Epigenetic mechanisms in Parkinsons disease
- 1. EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS IN PARKINSONS DISEASE PRESENTED BY : Uppala Sai Nikhil RT/2021/614 MS pharm 1st yr. Regulatory Toxicology 1 UNDER GUIDANCE OF Dr. Dharmendra khatri
- 2. EPIGENETICS ? Epigenetics is defined as study of potentially stable, ideally heritable change in gene expression or cellular phenotype that occurs without any changes in DNA base pairs. Mechanisms of epigenetic modifications DNA methylation Histone modification Inhibition of gene expression Gene expressed Decondensed ¨Cactive chromatin Condensed ¨C inactive chromatin 2 Evangalia et al,Front. Genet., 18 September
- 3. Factors inducing epigenetic modifications Kanherkar RR, Bhatia-Dey N, Csoka AB. Epigenetics across the human lifespan. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep 9;2:49. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00049. 3
- 4. 4 EPIGENETIC MODIFICATIONS IN PD GENES Aayana singh et al,Neurochem Res. ? Parkinson's is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity and bradykinesia and non motor symptoms like issues in GIT and mental health.
- 5. 5 Chiara et alInt. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14(9), 17643-17663 Zhu X, Chen et al,Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jun DNA methylation in PD pathology
- 6. DNA methylation in PD ? DNA methylation involves addition of methyl groups at cpg dinucleotides that are majorly present at the promoter region. ? Many genes involved in PD undergo methylation and demethylation at specific sites which are major causes for sporadic form of Parkinsons disease. 5- cytosine S-adenosyl methionine(SAM) DNA methyl transferase(DNMT) SAH 5-methyl cytosine Hyper methylation- PGC-1? TRIM10 GFPT2 TMEM9 MAPT Hypo methylation ¨C Cyp2E1 TNF- ? SNCA PARK-2 Hemant et al, Genes 2019, 10(2), 172 6
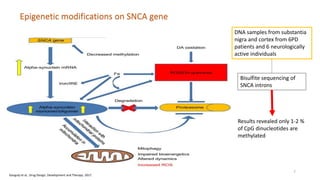
- 7. SNCA gene hypomethylated in SNPC Upregulation of gene by transcription factors Increased alpha-synuclein production Sequesters DNMT in cytoplasm and prevents gene methylation Alpha synuclein aggregation and mitochondrial dysfunction Dopaminergic neuronal cell death DNA samples from substantia nigra and cortex from 6PD patients and 6 neurologically active individuals Bisulfite sequencing of SNCA introns Results revealed only 1-2 % of CpG dinucleotides are methylated ˇýDNMT levels in nucleus Epigenetic modifications on SNCA gene 7 Ganguly et al,. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 2017.
- 8. ? Decreased expression of DNMT1 levels in PD is evidenced by ELISA assays. ? The mis localization of DNMT is limited to neuronal cells which is evidenced using neuronal (NeuN) marker. Paula et al, JBC Papers in Press, February 4, 2011 8
- 9. TeT2 overexpression Activation of Cdkn2A pathway Activation of transcripts(P14,P16) Dopaminergic neuronal injury 9 Fig showing accumulation of TET2 in nucleus and increased TET2 upon MPTP treatment Human Molecular Genetics, Volume 29, Issue 8, 15 April 2020,
- 10. In PD condition PGC-1alpha Hypermethylation Mt transcription factors cannot access the DNA Decreased Mitochondrial biogenesis Mitochondrial dysfunction Compromised antioxidant defence Dysregulation of ER stress and inflammatory signalling Neuro inflammation 10 Qi, Zhengtang & Ding, Shuzhe et al,.PPAR research. 2012. 348245. 10.1155/2012.
