EQ VS IQ
Download as pptx, pdf36 likes35,290 views
Emotional intelligence (EI) encompasses the ability to recognize and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others, significantly impacting personal and professional success. While traditional education emphasizes IQ, EI is critical for effective interactions, emotional management, and achieving long-term happiness, with research suggesting it accounts for 80% of success. EI can be developed at any stage of life, contrasting with the largely static nature of IQ, highlighting the importance of cultivating emotional skills in both personal and professional contexts.
1 of 20
Downloaded 1,758 times



















Ad
Recommended
EQ V/S IQ
EQ V/S IQKriti Mittal
╠²
EQ refers to emotional intelligence, which describes one's ability to perceive, assess, and manage emotions in oneself and others. It is measured by one's emotional quotient (EQ). While IQ helps one learn and understand logical skills, EQ involves skills like self-awareness, relationship management, and self-management. Studies show that EQ accounts for a smaller portion of job performance than IQ, but EQ supporters argue that it is more important for success in life. EQ can be developed through skills like recognizing emotions in oneself and others, motivating oneself, managing emotions effectively, and handling relationships well. Developing high EQ involves understanding both emotions and reasoning abilities.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligencegihan aboueleish
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to understand and manage one's own emotions as well as those of others, comprising components such as self-awareness, empathy, motivation, and relationship handling. It contrasts with IQ, which is fixed, as EQ can be improved throughout life and is crucial for personal and professional success. Developing EI involves practices like emotional literacy, self-regulation, and acknowledging feelings to make informed decisions and foster better relationships.Eq & iq
Eq & iqNitin Marwal
╠²
The document defines IQ as a score derived from standardized tests measuring intelligence through cognitive abilities like learning, understanding, and problem-solving. It defines EQ as a form of social intelligence involving the ability to monitor one's own and others' emotions to guide thinking and actions. EQ is often measured as an Emotional Intelligence Quotient and describes the capacity to perceive, assess, and manage emotions in oneself and relationships. While IQ measures innate cognitive skills, EQ involves social and emotional skills that can be learned and improved over time to achieve greater success.Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace by Gina Willoughby
Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace by Gina WilloughbyThe HR SOURCE
╠²
The document discusses the significance of emotional intelligence (EQ) in the workplace, highlighting its essential competencies such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and effective relationship management. It outlines the benefits of high EQ, including improved stress management, better relationships with colleagues, and increased productivity. Additionally, it provides strategies for enhancing emotional intelligence and emphasizes its continuous improvement as a key to personal and professional success.Emotional quotient
Emotional quotientClara Novy
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its components. It explains that EQ involves self-awareness of one's own emotions and the emotions of others, self-management of emotions, and social skills. The five main components of EQ are identified as emotional self-awareness, managing emotions, using emotions to maximize thinking, developing empathy, and social skills. Further models and research on EQ are presented, including Goleman's competency model and studies on childhood development and EQ. emotional intelligence
emotional intelligenceRajpal Aulakh
╠²
This document presents information on emotional intelligence. It defines emotional intelligence as the ability to identify, assess, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. The document discusses models of emotional intelligence proposed by Salovey and Mayer and Goleman. It outlines components of emotional intelligence like self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document also compares emotional intelligence to IQ and argues that EQ accounts for a larger portion of success than IQ. It provides tips for developing emotional intelligence at work and enhancing brain power.Eq is more important than iq
Eq is more important than iqYashank bhola
╠²
The document discusses the importance of emotional intelligence (EQ) compared to intelligence quotient (IQ). It states that EQ, which refers to one's ability to use emotions and think critically, accounts for 80% of success in life while IQ only contributes to 20%. Additionally, while IQ is fixed, EQ can be developed by improving emotional skills like empathy, flexibility and stress management. Overall, the document argues that EQ is more important to achieve happiness and success than IQ, which is primarily useful for academic performance.Time Management
Time ManagementOssama Motawae
╠²
The document discusses time management techniques and skills. It covers setting priorities and goals, effective planning, focusing on important tasks, being organized and punctual, and managing distractions. Time management allows individuals to maximize their productivity and minimize stress. Proper time management is important for both personal and professional success.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceAndrew Schwartz
╠²
The document outlines the objectives and importance of emotional intelligence (EI) in the workplace, emphasizing its role in enhancing productivity, leadership, and interpersonal relationships. It highlights that EI is often more crucial for success than IQ, with a significant impact on career advancement. The content also provides various resources and tips for improving emotional intelligence in organizational contexts.Eq n iq ppt (r.g)
Eq n iq ppt (r.g)Radhika Goyal
╠²
The document discusses the importance of emotional intelligence (EQ) compared to intelligence quotient (IQ), emphasizing that EQ is crucial for success and happiness in life while IQ is more academic. It outlines various competencies of EQ, such as empathy and self-awareness, and contrasts the two forms of intelligence in different life scenarios. Additionally, it illustrates the application of EQ through a practical example involving emotional coaching for children.Why is emotional intelligence so important
Why is emotional intelligence so importantIES MCRC, Bandra
╠²
This document presents information on emotional intelligence. It was presented by 5 students. Emotional intelligence involves self awareness, social awareness, self management, and relationship management. It allows people to relate better to others, form healthier relationships, achieve greater success at work, and lead a more fulfilling life. The document discusses each of the four components of emotional intelligence and provides examples. It explains why emotional intelligence is important for performance at work, physical and mental health, and relationships. The document provides tips on how to develop emotional intelligence and concludes that while IQ is important, emotional intelligence may be more important for success in life.What Is Emotional Intelligence?
