Environment 4 geography project ppt.pptx
- 3. Weather refers to the state of the atmosphere over an area at any point of time. The elements of weather are temperature, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, humidity and precipitation. FOR EXAMPLE : todayŌĆÖs weather :- temp. : max. : 29 ╦ÜC min. : 24 ╦ÜC atmospheric pressure : 74 % wind speed : 10 kmph ŌĆō 35 kmph humidity : 68 % - 75 % precipitation : nill.
- 4. Climate refers to the average weather condition and variations over a large area for a long period of time (more than 30 years). There are many types of climates ŌĆō Monsoon type of climate, Desert type of climate, Caribbean type of climate, etc.
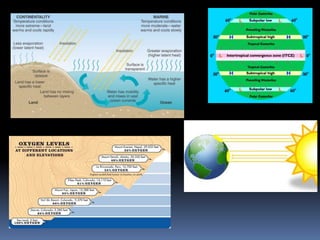
- 5. There are six major controls of the climate of any place ŌĆō 1) Latitude ŌĆō due to the curvature of the earth, the amount of solar energy received varies according to latitude. 2) Altitude ŌĆō as one goes from the surface of the earth to higher altitudes, the atmosphere becomes less dense and temperature decreases. 3) Pressure & wind system : the pressure and wind system of any area depend on the latitude and altitude of the place. Thus it influences the temperature and rainfall pattern. 4) Distance from the sea (continentality) : as the distance from the sea increases, its moderating influence decreases and the people experience extreme weather conditions. This condition is known as continentality.
- 6. 5) Ocean currents : ocean currents along with onshore winds affect the climate of the area, for example, any coastal area with warm or cold ocean currents flowing past it, will be warmed or cooled if the winds are onshore. 6) Relief : relief plays a major role in determining the climate of a place. High mountains act as barriers for cold or hot winds ; they may also cause rainfall if they are high enough and lie in the path of rain bearing winds.
- 10. 1) Latitude : the Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of the country from the Rann of Kuchh in the west to Mizoram in the east. Almost half of the country lying south of the Tropic of Cancer, belongs to the tropical area. All the remaining area, north of the Tropic, lies in the sub ŌĆō tropics. 2) Altitude : India has mountains to the north which have an average elevation of 6000 metres. India also has a vast coastline area where the maximum elevation is about 30 metres. The Himalayas prevent the cold winds from central Asia from entering the sub ŌĆō continent. It is because of these mountains that this sub ŌĆō continent experiences comparatively milder winters than central Asia.
- 11. 3) Pressure and wind system : the climate and associated weather conditions in India are governed by the following atmospheric conditions ŌĆō ’āś pressure and surface winds ’āś upper air circulation ’āś western cyclonic disturbances and tropical cyclones 4) Ocean currents : ocean currents along with onshore winds affect the climate of the area, for example, any coastal area with warm or cold ocean currents flowing past it, will be warmed or cooled if the winds are onshore. 5) Distance from the sea : as the distance from the sea increases, its moderating influence decreases and the people experience extreme weather conditions. This condition is known as continentality. 6) Relief features : High mountains act as barriers for cold or hot winds ; they may also cause rainfall if they are high enough and lie in the path of rain bearing winds. The leeward side of the mountain remains relatively dry.
- 12. An apparent force caused by the earthŌĆÖs rotation, the coriolis force is responsible for deflecting towards the right in the northern hemisphere and towards the left in the southern hemisphere.
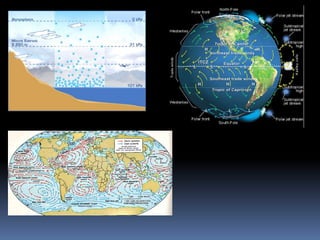
- 14. India lies in the region of north ŌĆō easterly winds. These winds originate from the sub ŌĆō tropical high pressure belt of the northern hemisphere. They blow south, get deflected to the right due to the coriolis force and move on towards the equatorial low pressure zone. These winds carry very little moisture as they originate and blow over land. Therefore, they bring little or no rainfall. The pressure and wind condition over India are unique. During winter, there is a high pressure area north of the Himalayas. Cold, dry winds blow from this region to the south. In summer, a low pressure area develops over interior Asia as well as over north ŌĆō western India. This causes a complete reversal of the direction of the winds during summer. Air moves from the high pressure area over the southern Indian Ocean, in
- 15. direction, crosses the equator and turns right towards the low pressure area over the Indian sub ŌĆō continent. These are known as southwest monsoon winds.