- 11. ? Genomic DNA isolated upon bisulfite sequencing showed that PGC-1¦Á hypermethylation in substantia nigra of PD patients when compared with controls. ? Unlike the most methylations ,Cpg dinucleotides are unaffected rather they were non canonical methylated residues and results showed an increase in methylation by 1.6 times. ? PGC-1 alpha expression was also found to decrease by 53% in PD when compared with controls due to hyper methylation. 11 Su, Xiaomin & Chu et al,journal pLoS ONE. Aug 2015
- 12. ? Studies made in adult mice where a knockdown of DNMT3A showed reduced levels of CpH methylation but not CpG methylation. ? Another hypothesis is that increased free fatty acids concentration also increases hypermethylation of PGC-1 alpha. Palmitate added to neuronal cultures in 0.1 and 0.5mM concentrations DNA isolation and bisulfite sequencing performed 0.5mM concn palmitate showed significant methylation in promotor region of PGC1 alpha Methylation at promotor increased by 180.2% compared to control with 0.5mM conc PGC-1alpha gene expression was decreased by 89.1% when compared to PBS control Ratio of Mt DNA to nuclear DNA decreased by 49.7% compared to control 12 Su, Xiaomin & Chu et al,journal pLoS ONE. Aug 2015
- 13. CYP2E1 hypomethylation in PD Cyp2E1 hypomethylation Expression increased in basal ganglia Produces toxic metabolites and produces free radical metabolism 13 Oliver et al,Life 2022, 12(4), 502 Shah et al, Curr Drug Metab. 2021 Fig showing CYP2E1 expression Fig showing ˇý ?synuclein levels in K.O mice
- 14. ? MAPT gene is majorly associated with idiopathic PD where its over expression causes tau protein deposition. ? In studies performed by Coupland they focused on aberrant methylation of MAPT gene where it showed diplotype specific, gender specific patterns of methylation. ? Sex specific MAPT methylation is an independent predictor of disease onset but higher methylation in women compared to men explains the reason for more susceptibility of men to PD. ? H1/H1 diplotype is more methylated than H2/H2 diplotype which explains the diplotype specific pattern of methylation which could be due to presence of more CpG dinucleotides in the former region. 14
- 15. ? PARK16 locus has 5 genes of which 3(RAB29,SLC41A1,NUCKS1) are differentially methylated involved in PD pathogenesis. ? RAB29 methylation causes over recruitment of LRRK2 and increased lysosomal autophagy. However SLC41A1 which is involved in mg homeostasis if downregulated leads to neurodegeneration. ? In contrast, NUCKS1 overexpression leads to increased activation of inflammatory immune response pathways. 15
- 16. Reversing epigenetic modification 5-azatidine zebularine MG98 RG108 Protein methyl transferase inhibitors BIX-01294 UNC0646 UNCO638 Diet rich in folates and methionine HDAC inhibitors Ex-short chain FA Hydroximic acids 16 Hegarty et al,Neural Regen Res. 2016 Nov;11
- 17. LEVODOPA ˇüMethylation in SNCA gene SIRTUIN SIRT 1 Regulate Mt activation Inhibit oxidative stress PGC-alpha activation SIRT2 Inhibits alpha synuclein toxicity Epigallocatechin DNMT and HAT inhibitor Inhibits TNFalpha,IL-? IL-6. Activates astrocytes caffeine ˇüDopamine content ˇýProinflammatory cells 17 Liu Y et al, Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jan10.
- 18. ? On a final note, epigenetics is more of an experience related heritable changes that alter gene expression, many other biological factors and enzymes also influence epigenetic mechanisms which one way or the other involve in disease progression. ? Moreover, many of the gene modifications were found to be age related, gender specific and also based on the dietary factors. ? Many studies were done which provide a base evidence for epigenetic mechanisms in disease related genes which help unveil the targets for therapy. ? In contrast natural agents such as phytochemicals, vitamins are found to much helpful for reducing the disease progression. maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle can probably protect from many epigenetic diseases. 18