What Is Emotional Intelligence?taylor_keele
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its significant role in leadership, highlighting its historical evolution and various definitions by key figures. It emphasizes that while EI and IQ are distinct, they are complementary, with EI being crucial for effective leadership and interpersonal relationships. Great leaders utilize emotional intelligence to inspire and motivate others, making it a vital aspect of successful leadership.Emotional Intelligence Presentation (Preeti)
Emotional Intelligence Presentation (Preeti)preetisirohi16
╠²
The document discusses the concept of emotional intelligence (EQ), introduced by Daniel Goleman in 1996, emphasizing its importance in workplace relationships and management. It outlines the different types of emotions, the components of emotional intelligence, and contrasting characteristics of individuals with low versus high EQ. Additionally, it provides tips for managing emotions and highlights the consequences of lacking emotional intelligence, including poor decision-making and relationship problems.Eq at Workplace
Eq at WorkplaceTimothy Wooi
╠²
The document explores the concept of emotional intelligence (EQ) in the workplace, emphasizing its critical role in enhancing performance and productivity through self-awareness and effective interpersonal skills. It distinguishes EQ from IQ and highlights competencies that can be developed, such as initiative, teamwork, flexibility, and communication. Additionally, it provides strategies for applying EQ to address workplace challenges and support effective change management.Emotional intelligence at work
Emotional intelligence at workNursing Hi Nursing
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its importance compared to IQ. It defines EQ as understanding one's own emotions and the emotions of others, and explains that EQ accounts for 80% of success in life while IQ only accounts for 20%. It discusses various emotions and emotional skills that contribute to high or low EQ, such as self-awareness, empathy, and handling stress. Research studies are presented showing a link between high EQ and life accomplishments, job performance, and health. The document argues that EQ can be developed through upgrading emotional skills at any stage of life.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceSanchita Singh
╠²
1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) involves the capacity for self-awareness, managing emotions and relationships. It is important for behavior, social skills and life choices.
2. EQ has five domains - intrapersonal skills like self-awareness; interpersonal skills like empathy; adaptability skills like problem-solving; stress management skills; and general mood skills like optimism.
3. EQ can be developed through activities that improve skills like stress tolerance, impulse control, empathy and flexibility. Regular practice can increase a person's EQ over time.Emotional intelligance
Emotional intelliganceMohamed ELBaz
╠²
The document provides an overview of the history and concepts of emotional intelligence. It discusses how emotional intelligence was emphasized in leadership studies in the 1940s and how the term was coined in 1990. Daniel Goleman further popularized the topic in his 1995 book. Emotional intelligence is defined as involving self and social awareness and management. It can be learned and differs from IQ in emphasizing competencies like leadership, influence, and conflict resolution. Various models of emotional intelligence are presented.Emotional intelligence at work
Emotional intelligence at workNidhi Gupta
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EI) is crucial for understanding and managing emotions, both personally and in a leadership context. The educational system often prioritizes IQ over EQ, neglecting the teaching of emotional coping skills, which are essential for success in the workplace. Developing EI can enhance workplace relationships, improve feedback mechanisms, and effectively deal with conflicts and stress.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceoyestontech
╠²
The document provides an introduction to emotional intelligence (EI) over the course of a 2 hour seminar. It defines EI and explains why it is important, covering both the physiological and psychological aspects. It discusses the development of EI and ways it can be assessed. The seminar aims to introduce the basic concepts of EI, explain how physiological factors influence behavior, and involve guest speakers and exercises.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceGREESHMAPR
╠²
Emotional intelligence was coined in 1990 by Salovey and Mayer to describe an individual's ability to perceive, assess, and manage emotions. It involves monitoring one's own and others' emotions and using this information to guide thinking and behavior. Goleman popularized the term through his 1995 book and defined emotional intelligence as recognizing our own and others' feelings and managing emotions well in ourselves and relationships. Goleman identified five domains of emotional intelligence: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceAditi Singh
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance. It defines EI as the ability to understand one's own and other people's feelings and to use this awareness to motivate oneself and manage relationships effectively. The document notes that while IQ is important, EI may contribute more to success. It outlines four clusters of EI abilities - self awareness, self management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document provides details on self awareness competencies like emotional awareness and tips for improving self awareness skills.Emotional Intelligence - Emotional Quotient
Emotional Intelligence - Emotional QuotientUdit Mukherjee
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is crucial for personal and professional success, often allowing those with average intelligence to outperform highly intelligent individuals. It encompasses recognizing and managing one's own emotions and understanding others' feelings, which leads to improved team performance, leadership skills, and decision-making. Practice can help enhance EQ despite the brain's natural inclination to prioritize emotions over rational thought.Working with Emotional Intelligence
Working with Emotional IntelligenceIrshad Ahmed
╠²
