog of KRIs ŌĆō Map new KRIs to risk areas ’é¦ Reduce variability and uncertainty ŌĆō Each event is a learning environment: monitored, measured, analyzed and communicated to risk management teams ’é¦ Maintain Risk Management Maturity Model ŌĆō Managed growth of GRC capability in the enterprise SERVICES practice building TOOLING SERVICES practice building SERVICES practice building
- 15. david.daniel@casewise.com David Daniel ŌĆ£If you donŌĆÖt have the time to do something right, where are you going to find the time to fix it?ŌĆØ - Stephen King