Example of science gcse lesson checklist 3 (zs)
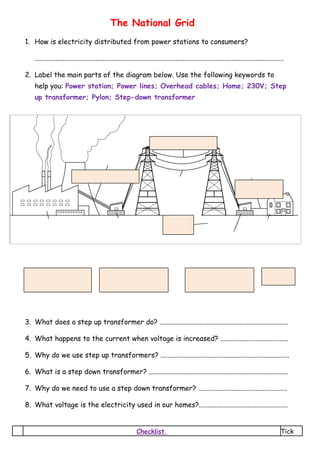
- 1. The National Grid 1. How is electricity distributed from power stations to consumers? ............................................................................................................................................... 2. Label the main parts of the diagram below. Use the following keywords to help you: Power station; Power lines; Overhead cables; Home; 230V; Step up transformer; Pylon; Step-down transformer 3. What does a step up transformer do? .......................................................................... 4. What happens to the current when voltage is increased? ....................................... 5. Why do we use step up transformers? .......................................................................... 6. What is a step down transformer? ................................................................................ 7. Why do we need to use a step down transformer? ................................................... 8. What voltage is the electricity used in our homes?................................................... Checklist Tick
- 2. 1 Electricity is distributed from power stations to consumers along the National Grid 2 I can label and identify the main parts of the National Grid 3 For a given power increasing the voltage reduces the current required and this reduces the energy losses in the cables 4 I know why transformers are an essential part of the National Grid 5 I can compare the advantages and disadvantages of overhead power lines and underground cables