Daniel Goleman is a psychologist and science journalist who wrote about emotional intelligence in his bestselling book Working with Emotional Intelligence. The book discusses what emotional intelligence is, its importance, and its four main components: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. Studies have shown that emotional intelligence is essential for effective leadership and impacts work performance, as managers with higher emotional intelligence tend to be more successful. Understanding and managing emotions helps individuals and leaders handle interpersonal interactions, motivate teams, and improve work outcomes. The book argues that emotional intelligence is a learned skill that can be developed to achieve better results.Skills For Developing Emotional Intelligence
Skills For Developing Emotional IntelligenceCommLab India ŌĆō Rapid eLearning Solutions
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is crucial for effective management and leadership, significantly impacting organizational performance alongside intelligence quotient (IQ). It encompasses self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management, which are essential for teamwork and communication. Developing EQ involves managing stress, understanding emotions, and improving conflict resolution skills to enhance overall workplace effectiveness.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceRatish Kakad
╠²
Emotional intelligence involves the ability to understand and manage one's own emotions and recognize emotions in others. It includes skills such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social skills. While IQ is relatively fixed, EQ can increase over time through learning and practice. Emotional intelligence became popular in the 1990s through academic research and was brought to the mainstream by Daniel Goleman's 1995 bestselling book. Developing strong EQ involves competencies in self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceRavikeerthi Rao
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to identify, assess, and manage emotions in oneself and others, playing a crucial role in personal and professional relationships. It comprises four components: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management, all essential for effective communication and conflict resolution. High emotional intelligence not only contributes to workplace success but also positively impacts physical and mental health.The Art of Empathy
The Art of Empathy Lynn Johnson
╠²
The document discusses the importance of empathy, emphasizing the need to listen and share personal stories to understand each other better. It highlights the role of theater and emotion coaching in fostering empathy and offers practical steps for engaging children in recognizing and expressing their feelings. Additionally, it provides resources for further exploration of empathy in education and personal development.Eq presentation
Eq presentationPraneta Pardikar
╠²
This document discusses theories of intelligence and emotional intelligence. It defines intelligence as the ability to learn, reason, and problem solve. While IQ measures cognitive abilities, emotional intelligence involves self-awareness, managing emotions, and social skills. The document examines models of emotional intelligence proposed by Mayer and Salovey, Bar-On, and Goleman. It describes Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences including interpersonal and intrapersonal skills. The Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) is presented as an ability-based measure of emotional intelligence involving identifying, using, understanding and managing emotions.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligencedirecac
╠²
Emotional intelligence is the ability to properly monitor and manage one's own emotions and understand the emotions of others. It involves recognizing emotions, managing emotions well in relationships, and motivating oneself. Developing emotional intelligence can help with empathy, overcoming challenges, making rational decisions when emotional, and improving relationships, health, career performance, and decision-making. While IQ is important, emotional intelligence is also key to success. Emotional intelligence can be developed at any age through reducing stress, connecting with others nonverbally, using humor, resolving conflicts positively, and perceiving, understanding, and prioritizing emotional responses.Eq pp
Eq pp Aakash Jalan
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its importance over IQ. It defines EQ as understanding one's own emotions and the emotions of others in order to manage relationships and stress. Research shows EQ is about 80% responsible for life success, compared to 20% for IQ. While IQ can be measured through tests, EQ involves skills that can be developed through education and awareness of emotions. Higher EQ is linked to better performance, health, and relationships.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceAndrew Schwartz
╠²
The document outlines the objectives and importance of emotional intelligence (EI) in the workplace, emphasizing its role in enhancing productivity, leadership, and interpersonal relationships. It highlights that EI is often more crucial for success than IQ, with a significant impact on career advancement. The content also provides various resources and tips for improving emotional intelligence in organizational contexts.Eq n iq ppt (r.g)
Eq n iq ppt (r.g)Radhika Goyal
╠²
The document discusses the importance of emotional intelligence (EQ) compared to intelligence quotient (IQ), emphasizing that EQ is crucial for success and happiness in life while IQ is more academic. It outlines various competencies of EQ, such as empathy and self-awareness, and contrasts the two forms of intelligence in different life scenarios. Additionally, it illustrates the application of EQ through a practical example involving emotional coaching for children.Why is emotional intelligence so important
Why is emotional intelligence so importantIES MCRC, Bandra
╠²
This document presents information on emotional intelligence. It was presented by 5 students. Emotional intelligence involves self awareness, social awareness, self management, and relationship management. It allows people to relate better to others, form healthier relationships, achieve greater success at work, and lead a more fulfilling life. The document discusses each of the four components of emotional intelligence and provides examples. It explains why emotional intelligence is important for performance at work, physical and mental health, and relationships. The document provides tips on how to develop emotional intelligence and concludes that while IQ is important, emotional intelligence may be more important for success in life.What Is Emotional Intelligence?