- 19. 1. Paula Desplats, Brian Spencer, Elizabeth Coffee, Pruthul Patel, Sarah Michael, Christina Patrick, Anthony Adame, Edward Rockenstein, Eliezer Masliah,¦Á-Synuclein Sequesters Dnmt1 from the Nucleus: A NOVEL MECHANISM FOR EPIGENETIC ALTERATIONS IN LEWY BODY DISEASES*,Journal of Biological Chemistry,https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C110.212589. 2. Heerboth S, Lapinska K, Snyder N, Leary M, Rollinson S, Sarkar S. Use of epigenetic drugs in disease: an overview. Genet Epigenet. 2014;6:9-19. Published 2014 May 27. doi:10.4137/GEG.S12270 3. Wu TT, Liu T, Li X, Chen YJ, Chen TJ, Zhu XY, Chen JL, Li Q, Liu Y, Feng Y, Wu YC. TET2-mediated Cdkn2A DNA hydroxymethylation in mid brain dopaminergic neuron injury of Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2020 May 28;29(8):1239-1252. doi: 10.1 093/hmg/dda a02 2.Erratum in: Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Jun 9;30(12):1172-1173. PMID: 32037456. 4. Su X, Chu Y, Kordower JH, Li B, Cao H, Huang L, Nishida M, Song L, Wang D, Federoff HJ. PGC-1¦Á Promoter Methylation in Parkinson's Disease. PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0134087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134087. PMID: 26317511; PMCID: PMC4552803. 5. Kaut, Oliver and Schmitt, Ina and Stahl, Fabian and Fr??hlich, Holger and Hoffmann, Per and Gonzalez, Frank J. and W??llner, Ullrich,Epigenome-Wide Analysis of DNA Methylation in Parkinson DiseaseCortex,Life,12,2022,4. 6. Pieper HC, Evert BO, Kaut O, Riederer PF, Waha A, W¨ąllner U. Different methylation of the TNF-alpha promoter in cortex and substantia nigra: Implications for selective neuronal vulnerability. Neurobiol Dis. 2008 Dec;32(3):521-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.09.010. Epub 2008 Sep 30. PMID: 18930140. 7. Coupland, K. G., Mellick, G. D., Silburn, P. A., Mather, K., Armstrong, N. J., Sachdev, P. S., Brodaty, H., Huang, Y., Halliday, G. M., Hallupp, M., Kim, W. S., Dobson-Stone, C., & Kwok, J. B. (2014). DNA methylation of the MAPT gene in Parkinson's disease cohorts and modulation by vitamin E in vitro. Movement disorders : official journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 29(13), 1606¨C1614. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25784 8. Goldstein O, Gana-Weisz M, Casey F, Meltzer-Fridrich H, Yaacov O, Waldman YY, Lin D, Mordechai Y, Zhu J, Cullen PF, Omer N, Shiner T, Thaler A, Bar-Shira A, Mirelman A, John S, Giladi N, Orr-Urtreger A. PARK16 locus: Differential effects of the non-coding rs823114 on Parkinson's disease risk, RNA expression, and DNA methylation. J Genet Genomics. 2021 Apr 20;48(4):341-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2020.10.010. Epub 2021 Jan 29. PMID: 33736926. REFERENCES 19
- 20. 9. Copped¨¨ F. One-carbon epigenetics and redox biology of neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Jul;170:19- 33. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.002. Epub 2020 Dec 8. PMID: 33307166. 10. L. Navarro-S? anchez, B. Agueda-G ? omez, ? S. Aparicio, J. P?erez-Tur, Epigenetic study in ParkinsonˇŻs disease: a pilot analysis of DNA methylation in candidate genes in brain, Cells 7 (2018) 150, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100150. 11. Pavlou MAS, Outeiro TF. Epigenetics in Parkinson's Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;978:363-390. doi: 10.1007/978- 3-319-53889-1_19. PMID: 28523556. 12. JOURRenani, Pedram,Taheri, Forogh,Rostami, Daryoush,Farahani, Najma,Abdolkarimi, Hamed,Abdollahi, Elahe, Taghizadeh, Eskandar,Gheibihayat, Seyed Mohammad2019/04/01Involvement of aberrant regulation of epigenetic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease andepigenetic©\based therapies 23410.1002/ jcp.2862 Journal of Cellular Physiology 13. Feng Y, Jankovic J, Wu YC. Epigenetic mechanisms in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2015 Feb 15;349(1-2):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.12.017. Epub 2014 Dec 18. PMID: 25553963. 14. W¨ąllner U, Kaut O, deBoni L, Piston D, Schmitt I. DNA methylation in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1:108-120. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13646. Epub 2016 Jun 10. PMID: 27120258. 15. Kanherkar RR, Bhatia-Dey N, Csoka AB. Epigenetics across the human lifespan. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Sep 9;2:49. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00049. PMID: 25364756; PMCID: PMC4207041. 20
- 21. 21