Environmental case lead
- 1. Environmental Case Dr Momin Kashif
- 2. Doctor as Detective A father brings his two children (M-6, F-4) who have complain of abdominal pain, loss of appetite, constipation, weakness and tiredness. Their father also complained that his children have become irritable and disturbing. He also reported that his neighbour's 3 or 4 children are having similar complaints. They use well water for drinking and cooking purposes which is in their home vicinity. He has business of selling old/discarded batteries. you suspected some environmental factors for their ill health.... 1. What line of investigations u can plan for the diagnosis? In chilren In surrounding environment In other people 2. How father's business is associated with the children disease? 3. What are your suggestions for prevention and protection. 4. Make a Information leaflet in regional language for public awareness of this environmental hazard.
- 3. What are the symptoms
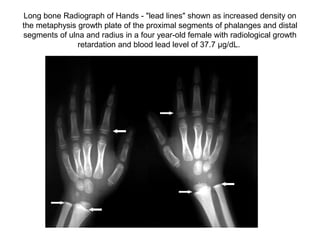
- 6. Long bone Radiograph of Hands - "lead lines" shown as increased density on the metaphysis growth plate of the proximal segments of phalanges and distal segments of ulna and radius in a four year-old female with radiological growth retardation and blood lead level of 37.7 µg/dL.
- 7. What are the symptoms • Symptoms of lead poisoning are varied. They may affect many parts of the body. Most of the time, lead poisoning builds up slowly. • It follows repeated exposures to small quantities of lead. • Lead toxicity is rare after a single exposure or ingestion of lead.
- 8. Continuum of signs and symptoms of ongoing lead exposure • Lowest Exposure Dose Signs and Symptoms: Impaired Abilities (patient may appear asymptomatic) 1. Decreased learning and memory 2. Lowered IQ 3. Decreased verbal ability 4. Impaired speech and hearing functions 5. Early signs of hyperactivity or ADHD • Low Exposure Dose Signs and Symptoms 1. Myalgia or paresthesia 2. Mild fatigue 3. Irritability 4. Lethargy 5. Occasional abdominal discomfort
- 9. Continuum of signs and symptoms of ongoing lead exposure • Moderate Exposure Dose Signs and Symptoms 1. Arthralgia 2. General fatigue 3. Difficulty concentrating/Muscular exhaustibility 4. Tremor 5. Headache 6. Diffuse abdominal pain 7. Vomiting 8. Weight loss 9. Constipation • High Exposure Dose Signs and Symptoms 1. Paresis or paralysis 2. Encephalopathy—may abruptly lead to seizures, changes in consciousness, coma, and death 3. Lead line (blue-black) on gingival tissue 4. Colic (intermittent, severe abdominal cramps)
- 10. What causes lead poisoning? • house paints • toys and household items painted • toys made and painted • bullets, curtain weights, and fishing sinkers made of lead • pipes and sink faucets, which can contaminate drinking water • paint sets and art supplies • jewelry, pottery, and lead figures • storage batteries • kohl or kajal eyeliners • some traditional ethnic medicines • soil polluted by car exhaust or chipping house paint
- 11. Who is at risk for lead poisoning? • Children are at the highest risk of lead poisoning, especially if they live in old houses with chipping paint • People in developing countries are also at a higher risk
- 12. How is lead poisoning diagnosed? • blood lead test • CBC • amount of iron storing cells in the blood • X-rays, • and possibly a bone marrow biopsy
- 13. How is lead poisoning treated? • The first step of treatment is to locate and remove the source of the lead. • Keep children away from the source. • If it cannot be removed, it should be sealed. • In more severe cases, a procedure known as chelation therapy can be used. This treatment binds to lead that has accumulated in your body. The lead is then excreted in your urine. • Activated charcoal can be used to bind the lead in the gastrointestinal tract and encourage elimination via defecation. A chemical called EDTA may also be used • Even with treatment, it can be hard to reverse the effects of chronic exposure.
- 14. What is the outlook for lead poisoning? • Adults with moderate exposure usually recover without any complications. • In children, recovery can take time. Even low lead exposure can cause permanent intellectual disability.
- 15. How can lead poisoning be prevented? Simple steps can help you prevent lead poisoning. These include: 1.Avoid painted toys and canned goods. 2.Keep your home free from dust. 3.Use only cold water to prepare foods and drinks. 4.Make sure everyone washes their hands before eating. 5.Clean faucets and aerators regularly. 6.Wash children’s toys and bottles regularly. 7.Teach your children to wash their hands after playing. 8.Use lead-free paint in your home. 9.Avoid areas where lead-based paint may have been used.
- 16. How can lead poisoning be prevented? for patients • Eliminate source of lead exposure • Flushing the standing water from the lines and faucet for a few minutes before use and using cold water for drinking may reduce exposure. • maintain a diet high in calcium and iron • continue to monitor blood lead levels.
- 17. Other Environmental Hazards • Arsenic • Nitrates • Excess or less flourides • Radioactive substances • Cadmium • Organic materials degradation
- 18. The Environmental Series continue…. What changes you wish to bring in your life and in your environment for better health… 1. 2. 3. …………. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- For individuals with high or chronic past exposure, however, BLLs often under-represent the total body burden because most lead is stored in the bone and may have “normal” levels in the blood.
- Calcium supplementation will replace bone lead and get eliminated