What Is Emotional Intelligence?taylor_keele
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its significant role in leadership, highlighting its historical evolution and various definitions by key figures. It emphasizes that while EI and IQ are distinct, they are complementary, with EI being crucial for effective leadership and interpersonal relationships. Great leaders utilize emotional intelligence to inspire and motivate others, making it a vital aspect of successful leadership.Emotional Intelligence Presentation (Preeti)
Emotional Intelligence Presentation (Preeti)preetisirohi16
╠²
The document discusses the concept of emotional intelligence (EQ), introduced by Daniel Goleman in 1996, emphasizing its importance in workplace relationships and management. It outlines the different types of emotions, the components of emotional intelligence, and contrasting characteristics of individuals with low versus high EQ. Additionally, it provides tips for managing emotions and highlights the consequences of lacking emotional intelligence, including poor decision-making and relationship problems.Eq at Workplace
Eq at WorkplaceTimothy Wooi
╠²
The document explores the concept of emotional intelligence (EQ) in the workplace, emphasizing its critical role in enhancing performance and productivity through self-awareness and effective interpersonal skills. It distinguishes EQ from IQ and highlights competencies that can be developed, such as initiative, teamwork, flexibility, and communication. Additionally, it provides strategies for applying EQ to address workplace challenges and support effective change management.Emotional intelligence at work
Emotional intelligence at workNursing Hi Nursing
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its importance compared to IQ. It defines EQ as understanding one's own emotions and the emotions of others, and explains that EQ accounts for 80% of success in life while IQ only accounts for 20%. It discusses various emotions and emotional skills that contribute to high or low EQ, such as self-awareness, empathy, and handling stress. Research studies are presented showing a link between high EQ and life accomplishments, job performance, and health. The document argues that EQ can be developed through upgrading emotional skills at any stage of life.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceSanchita Singh
╠²
1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) involves the capacity for self-awareness, managing emotions and relationships. It is important for behavior, social skills and life choices.
2. EQ has five domains - intrapersonal skills like self-awareness; interpersonal skills like empathy; adaptability skills like problem-solving; stress management skills; and general mood skills like optimism.
3. EQ can be developed through activities that improve skills like stress tolerance, impulse control, empathy and flexibility. Regular practice can increase a person's EQ over time.Emotional intelligance
Emotional intelliganceMohamed ELBaz
╠²
The document provides an overview of the history and concepts of emotional intelligence. It discusses how emotional intelligence was emphasized in leadership studies in the 1940s and how the term was coined in 1990. Daniel Goleman further popularized the topic in his 1995 book. Emotional intelligence is defined as involving self and social awareness and management. It can be learned and differs from IQ in emphasizing competencies like leadership, influence, and conflict resolution. Various models of emotional intelligence are presented.Emotional intelligence at work
Emotional intelligence at workNidhi Gupta
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EI) is crucial for understanding and managing emotions, both personally and in a leadership context. The educational system often prioritizes IQ over EQ, neglecting the teaching of emotional coping skills, which are essential for success in the workplace. Developing EI can enhance workplace relationships, improve feedback mechanisms, and effectively deal with conflicts and stress.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceoyestontech
╠²
The document provides an introduction to emotional intelligence (EI) over the course of a 2 hour seminar. It defines EI and explains why it is important, covering both the physiological and psychological aspects. It discusses the development of EI and ways it can be assessed. The seminar aims to introduce the basic concepts of EI, explain how physiological factors influence behavior, and involve guest speakers and exercises.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceGREESHMAPR
╠²
Emotional intelligence was coined in 1990 by Salovey and Mayer to describe an individual's ability to perceive, assess, and manage emotions. It involves monitoring one's own and others' emotions and using this information to guide thinking and behavior. Goleman popularized the term through his 1995 book and defined emotional intelligence as recognizing our own and others' feelings and managing emotions well in ourselves and relationships. Goleman identified five domains of emotional intelligence: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceAditi Singh
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance. It defines EI as the ability to understand one's own and other people's feelings and to use this awareness to motivate oneself and manage relationships effectively. The document notes that while IQ is important, EI may contribute more to success. It outlines four clusters of EI abilities - self awareness, self management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document provides details on self awareness competencies like emotional awareness and tips for improving self awareness skills.Emotional Intelligence - Emotional Quotient
Emotional Intelligence - Emotional QuotientUdit Mukherjee
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is crucial for personal and professional success, often allowing those with average intelligence to outperform highly intelligent individuals. It encompasses recognizing and managing one's own emotions and understanding others' feelings, which leads to improved team performance, leadership skills, and decision-making. Practice can help enhance EQ despite the brain's natural inclination to prioritize emotions over rational thought.Working with Emotional Intelligence
Working with Emotional IntelligenceIrshad Ahmed
╠²
Daniel Goleman is a psychologist and science journalist who wrote about emotional intelligence in his bestselling book Working with Emotional Intelligence. The book discusses what emotional intelligence is, its importance, and its four main components: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. Studies have shown that emotional intelligence is essential for effective leadership and impacts work performance, as managers with higher emotional intelligence tend to be more successful. Understanding and managing emotions helps individuals and leaders handle interpersonal interactions, motivate teams, and improve work outcomes. The book argues that emotional intelligence is a learned skill that can be developed to achieve better results.Skills For Developing Emotional Intelligence
Skills For Developing Emotional IntelligenceCommLab India ŌĆō Rapid eLearning Solutions
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is crucial for effective management and leadership, significantly impacting organizational performance alongside intelligence quotient (IQ). It encompasses self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management, which are essential for teamwork and communication. Developing EQ involves managing stress, understanding emotions, and improving conflict resolution skills to enhance overall workplace effectiveness.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceRatish Kakad