- 16. These are a narrow belt of high altitude westerly winds in the troposphere. These streams are located approximately over 27˚ to 30˚ north latitude, therefore they are called sub tropical westerly jet streams. Their speed varies from 110 kmph in summer to 184 kmph in winter.
- 18. The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a broad trough of low pressure in equatorial latitudes. This is where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. This convergence zone lies more or less parallel to the equator but moves north or south with the apparent movement of the sun.
- 19. Normally when the tropical eastern south Pacific Ocean experiences high pressure, the tropical eastern Indian Ocean experiences low pressure. But in certain years, there is a reversal in the pressure conditions. This periodic change is known as southern oscillation or SO. The difference in pressure over Tahiti and Darwin in northern Australia is computed to predict the intensity of the monsoons. A feature connected with SO is the El Nino phenomenon in which a warm ocean current that flows past the Peruvian Coast, in place of the cold Peruvian current , every 2 ŌĆō 5 yrs. The changes in pressure conditions are connected to the El Nino. Therefore, the phenomenon is referred to as ENSO (El Nino Southern Oscillation).
- 21. The monsoon, unlike the traders, are not steady winds but are pulsating in nature, affected by different atmospheric conditions encountered by it, on its way over the warm tropical seas. The duration of the monsoon is between 100 ŌĆō 120 days from early June to mid ŌĆō September. Around the time of its arrival, the normal rainfall increases suddenly and continues for several days. This is known as the burst of monsoon.
- 23. There are four main seasons in India. They are ŌĆō i) The cold weather season (winter) ii) The hot weather season (summer) iii) Advancing monsoon (the rainy season) iv) Retreating monsoon (the transition season)
- 24. The cold weather season begins from mid ŌĆō November in northern India and stays till February. December and January are the coldest months in the northern part of India. During this season, the northeast trade winds prevail over the country. The weather is normally marked by clear skies, low temperatures and low humidity and feeble variable winds. The peninsular region does not have a well defined cold season. This season is important for Rabi crops.
- 26. The hot weather season begins from March and continues up to May. In March, the highest temperature is about 38╦ÜC recorded in the Deccan plateau. In peninsular India, temperatures remain lower due to the moderating influence of the oceans. A striking feature of the hot weather season is the ŌĆślooŌĆÖ. These are strong, gusty, hot and dry winds blowing during the day. Dust storms are very common during the month of May in northern India. In West Bengal it is known as ŌĆśkaal baisakhiŌĆÖ. Towards the end of the summer season, pre - monsoon showers are common in Kerala and Karnataka.
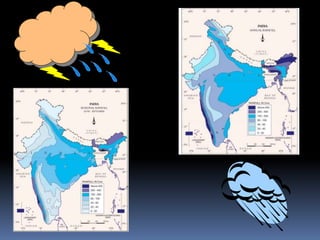
- 28. By early June, the low pressure condition over the northern plains intensifies. It attracts the trade winds of the southern hemisphere. As these winds blow over warm oceans, they bring abundant moisture to the sub ŌĆō continent. The in flow of the southwest monsoon in India brings about a total change in the weather. The maximum rainfall of this season is received in the northeastern part of the country. Another phenomenon associated with the monsoon is its tendency to have ŌĆśbreaksŌĆÖ in rainfall. Thus, it has wet and dry spells. These breaks in monsoon are related to the movement of the monsoon trough. The monsoon is known for its ŌĆśuncertaintyŌĆÖ. The alteration of dry and wet spells vary in intensity. It may be responsible for droughts or floods.
- 31. During October ŌĆō November with the apparent movement of the sun towards the south, the monsoon or the low pressure trough becomes weaker. This gradually replaced by a high pressure system. By the beginning of October, the monsoon withdraws from the northern plains. It is marked by clear sky and rise in temperature. The low pressure conditions, over northwestern India get transferred to the Bay of Bengal by early November.