╠²
Emotional intelligence involves the ability to understand and manage one's own emotions and recognize emotions in others. It includes skills such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social skills. While IQ is relatively fixed, EQ can increase over time through learning and practice. Emotional intelligence became popular in the 1990s through academic research and was brought to the mainstream by Daniel Goleman's 1995 bestselling book. Developing strong EQ involves competencies in self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceRavikeerthi Rao
╠²
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to identify, assess, and manage emotions in oneself and others, playing a crucial role in personal and professional relationships. It comprises four components: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management, all essential for effective communication and conflict resolution. High emotional intelligence not only contributes to workplace success but also positively impacts physical and mental health.The Art of Empathy
The Art of Empathy Lynn Johnson
╠²
The document discusses the importance of empathy, emphasizing the need to listen and share personal stories to understand each other better. It highlights the role of theater and emotion coaching in fostering empathy and offers practical steps for engaging children in recognizing and expressing their feelings. Additionally, it provides resources for further exploration of empathy in education and personal development.Eq presentation
Eq presentationPraneta Pardikar
╠²
This document discusses theories of intelligence and emotional intelligence. It defines intelligence as the ability to learn, reason, and problem solve. While IQ measures cognitive abilities, emotional intelligence involves self-awareness, managing emotions, and social skills. The document examines models of emotional intelligence proposed by Mayer and Salovey, Bar-On, and Goleman. It describes Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences including interpersonal and intrapersonal skills. The Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) is presented as an ability-based measure of emotional intelligence involving identifying, using, understanding and managing emotions.Similar to EQ VS IQ (20)
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligencedirecac
╠²
Emotional intelligence is the ability to properly monitor and manage one's own emotions and understand the emotions of others. It involves recognizing emotions, managing emotions well in relationships, and motivating oneself. Developing emotional intelligence can help with empathy, overcoming challenges, making rational decisions when emotional, and improving relationships, health, career performance, and decision-making. While IQ is important, emotional intelligence is also key to success. Emotional intelligence can be developed at any age through reducing stress, connecting with others nonverbally, using humor, resolving conflicts positively, and perceiving, understanding, and prioritizing emotional responses.Eq pp
Eq pp Aakash Jalan
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its importance over IQ. It defines EQ as understanding one's own emotions and the emotions of others in order to manage relationships and stress. Research shows EQ is about 80% responsible for life success, compared to 20% for IQ. While IQ can be measured through tests, EQ involves skills that can be developed through education and awareness of emotions. Higher EQ is linked to better performance, health, and relationships.Eq n iq ppt
Eq n iq pptsonalsachdeva88
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance. It begins by defining key terms like IQ, EQ, and EI. It then explores what emotions are and their physiological and psychological aspects. The document discusses models of EI by Daniel Goleman and Dalip Singh. It provides examples of high and low EI personalities. The document also summarizes several studies that demonstrate benefits of high EI, such as better health, life success, school and business performance. It explores whether EI can be developed and debunks some myths about EI. Overall, the document advocates that EI is important and can be improved at any stage in life.Emotional Intelligence Psychological test.pptx
Emotional Intelligence Psychological test.pptxShashikalaPatel3
╠²
The document discusses the concept of emotional intelligence (EI), highlighting its importance for personal and professional success, which includes skills such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social skills. It outlines Daniel Goleman's theory and components of EI, suggests a test for assessing emotional intelligence, and provides methods for development in personal and professional contexts. The conclusion emphasizes that EI is a crucial skill that can be cultivated to enhance life and relationships.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceUniversity of Engineering and Technology Taxila
╠²
The document compares and contrasts emotional quotient (EQ) and intelligence quotient (IQ). It states that EQ involves interpersonal skills like empathy, stress management, and social awareness. EQ can be developed at any age through learning, while IQ is established at birth and fixed. High EQ is more important for success in life than high IQ. The document then discusses the importance of EQ and provides suggestions for developing one's own EQ, such as becoming emotionally literate and taking responsibility for one's feelings.Emotional Intelligence
Emotional IntelligenceJoanMalone
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its importance for career success. It notes that EI is the top reason new hires fail and that employers are increasingly looking for strong EI in candidates. The document defines EI and its five core competencies - self awareness, self regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. It provides strategies for developing high EI, such as developing self awareness and managing emotions. Overall, the document advocates that career seekers focus on strengthening their EI in order to improve their job search and career success.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceJoanMalone
╠²
The document discusses the significance of emotional intelligence (EI) in professional settings, highlighting its role in enhancing job performance and career advancement. It outlines the five key EI competencies: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, and emphasizes the importance of these skills during the hiring process and in interviews. Additionally, it provides strategies for managing emotional responses and improving EI over time, suggesting that maturity contributes to better emotional capabilities.emotionalintelligence-151226115319.pdf
emotionalintelligence-151226115319.pdf2414AvinThomasThatti
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI), which refers to the ability to identify, assess, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others. EI involves four key components: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. The document argues that EI is important for success in life and career as it impacts how we behave, communicate, form relationships, and cope with stress. While IQ matters, research shows that EI accounts for a greater portion, up to 85%, of our financial and career success. Developing skills like stress management, empathy, and conflict resolution can help improve one's emotional intelligence.Emotional intelligence at the workplace day 1
Emotional intelligence at the workplace day 1Fabian Thomas
╠²
The document outlines the objectives and activities for a workplace workshop aimed at reducing stress, improving communication and teamwork. It provides guidance on how to make the workshop successful through active listening, ownership of words, validation of others' experiences, and maintaining confidentiality. Participants are asked to commit to these principles to have an open and productive discussion.Understanding emotional intelligende
Understanding emotional intelligende Mohie Ismail
╠²
Emotional intelligence involves being aware of one's own emotions and the emotions of others, managing emotions effectively in oneself and others, and using this awareness to guide thinking and behavior. High emotional intelligence is important for success in the workplace as it allows one to understand how emotions impact work and relationships. Models of emotional intelligence include ability-based, trait-based, and mixed models assessing skills like self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and social skills. Developing emotional intelligence competencies such as empathy, influence, and developing others can help improve productivity, relationships, and quality of life.Ei Presentation (Preeti)
Ei Presentation (Preeti)preetisirohi16
╠²
Emotional Intelligence was popularized by Daniel Goleman in 1996. It refers to an individual's ability to recognize and manage their own emotions and understand the emotions of others. There are five main components of emotional intelligence: self-awareness, self-management, self-motivation, empathy, and social skills. Research shows that emotional intelligence, or EQ, is more important for success than IQ, accounting for 80% of success in life. Developing emotional intelligence in the workplace helps people manage relationships effectively and stay focused on goals and vision.Ei Presentation (Preeti)
Ei Presentation (Preeti)preetisirohi16
╠²
Emotional Intelligence was popularized by Daniel Goleman in 1996. Emotional Intelligence refers to an individual's ability to manage their own emotions and relate well to others. It is comprised of self-awareness, self-management, social skills, empathy, and self-motivation. Research shows that EQ accounts for 80% of success in life while IQ only accounts for 20%. Developing emotional intelligence in the workplace helps employees manage relationships effectively and stay focused on goals.Emotionla intelligence presentation.ppt [autosaved] [autosaved]
Emotionla intelligence presentation.ppt [autosaved] [autosaved]Tawanda Chisiri
╠²
Emotionally intelligent leadership was the topic of the document. It began by stating emotional intelligence (EI) is more important for workplace success than IQ. EI allows people to work together harmoniously. The document then discussed the five competencies of EI - self awareness, self regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. It emphasized EI is about being aware of your own and others' emotions, not about being overly emotional. The document provided examples of how developing EI can benefit individuals and organizations through improved relationships, communication, and performance.Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligenceMaxwell Ranasinghe
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI), including its definition, importance in the workplace, impacts, and framework. It notes that EI involves perceiving, understanding, and managing emotions. Research shows EI is important for job performance and success more than IQ alone. The document outlines positive impacts of high EI like better productivity and leadership, and negative impacts of low EI. It discusses Daniel Goleman's model of EI comprising personal competence, self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy and social skills. The document also lists personnel in organizations that require EI training like top executives and high potential employees."Emotional Intelligence" another old concept with a new name board
"Emotional Intelligence" another old concept with a new name boardMaxwell Ranasinghe
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI), including its definition, importance in the workplace, impacts, and key areas. It notes that EI involves perceiving, understanding, and managing emotions, and that research shows EI is important for job performance. The document outlines positive impacts of high EI like better productivity and leadership, and negative impacts of low EI. It also provides Daniel Goleman's framework of EI, which includes personal competence, self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social skills.Increase Your Emotional intelligence-Basics for Beginners
Increase Your Emotional intelligence-Basics for BeginnersJoan Mullally
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and its significance compared to intelligence quotient (IQ) in achieving success in personal and professional areas. It outlines characteristics of emotionally intelligent people, practical ways to improve EI, and its role in relationships and conflict management. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of fostering EI in children and suggests methods for assessing and developing one's emotional intelligence.Daniel_Goleman_Emotional_Intelligence_SumitMehta
Daniel_Goleman_Emotional_Intelligence_SumitMehtaSumit Mehta
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EI) and Daniel Goleman's work on the topic. It provides definitions of EI, outlines the training objectives which are to understand the importance of EI, types of emotions, difference between IQ and EQ, core abilities and competencies of EI. It then discusses Goleman's background, provides statistics on lack of motivation and failure of change initiatives. Further, it explains the four core abilities of EI - self awareness, self management, social awareness and relationship management. It also outlines the five competencies of EI and key skills to develop EI.AIESECUD - Emotional intelligence
AIESECUD - Emotional intelligenceAIESEC UNDIP
╠²
The document discusses emotional intelligence (EQ) and its significance in both personal and professional success, emphasizing that EQ often outweighs IQ in determining overall effectiveness in life. It defines EQ as the ability to recognize and manage one's own emotions and those of others, highlighting the lack of EQ education in schools compared to IQ-focused curricula. Various studies underscore that higher EQ correlates with better job performance, interpersonal relationships, and resilience to stress.Emotional Intelligent
Emotional IntelligentVijaya Sawant,PMP, OCP
╠²
This document discusses emotional intelligence and its importance. It defines emotional intelligence as emotions plus intelligence. It explains that EQ involves self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. Developing emotional intelligence can help with personal and professional success by improving self-control, communication, leadership, and relationships. The document encourages looking inward and committing to developing areas like empathy, listening skills, and controlling negative emotions.Apprendre A Mieux Gerer Ses Emotions
Apprendre A Mieux Gerer Ses EmotionsGDE Coaching - Jean Noel Macaque
╠²
This document discusses ways to improve emotional intelligence. It defines emotional intelligence and explains its importance for leadership, decision making, and relationships. It identifies key competencies of emotional intelligence like self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management. It provides tips for increasing emotional intelligence such as reflecting on one's emotions, developing empathy, managing stress, and strengthening relationships through communication and understanding others' perspectives.Ad
Recently uploaded (12)
Women_Empowerment_LPU_Presentation.pptx.
Women_Empowerment_LPU_Presentation.pptx.jinny kaur
╠²
The presentation ŌĆ£Women Empowerment Initiatives at LPUŌĆØ highlights Lovely Professional UniversityŌĆÖs strong commitment to fostering gender equality and creating an inclusive environment for women. It explores LPUŌĆÖs various initiatives such as women-centric policies, leadership opportunities, student-run support clubs, and impactful events like workshops and mentorship programs. The university actively collaborates with external organizations and national campaigns to uplift and empower women, both on campus and in surrounding communities. Through these sustained efforts, LPU not only promotes academic and professional growth among its female students but also nurtures confident, capable leaders of tomorrow.Beyond the Lampshade Woody AllenŌĆÖs Unlikely Wisdom for Profound Personal Grow...
Beyond the Lampshade Woody AllenŌĆÖs Unlikely Wisdom for Profound Personal Grow...shikosham
╠²
Self-improvement. Personal growth. These terms often conjure images of intense seminars, complex philosophies, or relentless positivity. But what if the path to becoming a better, happier you was paved with wit, sarcasm, and a healthy dose of existential absurdity? Enter Woody Allen, the iconic filmmaker and comedian whose neurotic musings, surprisingly, offer profound insights into navigating the human condition. Forget the forced Zen; sometimes, the deepest growth sprouts from acknowledging lifeŌĆÖs inherent ridiculousness, just like Woody does.ßäéßģźßäŗßģ┤ ßäĆßģ¬ßäīßģ”ßäéßģ│ßå½ ßäÅßģ│ßå»ßäģßģĪßäŗßģ«ßäāßģ│ßäŗßģ” ßäŗßģĄßå╗ßäŗßģź_KTDS_ßäĆßģĄßåĘßäāßģ®ßå╝ßäÆßģ¦ßå½.pptx
ßäéßģźßäŗßģ┤ ßäĆßģ¬ßäīßģ”ßäéßģ│ßå½ ßäÅßģ│ßå»ßäģßģĪßäŗßģ«ßäāßģ│ßäŗßģ” ßäŗßģĄßå╗ßäŗßģź_KTDS_ßäĆßģĄßåĘßäāßģ®ßå╝ßäÆßģ¦ßå½.pptxssuserf8b8bd1
╠²
AWS Student Community Day 2025 Ē¢ēņé¼ņŚÉņä£ ņŚ░ņé¼ļĪ£ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░£Ēæ£ĒĢ£ ņ×ÉļŻīņ×ģļŗłļŗż.Map Reading & Where to Get Free Maps and Apps.pptx
Map Reading & Where to Get Free Maps and Apps.pptxBob Mayer
╠²
Most of us rely on GPS, whether in our car or via our ŌĆśsmart phonesŌĆÖ or a handheld GPS while hiking/camping.
However, that requires a number of things to be working:
The GPS satellites.
Cell phone coverage for the phone.
Power.
Do you know how to read a topographic map? Personal Development about Thinking and Emotions
Personal Development about Thinking and Emotionsadeborja
╠²
Understanding the Intensity and Differentiation of EmotionsPersonal Development 3.2.. Metacognition
Personal Development 3.2.. Metacognitionadeborja
╠²
Understanding the Intensity and Differentiation of EmotionsTitle Love Beyond the Screen The Truth About Social Media Relationships (1) f...
Title Love Beyond the Screen The Truth About Social Media Relationships (1) f...Vikash Gautam
╠²
Explore the reality of social media loveŌĆödoes it last or fade? This free eBook reveals truths, red flags, real stories, and expert tips for online relationships.
ßäéßģźßäŗßģ┤ ßäĆßģ¬ßäīßģ”ßäéßģ│ßå½ ßäÅßģ│ßå»ßäģßģĪßäŗßģ«ßäāßģ│ßäŗßģ” ßäŗßģĄßå╗ßäŗßģź_KTDS_ßäĆßģĄßåĘßäāßģ®ßå╝ßäÆßģ¦ßå½.pptx
ßäéßģźßäŗßģ┤ ßäĆßģ¬ßäīßģ”ßäéßģ│ßå½ ßäÅßģ│ßå»ßäģßģĪßäŗßģ«ßäāßģ│ßäŗßģ” ßäŗßģĄßå╗ßäŗßģź_KTDS_ßäĆßģĄßåĘßäāßģ®ßå╝ßäÆßģ¦ßå½.pptxssuserf8b8bd1
╠²
Ad
EQ VS IQ
- 1. Mayank Attri
- 2. What Exactly Is EQ Emotional intelligence is simply defined as: knowing what feels good, what feels bad, and how to get from bad to good. Knowing your emotions and knowing emotion of others. It refers to emotional management skills which provide competency to balance emotions and reason so as to maximize long term happiness.
- 3. Emotional Intelligence is ŌĆ£the capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships. Emotional intelligence describes abilities distinct from, but complementary to, academic intelligence.ŌĆØ Daniel Goleman (1998)
- 4. IQ v/s EQ (Intelligence Quotient v/s Emotional Quotient) The research shows that IQ can help you to be successful to the extent of 20 percent only in life. The rest of 80 percent success depends on your EQ 80% EQ 20% IQ
- 5. ARE YOU EMOTIONALLY INTELLIGENT? OR YOU STILL THINK (not feel) THAT IQ MATTERS MORE THAN EQ
- 6. Are we giving EI education in schools /colleges NO. Our educational system gives stress on IQ and not on EQ. We are taught History, Hindi, English, Geography, Physics, anthropology, Botany, Computers, Medicine, Engineering etc. We are not TAUGHT how to handle frustration, anxieties, stress, failure, depression, burnout, inferiority complexes, ego problems We are not told to learn how to manage emotions i.e.; interaction, coordination, Adjustment, communication We are expected to learn all these from our parents, peer group of other role models At the later stages of our lives we are told to master emotional competencies to be successful.
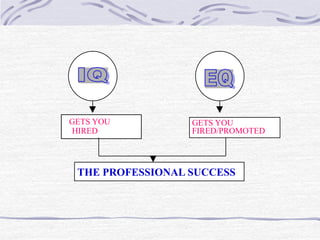
- 7. GETS YOU HIRED GETS YOU FIRED/PROMOTED THE PROFESSIONAL SUCCESS
- 8. THREE COMPONENTS of EI EMOTIONAL COMPETENCY EMOTIONAL MATURITY EMOTIONAL SENSITIVITY
- 9. I. EMOTIONAL COMPETENCY Tackling Emotional Upsets High Self-esteem Handling Egoism Handling Inferiority Complex
- 10. II. EMOTIONAL MATURITY Self-Awareness Developing Others Delaying Gratification Adaptability and Flexibility
- 11. III. EMOTIONAL SENSITIVITY Understanding Threshold of Emotional Arousal Empathy Improving Inter-personal Relations Communicability of Emotions
- 12. Characteristics of a High EI Person Is not afraid to express his/her feelings. Is not dominated by negative emotions. Balances feelings with reason, logic, and reality. Is independent, self-reliant and morally autonomous. Is not motivated by power, wealth, status, fame, or approval. Is interested in other people's feelings. Is not immobilized by fear or worry. A time to speak and a time to be silent, Is emotionally resilient.
- 13. Characteristics of a low EI Person Doesn't take responsibilities for his feelings; but blames you or others for them Is insensitive to your feelings. Has no empathy, no compassion. Is insecure and defensive and finds it hard to admit mistakes, express remorse, or apologize sincerely. Is insecure and defensive and finds it hard to admit mistakes, express remorse, or apologize sincerely Is a poor listener. Interrupts. Invalidates. Misses the emotions being communicated. Focusses on "facts" rather than feelings. Does not consider your feelings before acting.
- 14. A STUDY OF IAS OFFICERS After studying 60 IAS officers of Assam Cadre it was found that 77 % of them fall in the category of Average EQ. Only 15 % showed High EQ
- 15. CAN EQ BE DEVELOPED? YES. You can develop your EQ by upgrading your emotional skills. The popular thinking that EQ is entirely inherited is incorrect. Emotional Intelligence is not fixed at birth. There is no emotional intelligence genes as such that we know of today. It is something one has learned.
- 16. ContedŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. Can EI be developed at any stage/age of personal or professional life. The answer is YES. You can upgrade your emotional skills at any stage of your life. In fact, age and maturity are positively correlated with the EI. Same is not true about IQ which is more or less static.
- 17. SAMPLE QUESTION SITUATION: Imagine you are an insurance salesperson approaching prospective clients to purchase insurance policies. A dozen people in a row shut the door on your face. What will you do? a. Blame yourself and stop work for the day. b. Reassess your capabilities as an insurance salesperson. c. Come out with fresh strategies to overcome similar in future. d. Contact the clients again some other day.
- 18. In the business sector EI is important becauseŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. ŌĆóWe need people to sell/market; to manage finances; to produce a product; to provide a service. Productive employees literally make the organization succeed. Without them, an organization cannot operate. ŌĆóPoor employees cause the organization to fail with: high turnover; wasted selection time; absenteeism; labor disputes; wasted supervisory/training time; lowered productivity; wasted materials; costly delays; poor customer service; decreased sales and lower profits. ŌĆóTo succeed, an organization must select or develop good employees and avoid the poor ones. To succeed as a manager or executive, you must select and develop effective employees. ŌĆó Ask yourself a question? Are you consistently getting good employees? Are you able to consistently help employees overcome performance related problems?
- 19. CONCLUSION: Applying EI makes you feel comfortable within your own skin and with people around you. You can also understand what makes you incompatible with certain people or jobs and learn ways to deal with the emotional difficulties ease. You can also understand the specific feelings that cause you stress and learn ways to become more at peace.
- 20. QUOTES ŌĆ£There is nothing you can do angry that you canŌĆÖt do better when not angry.ŌĆØ ŌĆ£Anyone can be angryŌĆöthat is easy. But to be angry with the right person, to the right degree, at the right time, for the right purpose, and in the right way ŌĆö that is not easy.ŌĆØ
